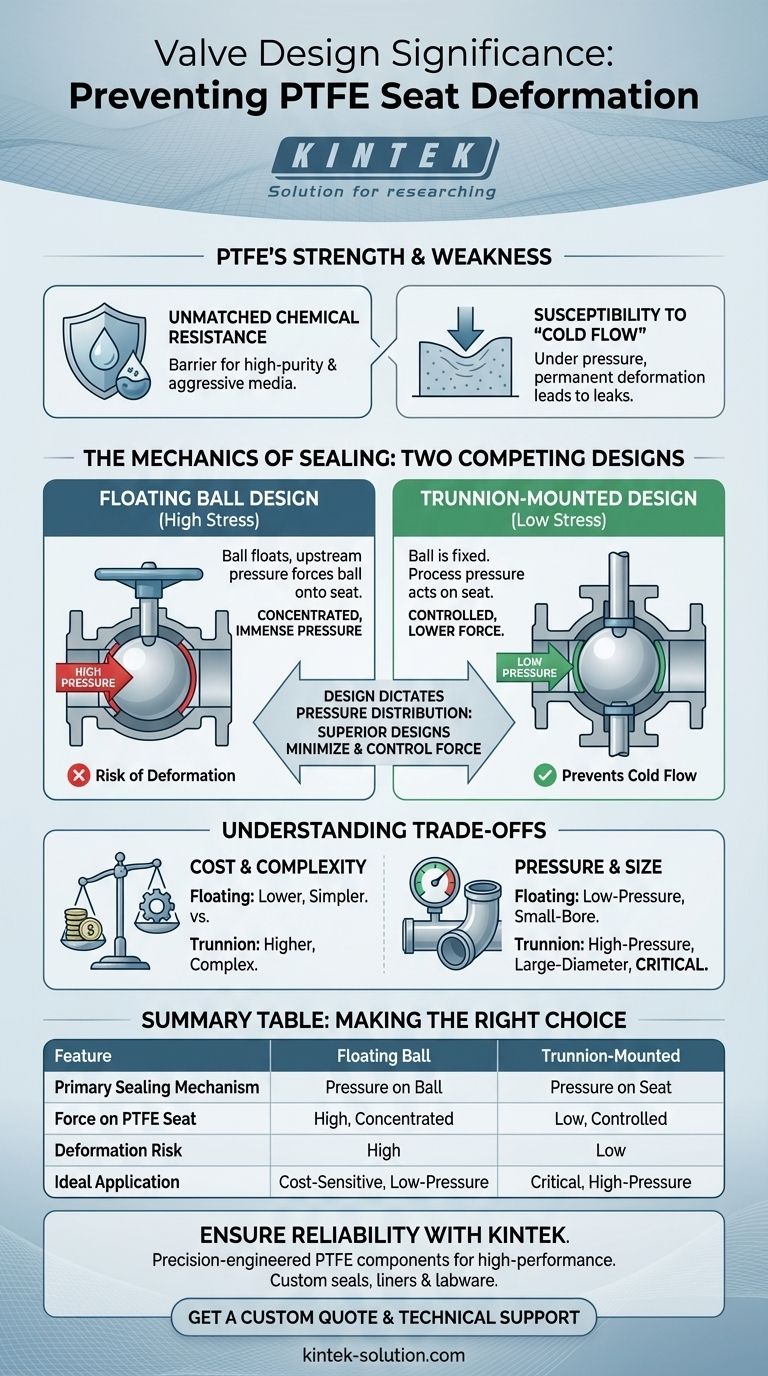
Valve design is the single most critical factor in preventing the deformation of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) seats. The way a valve is engineered dictates how mechanical stress and process pressure are distributed onto the soft PTFE material. Designs that minimize and control this force, such as a trunnion-mounted ball valve, are inherently superior at preventing deformation compared to designs like a floating ball valve, which can concentrate immense pressure onto the seat.
