In short, heat-setting is a manufacturing process that temporarily enlarges a PTFE seal's inner diameter to simplify installation. The process uses heat and mechanical stretching to set the seal to a larger size; once installed, the operational heat from friction causes the seal to "remember" and shrink back to its original, smaller dimension, creating a tight, effective seal.
The central challenge with PTFE is that it's a rigid plastic, not a flexible elastomer like rubber. The heat-set process cleverly uses PTFE's inherent "shape memory" to overcome this installation challenge, ensuring a damage-free assembly and a reliable seal in its final application.
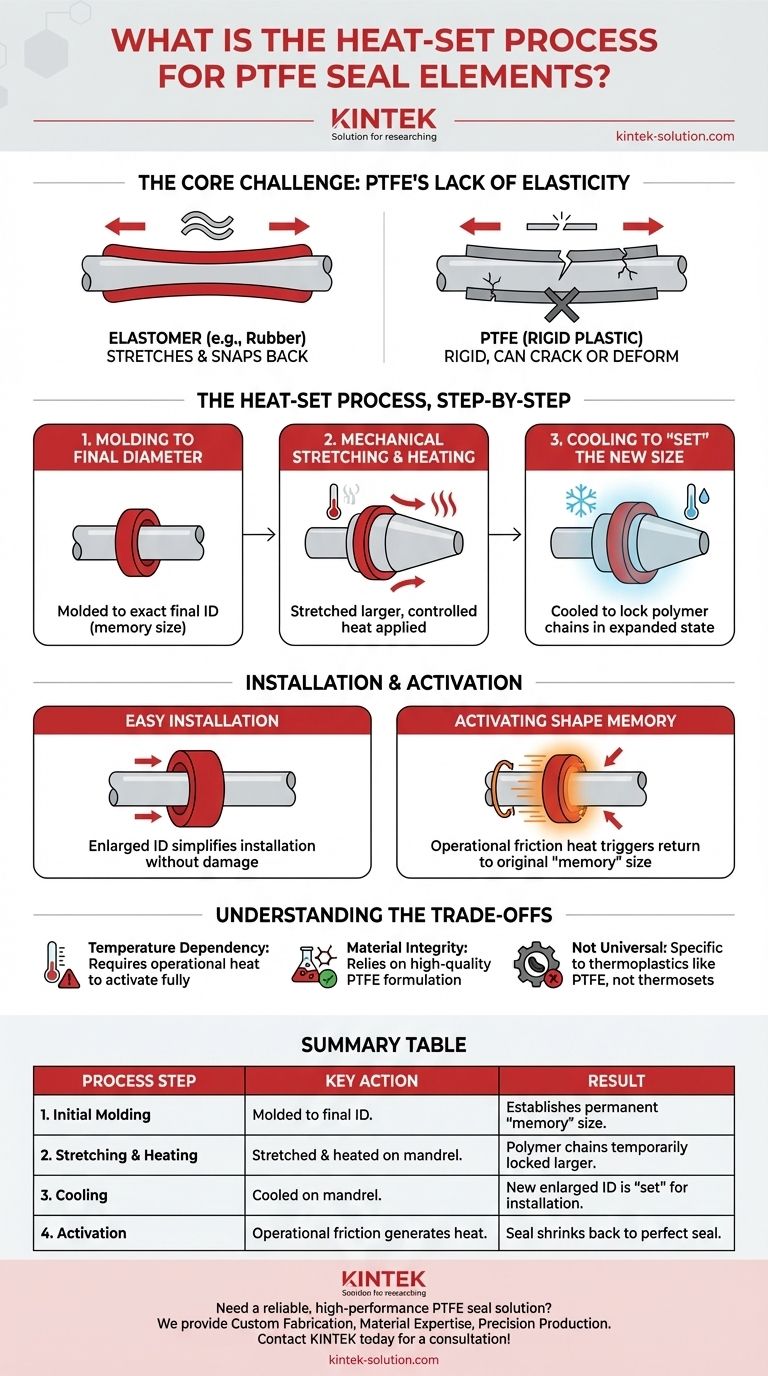
The Core Challenge: PTFE's Lack of Elasticity
To understand why heat-setting is necessary, we must first understand the material itself. PTFE is fundamentally different from common sealing materials like rubber or silicone.
