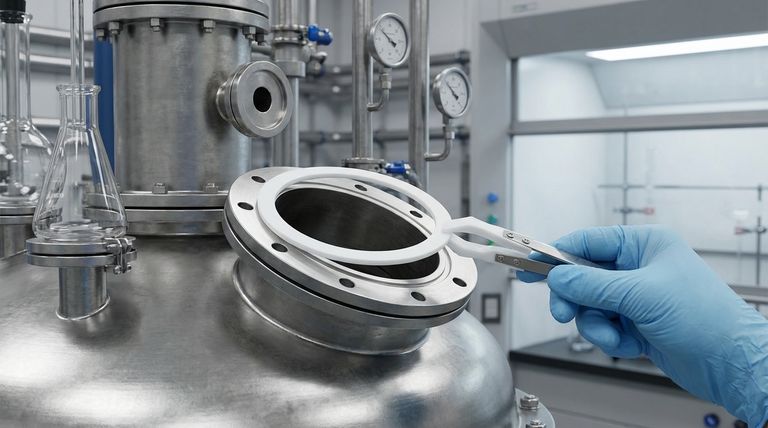
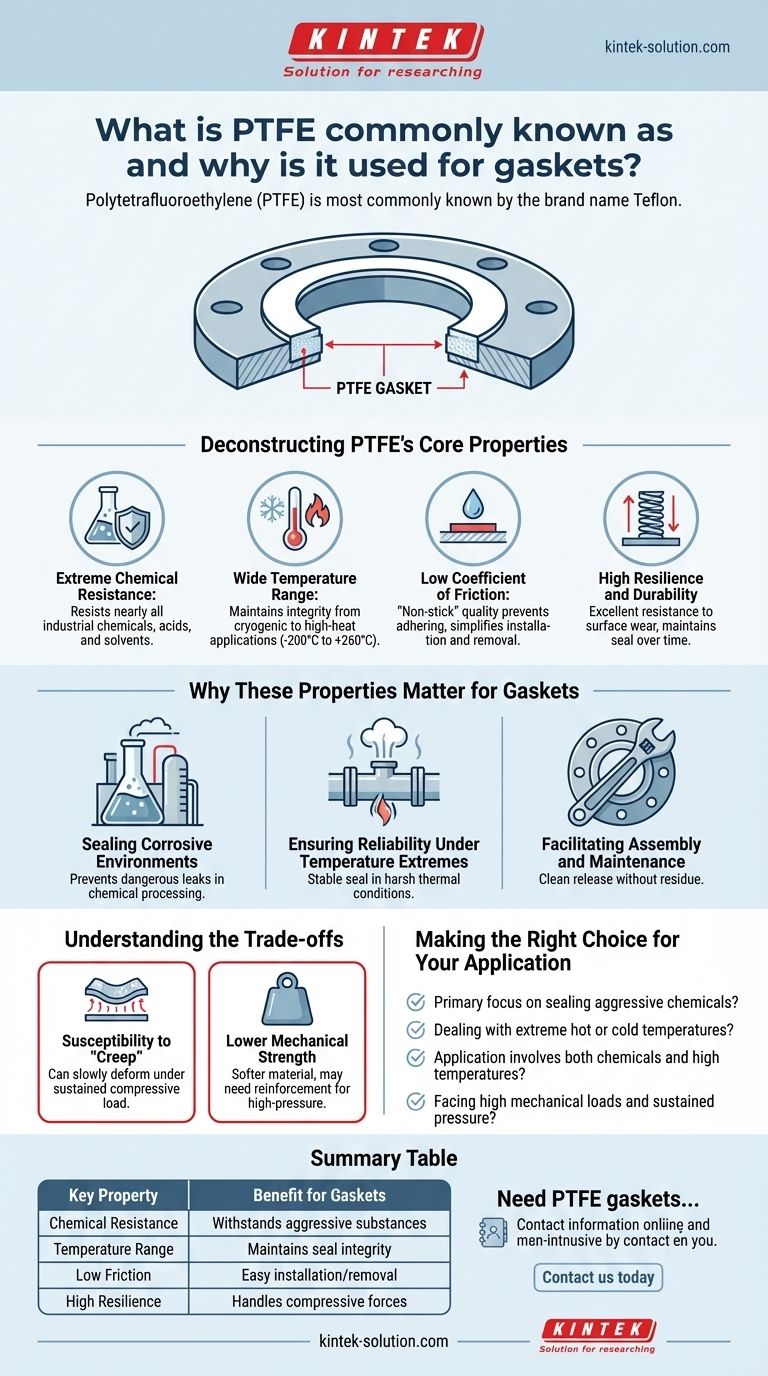
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is most commonly known by the brand name Teflon. It is a preferred material for gaskets because of its exceptional chemical resistance, ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures, and extremely low coefficient of friction, which prevents it from sticking to surfaces.
