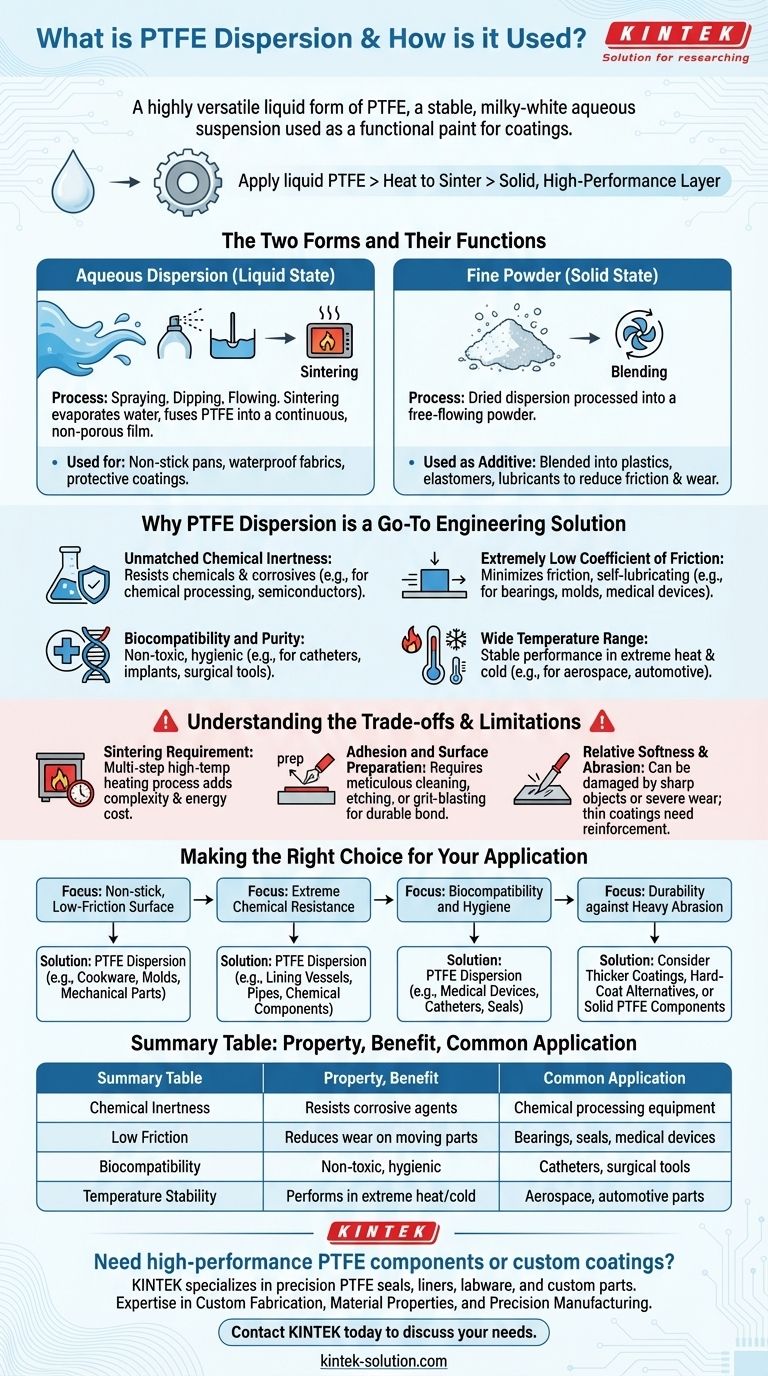
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) dispersion is a highly versatile liquid form of PTFE. It is a stable, milky-white aqueous suspension of extremely fine PTFE particles, produced through a process called dispersion polymerization. This liquid state is primarily used to apply thin, uniform coatings of PTFE onto various surfaces, which are then heated to create a solid, high-performance, non-stick layer.
The fundamental value of PTFE dispersion is its ability to act as a functional "paint." It allows the exceptional properties of solid PTFE—such as chemical inertness and low friction—to be applied to complex shapes and flexible materials where using a solid block of plastic would be impossible.

