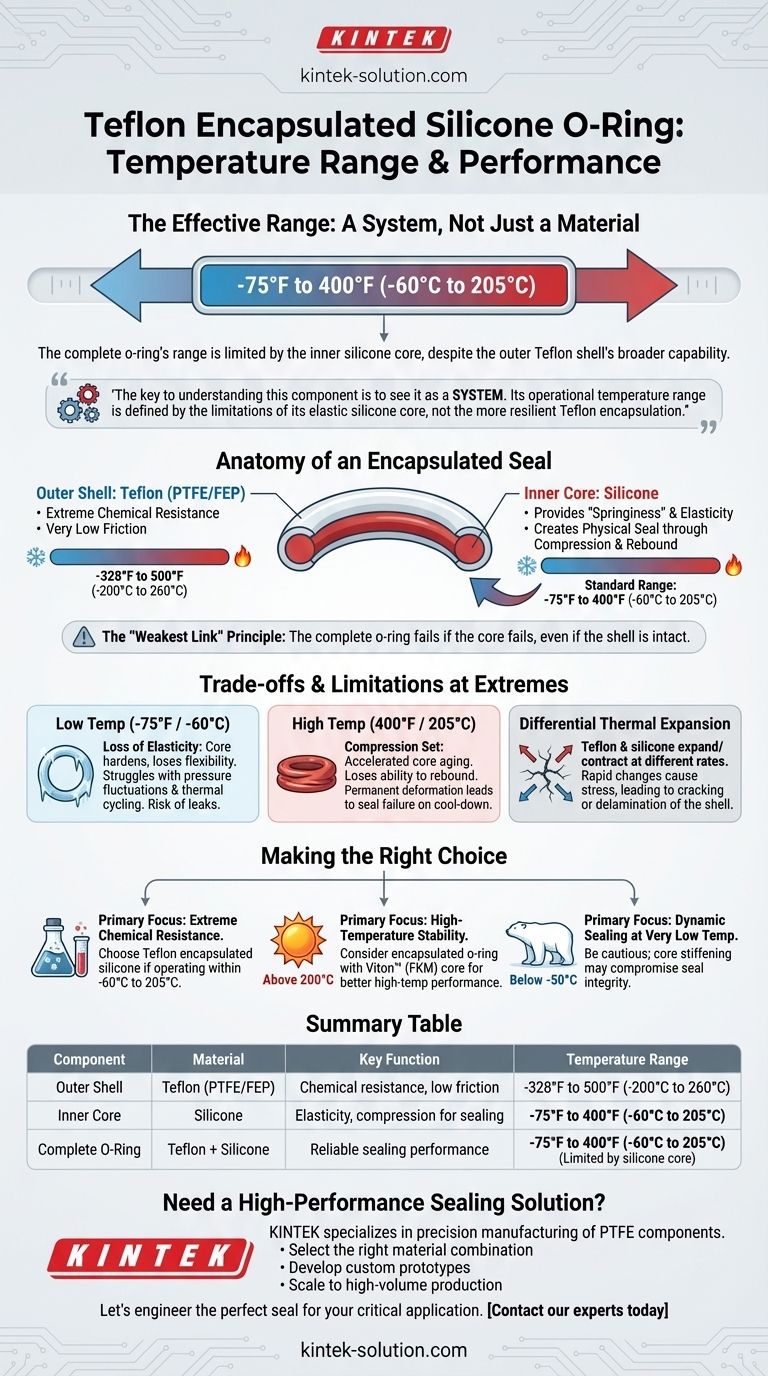
In short, the effective temperature range for a Teflon encapsulated silicone o-ring is typically from -75°F to 400°F (-60°C to 205°C). While the Teflon shell can withstand much more extreme temperatures, the o-ring's overall performance is dictated by its inner silicone core, which provides the necessary elasticity for sealing.
The key to understanding this component is to see it not as a single material, but as a system. The o-ring's operational temperature range is defined by the limitations of its elastic silicone core, not the more resilient Teflon encapsulation.
