In simple terms, suspension polymerization is a chemical process used to convert a liquid monomer into solid polymer grains. This is achieved by suspending tiny droplets of the monomer, like tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), in water and then initiating a reaction that turns each droplet into a solid particle of polymer, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
The core idea is to use water as a heat-transfer medium to control the reaction, creating uniform, bead-like polymer particles that are easy to handle and ideal for molding processes.
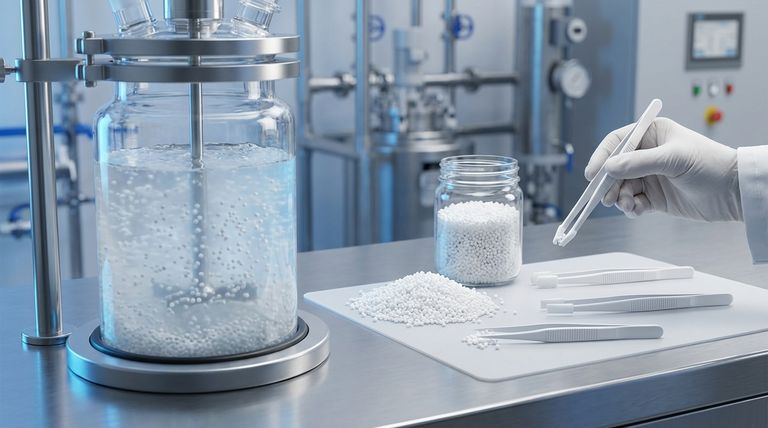

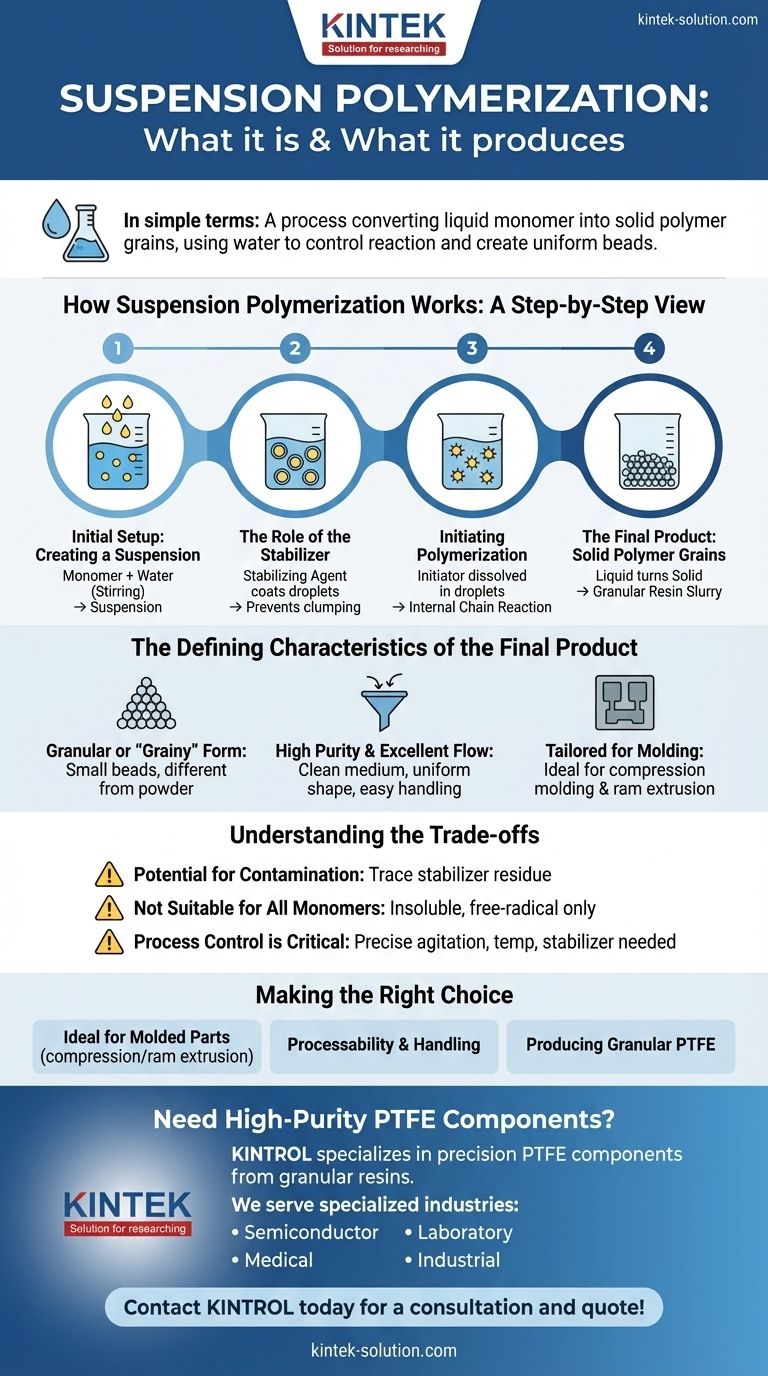
How Suspension Polymerization Works: A Step-by-Step View
This process can be visualized as creating countless tiny, self-contained reactors within a larger vessel of water. Each step is precisely controlled to produce the desired outcome.