The core reason PTFE excels as a gasket material is its unique combination of properties. It provides a reliable seal in harsh chemical and high-temperature environments where most other materials would quickly degrade and fail.

Deconstructing PTFE's Core Properties
To understand why PTFE is so effective, we must look at its fundamental characteristics. These properties work in concert to create a highly durable and versatile sealing material.
Extreme Chemical Resistance
PTFE is a fluoropolymer, meaning it is constructed from incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bonds. This molecular structure makes it almost completely inert, capable of resisting nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents.
Wide Temperature Range
The material maintains its integrity across a vast temperature spectrum. It has a high melting point, allowing it to be used in high-temperature applications, and it remains flexible and resilient even in cryogenic conditions.
Low Coefficient of Friction
Known for its "non-stick" quality, PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any solid material. This prevents the gasket from adhering to flange surfaces, simplifying installation and removal without damaging equipment.
High Resilience and Durability
PTFE exhibits excellent resistance to surface wear. It can handle the compressive forces required to create a tight seal and is resilient enough to maintain that seal over long periods.
Why These Properties Matter for Gaskets
The theoretical properties of PTFE translate directly into practical benefits for sealing applications, solving critical engineering challenges.
Sealing Corrosive Environments
In chemical processing plants, refineries, and laboratories, gaskets are constantly exposed to aggressive substances. PTFE's chemical inertness ensures the gasket will not corrode, dissolve, or contaminate the process media, preventing dangerous leaks.
Ensuring Reliability Under Temperature Extremes
For applications involving high-temperature steam, exhaust systems, or the transport of cryogenic liquids, a gasket must not become brittle or melt. PTFE’s stability ensures a consistent and reliable seal under these demanding thermal conditions.
Facilitating Assembly and Maintenance
The non-stick surface is a significant practical advantage. It allows for a clean release during disassembly, preventing gasket residue on expensive flange faces and reducing maintenance time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE is not without its limitations. Understanding these is key to using it correctly.
Susceptibility to "Creep"
The most notable drawback of pure PTFE is its tendency to "creep" or cold flow. Under sustained compressive load, especially at elevated temperatures, the material can slowly deform, potentially loosening the seal over time.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metallic gaskets, PTFE is a much softer material. For very high-pressure applications, it may not provide sufficient mechanical strength on its own, which is why filled or reinforced versions of PTFE exist.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a gasket material depends entirely on the operational demands. PTFE is often the definitive choice when specific environmental challenges are present.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals: PTFE is an industry standard due to its near-universal chemical inertness.
- If you are dealing with extreme hot or cold temperatures: Its stability from cryogenic levels to over 250°C (500°F) makes it a reliable choice where other polymers fail.
- If your application involves both chemicals and high temperatures: PTFE provides a rare combination of resistances that few other materials can match.
- If you face high mechanical loads and sustained pressure: Pure PTFE may creep, so you should consider a filled PTFE composite or an alternative material.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique combination of properties makes it one of the most versatile and dependable sealing materials for challenging industrial applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Gaskets |
|---|---|
| Extreme Chemical Resistance | Withstands aggressive acids, solvents, and chemicals without degradation |
| Wide Temperature Range (-200°C to +260°C) | Maintains seal integrity from cryogenic to high-heat applications |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Non-stick surface allows easy installation and removal without residue |
| High Resilience | Handles compressive forces and maintains seal integrity over time |
Need PTFE gaskets that can handle your most demanding applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get the perfect sealing solution—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE seals, liners, and labware can solve your toughest sealing challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