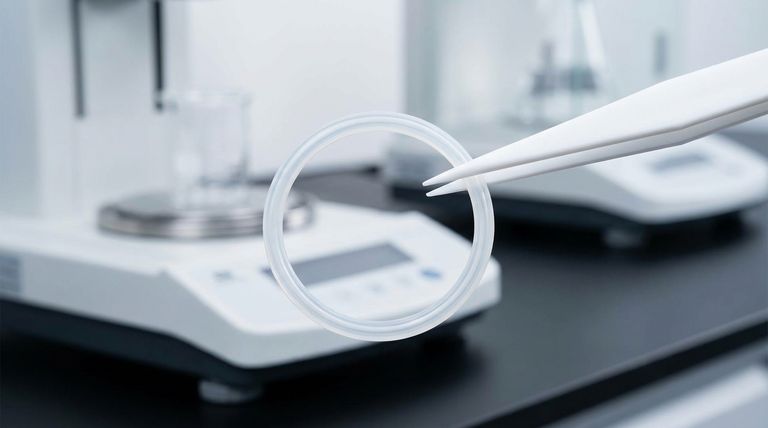

The Anatomy of an Encapsulated Seal
To properly evaluate if this o-ring is right for your application, you must understand how its two primary components work together—and where their limitations lie.
The Outer Shell: Teflon (PTFE/FEP)
The outer encapsulation is made of Teflon, typically PTFE or FEP. This layer provides the o-ring's primary benefits.
Its main role is to deliver extreme chemical resistance and a very low-friction surface.
From a temperature perspective, solid Teflon is exceptionally robust. It can maintain its structural integrity from cryogenic temperatures as low as -328°F (-200°C) up to 500°F (260°C).
The Inner Core: Silicone
The inner core provides the o-ring with its "springiness" or elasticity. This ability to compress and rebound is what creates a physical seal.
Silicone is used for its excellent flexibility and low compression set over a wide range of temperatures.
However, its functional temperature range is narrower than Teflon's. Standard silicone cores operate reliably from approximately -75°F (-60°C) to 400°F (205°C).
The "Weakest Link" Principle
The complete o-ring can only function as long as both parts are within their operational limits.
Because the silicone core will lose its essential elastic properties outside of its range, it becomes the limiting factor for the entire assembly. The seal will fail if the core becomes too rigid (at low temperatures) or permanently deforms (at high temperatures), even if the Teflon shell remains intact.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, these o-rings are not without their compromises, especially at the extremes of their temperature range. Understanding these is critical for reliable system design.
Loss of Elasticity at Low Temperatures
As the o-ring approaches its lower limit (-75°F / -60°C), the silicone core begins to harden and lose its flexibility.
While it may hold a static seal, it will struggle to respond to pressure fluctuations or thermal cycling. This loss of dynamic response can lead to leaks in applications that are not perfectly stable.
Compression Set at High Temperatures
Operating continuously near the upper temperature limit (400°F / 205°C) will accelerate the aging of the silicone core.
The material will gradually lose its ability to rebound after being compressed, a phenomenon known as compression set. Over time, this permanent deformation will compromise the seal, often leading to failure upon system cool-down.
Differential Thermal Expansion
Teflon and silicone expand and contract at different rates when heated or cooled.
Rapid or extreme temperature changes can create stress between the core and the encapsulation. This can potentially cause the thin Teflon shell to crack or delaminate from the core, leading to immediate seal failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if this component is the optimal choice for your specific design goals.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: This o-ring is an excellent choice, provided your operating temperatures remain comfortably within the -60°C to 205°C range.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability (above 200°C): Consider an encapsulated o-ring with a Viton™ (FKM) core, which offers slightly better high-temperature performance at the cost of some low-temperature flexibility.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing at very low temperatures (below -50°C): Be cautious, as the silicone core's stiffening may compromise seal integrity under fluctuating pressures.
Ultimately, selecting the right seal requires looking beyond a single number and understanding the behavior of the complete system.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material | Key Function | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Shell | Teflon (PTFE/FEP) | Chemical resistance, low friction | -328°F to 500°F (-200°C to 260°C) |
| Inner Core | Silicone | Elasticity, compression for sealing | -75°F to 400°F (-60°C to 205°C) |
| Complete O-Ring | Teflon + Silicone | Reliable sealing performance | -75°F to 400°F (-60°C to 205°C) (Limited by silicone core) |
Need a High-Performance Sealing Solution?
Understanding the precise limits of your components is key to system reliability. The Teflon encapsulated silicone o-ring is a perfect example of a specialized part where material science dictates performance.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components like custom seals, liners, and labware for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand that off-the-shelf solutions often don't meet the unique thermal, chemical, and pressure requirements of advanced engineering.
We can help you:
- Select the right material combination (e.g., Teflon encapsulation with silicone, Viton™, or other core materials) for your specific temperature and chemical environment.
- Develop custom prototypes to validate performance in your application.
- Scale to high-volume production with consistent, high-quality results.
Let's engineer the perfect seal for your critical application. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements for custom PTFE fabrication.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















