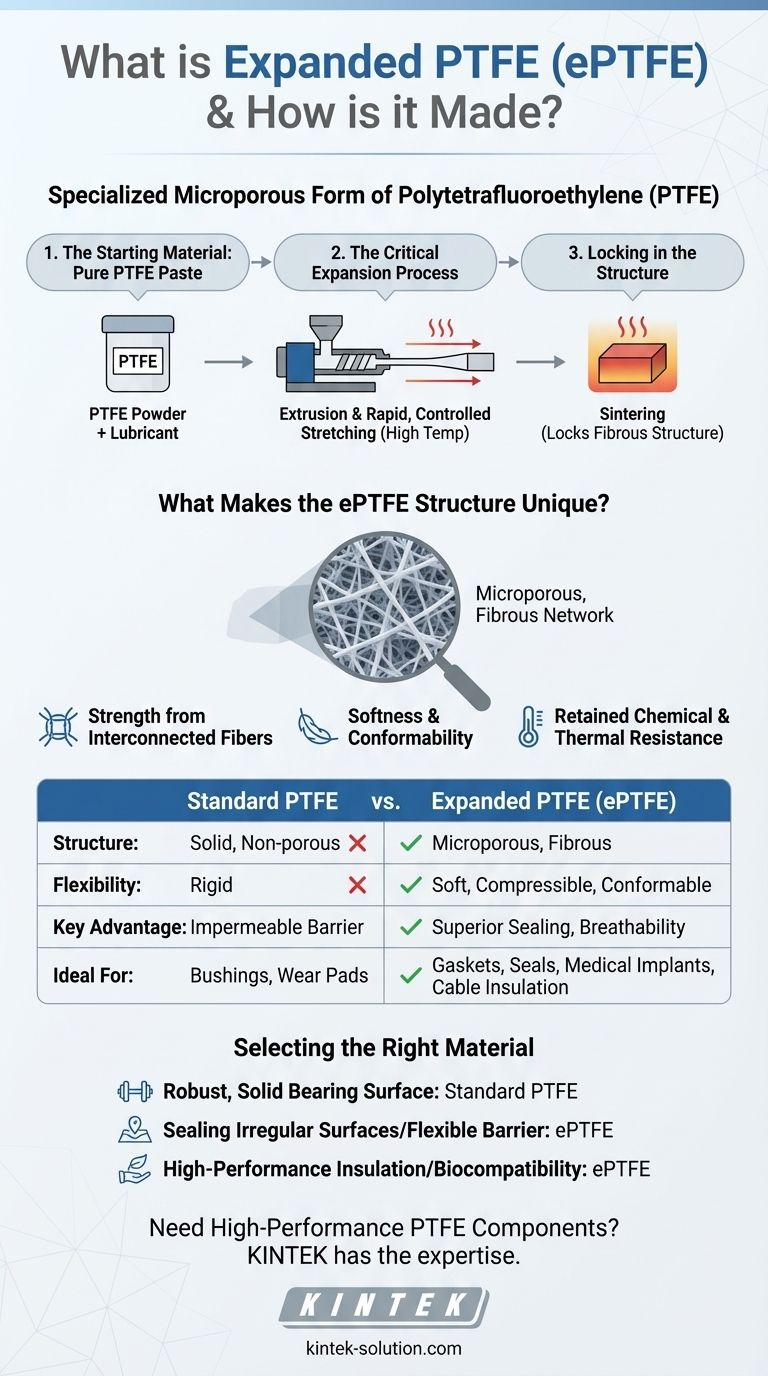
Expanded PTFE, or ePTFE, is a specialized form of Polytetrafluoroethylene created through a unique mechanical process. It is made by taking pure PTFE, typically in the form of a fine powder paste, extruding it, and then rapidly stretching it under controlled high temperatures. This expansion process reorganizes the solid material into a microporous structure of interconnected nodes and fibers, creating a material that is both strong and soft while retaining the exceptional chemical and thermal resistance of PTFE.
