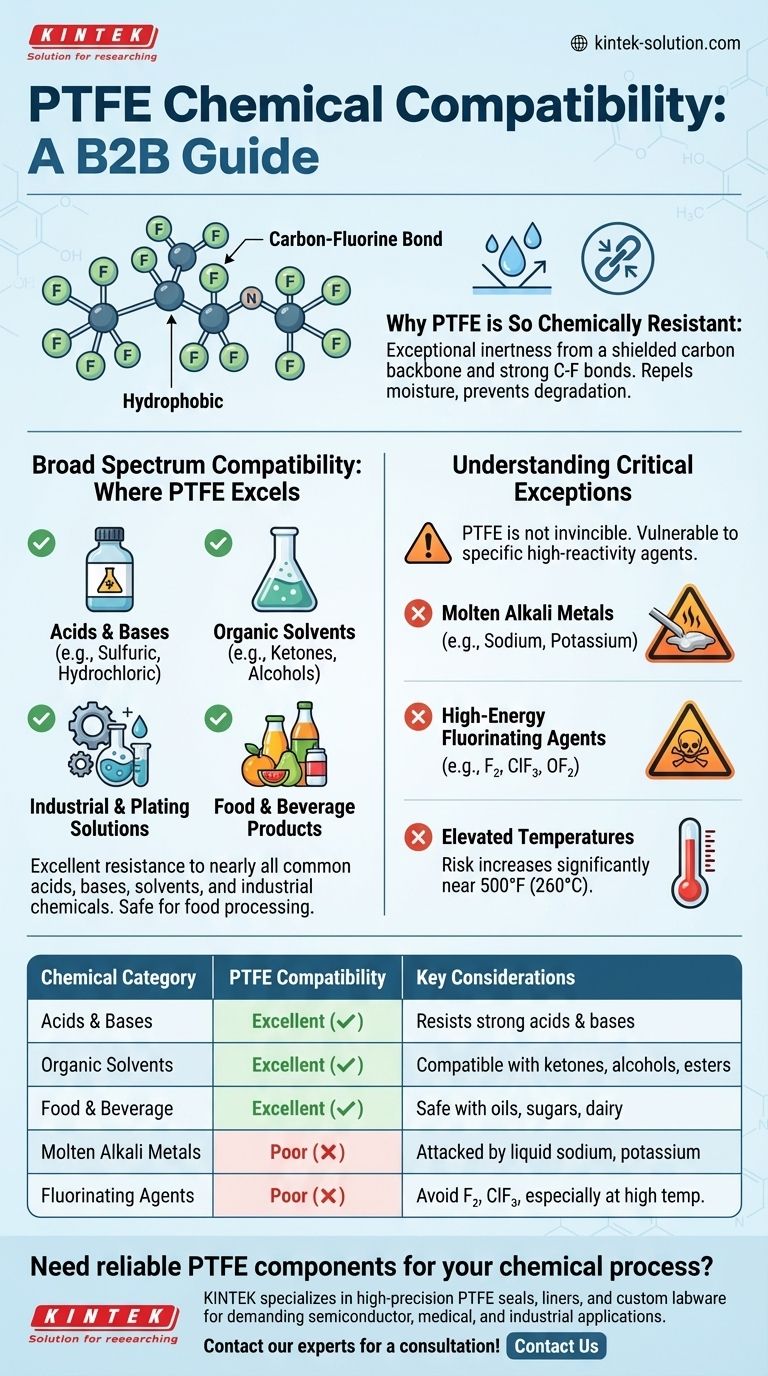
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most chemically inert materials known. It offers exceptional resistance to nearly all common acids, bases, solvents, and industrial chemicals. This broad compatibility makes it a default choice for demanding applications, but it is not completely invincible and has a few critical, well-defined exceptions.
The core principle to understand is that PTFE's chemical resistance is nearly universal for standard applications, but it can be attacked by highly reactive agents, specifically molten alkali metals and potent fluorinating agents, especially at elevated temperatures.

