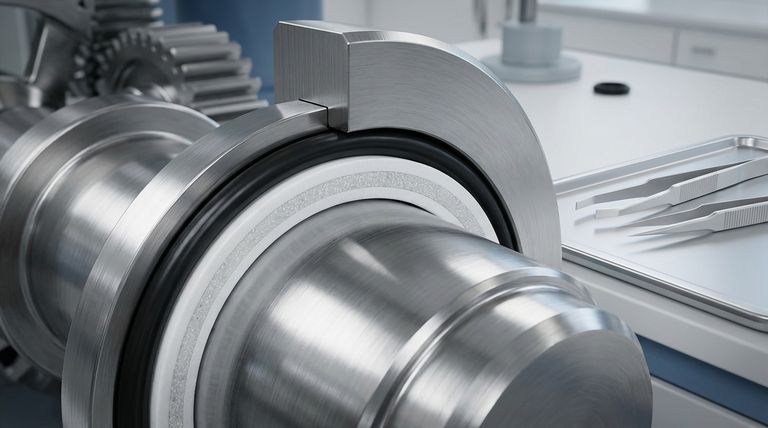
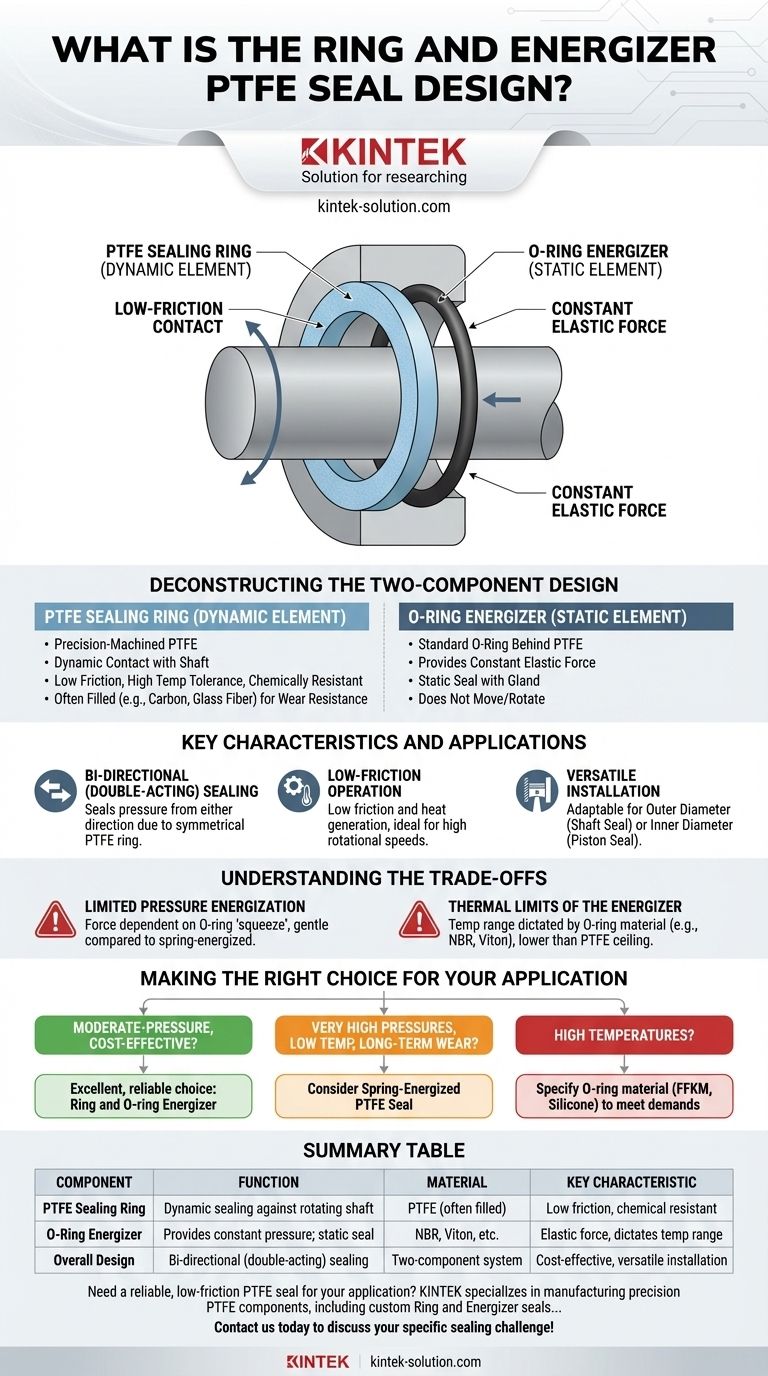
At its core, the Ring and Energizer PTFE seal is a two-component design intended for bi-directional rotary sealing. It combines a primary sealing ring, made from low-friction PTFE, with a standard O-ring that acts as a simple energizer to apply constant pressure. This design effectively separates the dynamic and static sealing functions into two distinct parts.