The core principle is simple: superior valve designs use process pressure to gently push a lightweight seat against a fixed ball, whereas lesser designs use that same pressure to force a heavy, unsupported ball into a stationary seat. This distinction in how force is applied is the primary determinant of a PTFE seat's longevity and sealing integrity.

Why PTFE is Used (And Why It Needs Protection)
The Benefit: Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE, often known by its brand name Teflon, is a fluoropolymer prized for its exceptional properties. Its primary role in a valve is to act as a barrier.
By lining or wrapping the valve's internal components, PTFE isolates the metal body from direct contact with the process media. This provides outstanding protection against corrosion and prevents product contamination, which is crucial in high-purity or aggressive chemical applications.
The Weakness: Susceptibility to "Cold Flow"
Despite its chemical resilience, PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under sustained mechanical pressure, it is prone to a phenomenon called cold flow, or creep.
This is a gradual, permanent deformation of the material. In a valve seat, cold flow results in a loss of a proper seal, leading to leaks, increased operating torque, and eventual valve failure. The goal of a good valve design is to mitigate this inherent weakness.
The Mechanics of Sealing: Two Competing Designs
The Floating Ball Design: A High-Stress Approach
In a standard floating ball valve, the ball is held in place only by the two seats and is free to move, or "float," slightly with the flow.
When the valve is closed, upstream process pressure pushes the entire surface of the ball against the downstream PTFE seat. This large force, concentrated on the seat, is a primary cause of seat deformation and cold flow, especially in higher-pressure systems.
The Trunnion-Mounted Design: A Low-Stress Solution
A trunnion-mounted valve design solves this problem by mechanically anchoring the ball at the top and bottom with a stem and a trunnion. The ball is fixed and cannot travel.
In this design, process pressure acts on the seat itself, pushing it from behind and toward the fixed ball to create a seal. Because the surface area on the back of the seat is much smaller than the area of the entire ball, the force applied is drastically lower. This intelligent use of physics prevents the crushing pressure that leads to seat deformation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost and Mechanical Complexity
A floating ball valve has a simpler construction with fewer parts, making it a more cost-effective option.
Trunnion-mounted valves require additional components and more precise manufacturing to accommodate the trunnion shaft, making them more complex and expensive.
Application Pressure and Valve Size
Floating ball designs are perfectly adequate and economical for many low-pressure and smaller-diameter applications where the total force on the ball is manageable.
Trunnion designs become essential in high-pressure or large-diameter systems. As pressure and valve size increase, the force exerted on a floating ball grows exponentially, making the trunnion's low-stress sealing mechanism a necessity for reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct valve design requires matching the engineering to the operational demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in low-pressure, smaller-bore lines: A floating ball valve is often a sufficient and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is reliability in high-pressure or large-diameter systems: A trunnion-mounted design is essential to prevent PTFE seat deformation and ensure a long-lasting, leak-free seal.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive or high-purity media: The choice of valve design (trunnion vs. floating) is as important as the choice of material (PTFE) to ensure the valve's structural integrity.
Understanding these mechanical principles empowers you to select a valve based on its engineering merits, ensuring the reliability of your entire system.
Summary Table:
| Design Feature | Floating Ball Valve | Trunnion-Mounted Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Sealing Mechanism | Process pressure forces ball into seat | Process pressure pushes seat against fixed ball |
| Force on PTFE Seat | High, concentrated pressure | Low, controlled pressure |
| Risk of Seat Deformation | High, especially in high-pressure systems | Low, designed to prevent cold flow |
| Ideal Application | Low-pressure, small-bore, cost-sensitive systems | High-pressure, large-diameter, critical reliability systems |
| Relative Cost | Lower | Higher |
Ensure your system's reliability with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
The right valve design is critical for preventing PTFE seat failure. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your components are designed and fabricated to withstand your specific operational pressures and media, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact us today to discuss how our precision PTFE solutions can enhance your system's performance and longevity.
Get a Custom Quote & Technical Support
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation



