Why PTFE is So Chemically Resistant
PTFE's remarkable inertness is a direct result of its molecular structure. The polymer chain is composed of a carbon backbone completely shielded by a tight helix of fluorine atoms.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable. This powerful bond makes the molecule very difficult for other chemicals to break apart or react with.
Hydrophobic and Non-Absorbent
PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and water-based substances. It does not absorb moisture, which prevents chemicals from seeping into the material and causing degradation from within. This also contributes to its self-cleaning properties.
Broad Spectrum Compatibility: Where PTFE Excels
For the vast majority of industrial, laboratory, and food processing applications, PTFE is considered to have excellent compatibility.
Acids, Bases, and Solvents
PTFE remains stable when exposed to a wide range of aggressive chemicals. This includes common acids like sulfuric and hydrochloric acid, strong bases, and organic solvents such as ketones, alcohols, esters, and hydrocarbons.
Industrial and Plating Solutions
Its inertness extends to many industrial chemicals like ammonia and hydrogen peroxide. It also shows excellent compatibility with various specialized plating solutions, including those for brass, bronze, cadmium, and arsenic plating.
Food and Beverage Products
PTFE is highly compatible with a multitude of food substances. It does not react with oils, sugars, dairy products, or fruit juices, making it a safe and reliable material for food processing equipment.
Understanding the Critical Exceptions
While its resistance is extensive, PTFE is not absolutely inert. Understanding its specific vulnerabilities is crucial for safe and effective material selection in extreme environments.
Molten Alkali Metals
The primary exception to PTFE's chemical inertness is its reaction with molten alkali metals, such as sodium or potassium. In their liquid state, these metals are reactive enough to strip fluorine atoms from the polymer backbone.
High-Energy Fluorinating Agents
Certain powerful fluorochemicals can attack PTFE, particularly under specific conditions. These include **elemental fluorine (F₂) **, especially in a turbulent liquid or gaseous state, as well as compounds like chlorine trifluoride (ClF₃) and oxygen difluoride (OF₂).
The Role of Elevated Temperatures
These reactions are often highly dependent on temperature. The risk of chemical attack by potent fluorinating agents increases significantly at elevated temperatures, approaching PTFE's continuous operating limit of 500°F (260°C).
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your decision should be based on a clear understanding of the chemical agents and operating conditions involved.
- If your primary focus is general chemical processing: PTFE is an exceptionally safe and reliable choice for handling the vast majority of acids, bases, solvents, and petroleum products.
- If your primary focus is an extreme, high-energy environment: You must verify that your process does not involve molten alkali metals or aggressive fluorinating agents, especially at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is food, beverage, or lab applications: PTFE offers excellent, non-reactive performance across a wide range of organic compounds and cleaning agents.
Ultimately, PTFE's reputation as a go-to material for chemical resistance is well-earned, provided you operate within its clearly defined limitations.
Summary Table:
| Chemical Category | PTFE Compatibility | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Acids & Bases | Excellent | Resists sulfuric, hydrochloric acids, strong bases. |
| Organic Solvents | Excellent | Compatible with ketones, alcohols, esters, hydrocarbons. |
| Food & Beverage | Excellent | Safe with oils, sugars, dairy, juices. |
| Molten Alkali Metals | Poor | Attacked by sodium, potassium in liquid state. |
| Fluorinating Agents | Poor | Avoid F₂, ClF₃, OF₂, especially at high temperatures. |
Need a reliable PTFE component for your chemical process?
PTFE's legendary chemical resistance makes it ideal for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—that ensure integrity and performance in aggressive environments.
We combine precision production with custom fabrication expertise, from prototypes to high-volume orders, to deliver solutions that meet your exact specifications.
Let's discuss how our PTFE components can enhance your project's safety and efficiency. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- When was PTFE discovered and developed? The Accidental Invention That Changed Industries
- What are the additional properties of PTFE? Beyond Non-Stick: Extreme Chemical, Thermal & Electrical Performance
- What are the similarities between PTFE and RPTFE? Unlocking the Core Fluoropolymer Identity
- What environmental resistances does PTFE offer? Unmatched Durability for Harsh Conditions
- What is Teflon and what is its chemical name? Unpacking the Science of PTFE



