This seal's core principle is to use a durable, low-friction PTFE ring to handle the demanding dynamic sealing against a rotating shaft, while a simple, static O-ring provides the necessary preload to ensure a consistent and reliable seal.

Deconstructing the Two-Component Design
To understand this seal, you must analyze its two distinct parts and how they work in synergy. The design is elegantly simple, assigning a specific job to each component.
The PTFE Sealing Ring (The Dynamic Element)
The main sealing component is a precision-machined ring made from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This material is chosen for its extremely low coefficient of friction, high-temperature tolerance, and excellent chemical resistance.
This ring is the dynamic portion of the assembly. It is in direct contact with the moving or rotating surface, preventing fluid leakage. To enhance performance, the PTFE is often blended with fillers like carbon, glass fiber, or bronze to improve wear resistance and dimensional stability.
The O-Ring Energizer (The Static Element)
Behind the PTFE ring sits a standard O-ring, which functions as the energizer. Its primary job is to provide a constant, elastic force, pushing the PTFE ring against the sealing surface.
This O-ring also serves as a static seal between the back of the PTFE ring and the seal gland or housing. It does not move or rotate; it simply provides the radial load required for the PTFE ring to function correctly.
Key Characteristics and Applications
The specific construction of the Ring and Energizer seal gives it a distinct set of performance characteristics suitable for many common rotary applications.
Bi-Directional (Double-Acting) Sealing
A key advantage of this design is its ability to seal pressure from either direction. The symmetrical nature of the PTFE ring allows it to function effectively regardless of the direction of pressure, making it a versatile, double-acting seal.
Low-Friction Operation
Because PTFE is the only material touching the rotating component, the seal generates very little friction and heat. This makes it ideal for applications with higher rotational speeds where other seal types might overheat and fail prematurely.
Versatile Installation
This design is highly adaptable. It can be installed to seal on its outer diameter (a shaft seal) or its inner diameter (a piston seal in a rotary actuator), making it a flexible solution for various hardware configurations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, this design is what the industry considers a "basic" rotary seal. It's crucial to understand its limitations compared to more advanced alternatives.
Limited Pressure Energization
The sealing force is entirely dependent on the "squeeze" from the O-ring. Unlike spring-energized seals that use a metal spring for a more aggressive load, the O-ring's force is relatively gentle. This can limit its effectiveness in very high-pressure applications or where significant wear must be compensated for over time.
Thermal Limits of the Energizer
The operational temperature range of the entire seal assembly is often dictated by the O-ring material, not the PTFE. While the PTFE ring can handle extreme temperatures, a standard NBR or Viton O-ring has a much lower temperature ceiling, making material selection for the energizer a critical design consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires matching the design's capabilities to your operational demands.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, bi-directional sealing in a moderate-pressure environment: The Ring and O-ring Energizer design is an excellent and highly reliable choice.
- If you are dealing with very high pressures, low temperatures, or require long-term wear compensation: Consider a spring-energized PTFE seal, which provides a more aggressive and consistent sealing force across a wider range of conditions.
- If you are operating at high temperatures: Ensure the O-ring energizer's material (e.g., FFKM, silicone) is specified to meet or exceed the thermal demands of your application.
By understanding this fundamental two-component system, you can confidently select the precise sealing solution for your specific rotary challenge.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Material | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE Sealing Ring | Dynamic sealing against rotating shaft | PTFE (often filled) | Low friction, chemical resistant |
| O-Ring Energizer | Provides constant pressure; static seal | NBR, Viton, etc. | Elastic force, dictates temp range |
| Overall Design | Bi-directional (double-acting) sealing | Two-component system | Cost-effective, versatile installation |
Need a reliable, low-friction PTFE seal for your application? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom Ring and Energizer seals, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures a perfect fit and optimal performance. Contact us today to discuss your specific sealing challenge!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