The defining characteristic of ePTFE is not a change in its chemical makeup, but a transformation of its physical structure. The expansion process creates a highly porous, fibrous material that combines the chemical resilience of its parent polymer with unique mechanical properties like softness, breathability, and high tensile strength.

The Transformation from PTFE to ePTFE
The creation of ePTFE is a multi-step physical process that fundamentally alters the material's properties. It begins with the same polymer but ends with a vastly different structure.
The Starting Material: Pure PTFE
The process begins with 100% pure Polytetrafluoroethylene, often referred to as virgin PTFE. This is the same chemically inert, temperature-resistant polymer known for its non-stick properties. It is typically prepared as a fine powder mixed with a lubricant to form a paste.
The Critical Expansion Process
The core of ePTFE manufacturing involves several precise steps. First, the PTFE paste is compressed and extruded through a die to create a basic shape. The key transformation occurs next, during a process of rapid, controlled stretching at high temperatures. This expansion can be done in one direction (uniaxial) or multiple directions (multi-directional).
Locking in the Structure
After stretching, the material is heated to a temperature near its melting point in a process called sintering. This final step locks the newly formed fibrous and porous structure into place, ensuring the material remains stable and does not revert to its original form.
What Makes the ePTFE Structure Unique?
The value of ePTFE lies in the unique microporous structure created during expansion. This structure is often described as having a texture similar to a dense marshmallow.
Strength from Interconnected Fibers
The stretching process pulls the PTFE molecules into a network of millions of microscopic fibers. These fibers are interconnected, creating a web-like structure that is surprisingly strong and durable despite being mostly empty space (porous).
Softness and Conformability
Unlike solid PTFE, which is relatively rigid, the porous nature of ePTFE makes it exceptionally soft, flexible, and compressible. This allows it to conform easily to irregular shapes, making it an excellent sealing agent for gaskets and seals.
Retained Chemical and Thermal Resistance
Crucially, the expansion process is physical, not chemical. This means ePTFE retains all of the remarkable properties of standard PTFE, including its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While ePTFE offers significant advantages, it's essential to understand its distinct characteristics compared to solid PTFE.
Porosity vs. Solid Barrier
The key feature of ePTFE is its microporosity. This is a major advantage for applications requiring breathability, such as medical implants or specialized vents. However, for applications that demand a completely impermeable solid barrier, standard molded or machined PTFE remains the better choice.
Mechanical Differences
ePTFE is soft and compressible, while solid PTFE is dense and rigid. If you need a material for a low-friction, load-bearing surface like a bushing or wear pad, the rigidity of solid PTFE is necessary. If you need a gasket to seal a flange, the conformability of ePTFE is superior.
Manufacturing Complexity
The multi-step expansion and sintering process is more complex than simply molding or machining a solid block of PTFE. This specialized manufacturing can influence the cost and availability of ePTFE components compared to their standard PTFE counterparts.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Understanding these properties allows you to choose effectively between standard PTFE and ePTFE for a specific technical challenge.
- If your primary focus is creating a robust, low-friction, solid bearing surface: Standard, solid PTFE is the superior choice for its rigidity and density.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular surfaces or requiring a flexible, breathable barrier: The conformable and microporous nature of ePTFE makes it the ideal material.
- If your primary focus is high-performance cable insulation or medical implants: ePTFE provides the necessary electrical properties and biocompatibility in a flexible, lightweight form.
Ultimately, choosing ePTFE is a decision to leverage a unique physical structure for performance that solid polymers simply cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard PTFE | Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Solid, non-porous | Microporous, fibrous |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Soft, compressible, conformable |
| Key Advantage | Impermeable barrier, rigidity | Superior sealing, breathability |
| Ideal For | Bushings, wear pads | Gaskets, seals, medical implants, cable insulation |
Need a high-performance PTFE component?
Whether your project requires the unique microporous structure of ePTFE for superior sealing or the rigidity of standard PTFE, KINTEK has the expertise. We specialize in the precision manufacturing and custom fabrication of PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We can guide you to the right material and deliver from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