The Two Forms and Their Functions
PTFE dispersion is not a single-use product. Its utility comes from its two primary states: the liquid suspension and the dried powder derived from it.
The Liquid State: Aqueous Dispersion
The dispersion in its initial liquid form is ideal for coating and impregnation. The small particles suspended in water can be applied evenly through spraying, dipping, or flowing.
Once applied, the substrate is heated in a process called sintering. This evaporates the water and melts the PTFE particles, causing them to fuse into a continuous, non-porous film that bonds to the surface. This is the process used to create non-stick pans and waterproof fabrics.
The Solid State: Fine Powder
The aqueous dispersion can also be dried and processed into a fine, free-flowing powder. This powder serves a different set of purposes.
It can be used as an additive, blended into other materials like plastics, elastomers, or lubricants (oils and greases) to lower their coefficient of friction and improve wear resistance.
Why PTFE Dispersion is a Go-To Engineering Solution
The widespread use of PTFE dispersion is due to the remarkable combination of properties inherent to the PTFE polymer itself. Applying it as a coating transfers these benefits to the host material.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is famously resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This makes it an ideal coating for equipment in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing, protecting components from degradation.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
Known as one of the most slippery materials in existence, PTFE minimizes friction between moving parts. This property is critical for creating self-lubricating bearings, non-stick industrial molds, and smooth-operating medical devices like syringe plungers.
Biocompatibility and Purity
PTFE is non-toxic and biocompatible, meaning it does not react with bodily fluids or tissues. This makes it an essential material in the medical field for coating catheters, surgical tools, and implants, where it helps prevent bacterial buildup and ensures hygienic performance.
Wide Temperature Range
PTFE coatings maintain their integrity and performance across a vast range of temperatures. This stability is crucial for applications in demanding environments like aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PTFE dispersion coatings are not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding their limitations.
The Sintering Requirement
Applying the dispersion is only the first step. The coating achieves its final properties only after being heated to a high temperature (sintered). This multi-step process adds complexity, energy cost, and equipment requirements to manufacturing.
Adhesion and Surface Preparation
Achieving a durable bond between the PTFE coating and the substrate is critical. This requires meticulous surface preparation, often including chemical etching or grit-blasting, to ensure proper adhesion. A failure in preparation will lead to a failure of the coating.
Relative Softness and Abrasion
PTFE coatings are relatively soft and can be damaged by sharp objects or severe abrasion. While suitable for low-friction sliding, they are not ideal for environments with high-impact or grinding wear without reinforcement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is creating a non-stick, low-friction surface: PTFE dispersion is an excellent choice for coating complex shapes in cookware, industrial molds, or mechanical parts.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: It is the industry standard for lining vessels, pipes, and components exposed to corrosive media in chemical processing plants.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and hygiene: The purity of PTFE makes it a premier choice for medical devices like catheters and pump seals where preventing contamination is critical.
- If your primary focus is durability against heavy physical abrasion: You should consider thicker coatings, alternative hard-coat materials, or using a solid PTFE component, as thin dispersion coatings can wear down under intense mechanical stress.
Ultimately, PTFE dispersion provides a powerful method for imparting the extraordinary properties of solid PTFE onto surfaces where it would otherwise be impractical to apply.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosive agents | Chemical processing equipment |
| Low Friction | Reduces wear on moving parts | Bearings, seals, medical devices |
| Biocompatibility | Non-toxic, hygienic | Catheters, surgical tools |
| Temperature Stability | Performs in extreme heat/cold | Aerospace, automotive parts |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents material adhesion | Cookware, industrial molds |
Need high-performance PTFE components or custom coatings?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom-fabricated components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We leverage the unique properties of PTFE to solve complex challenges, from chemical resistance to biocompatibility.
Our expertise ensures your project benefits from:
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume production runs.
- Material Expertise: Optimal application of PTFE properties for your specific needs.
- Precision Manufacturing: Components built to exact specifications for reliable performance.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