The Initial Setup: Creating a Suspension
The process begins by adding the monomer (the raw liquid chemical to be polymerized) to water. Since the monomer is insoluble in water, vigorous stirring or agitation is required to break it up into small, stable droplets, forming a suspension.
The Role of the Stabilizer
To prevent these tiny monomer droplets from clumping together into one large, unmanageable mass, a stabilizing agent is added to the water. This agent coats the surface of each droplet, keeping them separate and uniformly dispersed throughout the reaction.
Initiating Polymerization
An initiator, a chemical that kicks off the polymerization reaction, is dissolved directly into the monomer droplets. Once the system is heated, the initiator starts a chain reaction inside each individual droplet, converting the liquid monomer into a solid polymer.
The Final Product: Solid Polymer Grains
As the reaction completes, each liquid droplet transforms into a solid, bead-like particle of polymer. The result is a slurry of polymer grains suspended in water. These grains are then filtered out, washed, and dried to become the final granular product.
The Defining Characteristics of the Final Product
The method used to create a polymer directly influences its physical properties and how it can be used. Materials made via suspension polymerization have distinct advantages.
Granular or "Grainy" Form
The most notable characteristic is the physical form. The process naturally produces small beads or grains of polymer, often referred to as granular resin. This is fundamentally different from the fine powders produced by other methods.
High Purity and Excellent Flow
Because water is an effective and clean medium for removing heat, the reaction is well-controlled, leading to a high-purity polymer. The spherical or granular shape of the particles gives them excellent "free-flowing" properties, making them easy to pour, transport, and feed into processing equipment.
Tailored for Molding Applications
The free-flowing nature of these grains makes them exceptionally well-suited for specific manufacturing techniques. They are ideal for compression molding, where the resin must fill a mold cavity evenly under pressure, and for ram extrusion, a process used to create simple shapes like rods and tubes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, suspension polymerization is not a universal solution. It's important to recognize its limitations.
Potential for Contamination
Although the resulting polymer is generally pure, trace amounts of the stabilizing agent can remain on the surface of the grains. This residue can sometimes impact the optical clarity or electrical properties of the final product.
Not Suitable for All Monomers
This technique is primarily effective for monomers that are insoluble in water and undergo free-radical polymerization. It is not a viable method for water-soluble monomers or for other types of polymerization reactions.
Process Control is Critical
Achieving a consistent and narrow particle size distribution requires precise control over agitation speed, temperature, and the concentration of the stabilizer. Deviations can lead to inconsistent product quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a polymer often means selecting the polymerization method that yields the properties you need.
- If your primary focus is creating molded parts: The free-flowing granular resin from suspension polymerization is ideal for processes like compression molding and ram extrusion.
- If your primary focus is processability and handling: The uniform, bead-like particles are easier and cleaner to handle in an industrial setting than fine powders.
- If your primary focus is producing PTFE for specific applications: Suspension polymerization is the standard method for creating granular PTFE grades used in stock shapes, seals, and gaskets.
Ultimately, suspension polymerization provides a reliable and efficient pathway to producing high-quality, granular polymers perfectly suited for demanding molding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Liquid monomer is suspended in water and polymerized into solid grains. |
| Key Product | Granular or bead-like polymer resin (e.g., granular PTFE). |
| Primary Advantage | Excellent free-flow properties for easy handling and molding. |
| Ideal For | Compression molding, ram extrusion, and creating stock shapes. |
Need High-Purity PTFE Components for Your Application?
KINTROL specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components from granular resins produced via suspension polymerization. This ensures the material integrity and free-flow properties critical for creating high-performance seals, liners, labware, and custom parts.
We serve specialized industries, including:
- Semiconductor
- Medical
- Laboratory
- Industrial
Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—guarantees you get the exact component you need. Let us help you leverage the advantages of granular PTFE in your next project.
Contact KINTROL today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















