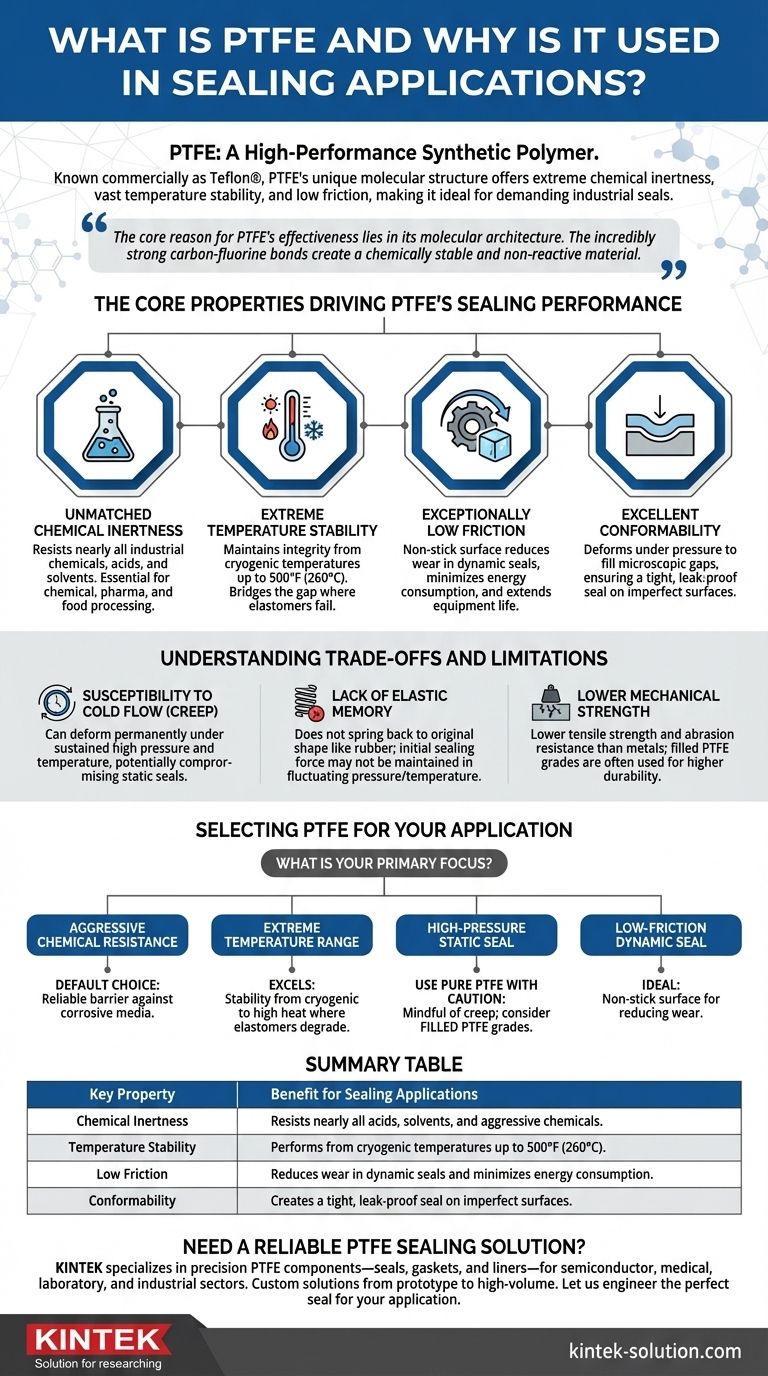
In essence, PTFE is a high-performance synthetic polymer prized in sealing for its unique combination of properties. Known commercially as Teflon®, its molecular structure gives it extreme chemical inertness, stability across a vast temperature range, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, making it an ideal material for creating reliable seals in demanding industrial environments.
The core reason for PTFE's effectiveness lies in its molecular architecture. The incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bonds create a chemically stable and non-reactive material that performs reliably where common elastomers and other plastics would quickly fail.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE's Sealing Performance
To understand why PTFE is a default choice for critical sealing applications, we must examine its fundamental characteristics. These properties are not isolated; they work together to create a uniquely robust sealing material.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The chemical structure of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) makes it resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents.
This makes PTFE seals and gaskets essential in industries like chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food production where contact with aggressive substances is constant.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its integrity and sealing capability across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows up to a continuous service temperature of 500°F (260°C).
It effectively bridges the gap where elastomeric seals fail due to heat or cold but where the application does not yet demand a metal seal.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, resulting in a non-stick surface.
In dynamic sealing applications, this property reduces wear and tear on moving parts, minimizes energy consumption, and extends the service life of the equipment.
Excellent Conformability
Despite its strength, PTFE is a relatively soft material that deforms under pressure to fill microscopic imperfections and gaps between mating surfaces.
This ability to conform ensures a tight, leak-proof seal, even on surfaces that are not perfectly uniform.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect for every situation. While PTFE's properties are exceptional, an objective analysis requires understanding its limitations, which are often direct consequences of its strengths.
Susceptibility to Cold Flow (Creep)
The same softness that allows PTFE to conform to surfaces also makes it susceptible to creep, or "cold flow."
Under sustained high pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, the material can slowly deform permanently, potentially compromising the seal over time. This is a critical design consideration for high-load static seals.
Lack of Elastic Memory
Unlike rubber or other elastomers, PTFE is not truly elastic. When compressed, it does not spring back to its original shape with the same force.
This means that in applications with fluctuating pressures or thermal cycling, the initial sealing force may not be maintained as effectively as with an elastomeric seal.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals or engineering plastics, pure PTFE has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
For applications requiring high mechanical durability, designers often specify filled PTFE grades, which incorporate materials like glass, carbon, or bronze to enhance these properties.
Selecting PTFE for Your Sealing Application
Choosing the right sealing material requires matching its properties to the specific demands of the environment.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical resistance: PTFE is the default choice, providing a reliable barrier against nearly all corrosive media.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature range: PTFE excels where standard elastomers become brittle or degrade, offering stability from cryogenic conditions to high heat.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure static seal: Use pure PTFE with caution and be mindful of potential creep; consider a filled PTFE grade for improved load-bearing capability.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction dynamic seal: PTFE's non-stick surface is ideal for reducing wear in rotating or sliding applications.
Ultimately, understanding both the strengths and weaknesses of PTFE empowers you to engineer a more reliable and long-lasting sealing solution.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Sealing Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all acids, solvents, and aggressive chemicals. |
| Temperature Stability | Performs from cryogenic temperatures up to 500°F (260°C). |
| Low Friction | Reduces wear in dynamic seals and minimizes energy consumption. |
| Conformability | Creates a tight, leak-proof seal on imperfect surfaces. |
Need a Reliable PTFE Sealing Solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, gaskets, and liners—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a standard part or a custom-fabricated solution from prototype to high-volume production, our expertise ensures a seal that delivers unmatched chemical resistance, thermal stability, and long service life.
Let us engineer the perfect seal for your demanding application. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