Why Standard Seals Stretch and Return
Elastomeric seals, like O-rings made from nitrile or Viton, are highly elastic. You can stretch them over a shaft, and their molecular structure naturally causes them to snap back to their original size, creating an immediate seal.
PTFE's Inherent Rigidity
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a plastic, not an elastomer. It has very low elasticity. Attempting to stretch a standard PTFE seal over a shaft can cause permanent deformation, cracks, or a complete failure of the sealing lip.
The Heat-Set Process, Step-by-Step
The heat-set process is an elegant solution that modifies the PTFE element to make installation possible without compromising its final sealing function.
Step 1: Molding to the Final Diameter
First, the seal is manufactured to the exact inner diameter (ID) required for its final operational state. This is the "memory" size that the seal will eventually return to.
Step 2: Mechanical Stretching and Heating
The finished seal is then stretched over a precisely sized mandrel or cone that is larger than the seal's original ID. While held in this stretched position, controlled heat is applied.
Step 3: Cooling to "Set" the New Size
The element is allowed to cool while still on the mandrel. This thermal cycle locks the polymer chains into their new, expanded position. The result is a PTFE seal with an ID that is intentionally larger than its final intended size.
Installation and Activation: The Final Steps
The magic of the heat-set process occurs after the seal leaves the factory.
Easing Installation
Because the seal's ID is now temporarily enlarged, it can be easily and safely slid over the shaft or into the housing without the need for excessive force. This prevents the microscopic tears and permanent stretching that would otherwise damage a rigid seal.
Activating the Shape Memory
Once the equipment is running, friction between the rotating shaft and the seal generates heat. This operational heat is the trigger for the seal's final transformation.
Returning to the Intended Size
The applied heat causes the PTFE's molecular structure to revert to its original, more stable state. The seal shrinks back down to the smaller ID it was initially molded to, creating a snug and highly effective seal against the shaft.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, the heat-set process relies on specific conditions and introduces considerations that are critical for success.
Temperature Dependency
The process fundamentally relies on operational heat to activate the seal. In applications that run too cool or operate intermittently, the seal may not shrink fully or consistently, potentially leading to suboptimal performance.
Material Integrity is Key
The effectiveness and predictability of the "shape memory" effect are highly dependent on the quality and specific formulation of the PTFE compound. Impurities or incorrect additives can hinder the process.
Not a Universal Solution
Heat-setting is specific to thermoplastics like PTFE that exhibit a distinct shape memory. It is not applicable to traditional thermoset elastomers like rubber, which do not share this property.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this process helps you select the right seal for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: Heat-set PTFE seals are an excellent choice, as the very heat that would destroy an elastomer is what activates and perfects the PTFE seal.
- If your primary focus is easy, damage-free assembly of rigid seals: The heat-set process is the enabling technology that makes installing dimensionally critical PTFE seals practical and reliable.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance in dynamic applications: Heat-setting allows you to leverage PTFE's superior chemical inertness without fighting its physical rigidity during installation.
Ultimately, heat-setting is a crucial manufacturing step that transforms a high-performance material from a difficult-to-install component into a practical and reliable sealing solution.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Initial Molding | Seal is molded to its final, intended inner diameter (ID). | Establishes the seal's permanent "memory" size. |
| 2. Stretching & Heating | Seal is stretched over a mandrel and heated while held in place. | Polymer chains are temporarily locked into a larger size. |
| 3. Cooling | Seal is cooled on the mandrel. | The new, enlarged ID is "set," simplifying installation. |
| 4. Activation | Operational friction generates heat during use. | Seal shrinks back to its original ID, creating a perfect seal. |
Need a reliable, high-performance PTFE seal solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including heat-set seals, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your seals are fabricated to the highest standards, guaranteeing easy installation and long-term reliability in your most demanding applications.
We provide:
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume production runs.
- Material Expertise: Optimal PTFE formulations for predictable shape memory and performance.
- Precision Production: Seals engineered to your exact specifications.
Let us help you solve your toughest sealing challenges. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















