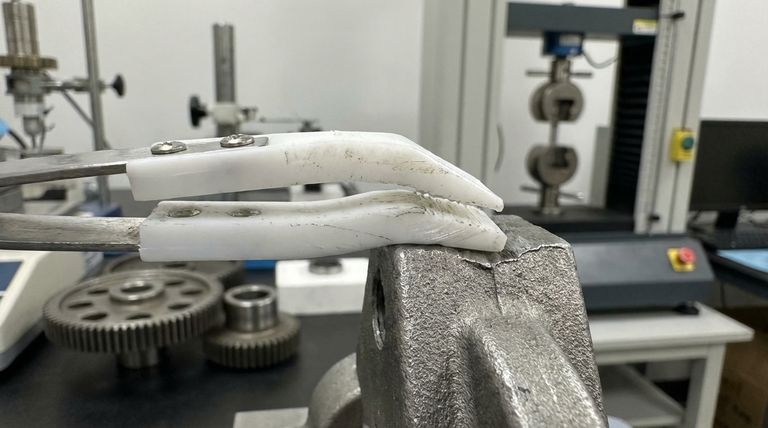
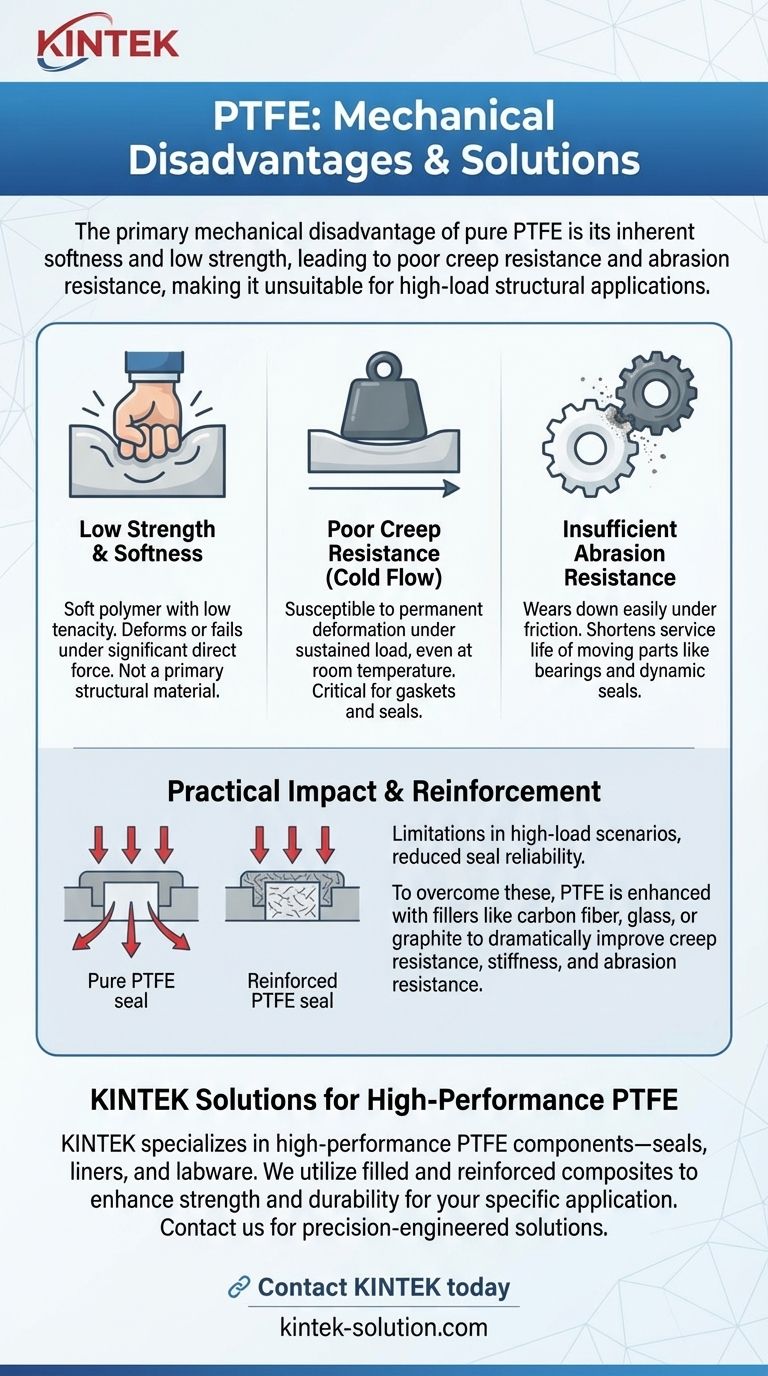
The primary mechanical disadvantage of PTFE is its inherent softness and low strength. This results in poor resistance to "creep"—the tendency to deform permanently under sustained pressure—and low resistance to abrasion, making it unsuitable for high-load structural applications in its pure form.
PTFE's exceptional non-stick properties and chemical inertness are a direct result of its molecular structure, but this same structure gives it a soft, low-strength nature. The core challenge is that it deforms under load and wears away easily, requiring reinforcement for most mechanical applications.

The Core Mechanical Weaknesses of PTFE
While valued for its unique surface properties, the mechanical limitations of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are significant and must be understood before it is specified for any component.
Low Strength and Softness
PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. It has a low mechanical tenacity and is soft enough that an imprint can be left with just a fingernail.
This softness means it cannot withstand significant direct force without deforming or failing, which is why it is almost never used as a primary structural material.
Poor Creep Resistance (Cold Flow)
One of the most critical disadvantages of PTFE is its susceptibility to creep, also known as cold flow.
This means that when a constant load or pressure is applied, the material will slowly and permanently deform, even at room temperature. It cannot return to its original shape.
This is a major point of failure for components like gaskets and seals, where maintaining a constant shape under pressure is essential for performance.
Insufficient Abrasion Resistance
Pure PTFE wears down easily when subjected to friction from other surfaces.
This lack of abrasion resistance can significantly shorten the service life of moving parts like bearings or dynamic seals, as the material is gradually worn away.
The Practical Impact on Applications
These fundamental weaknesses translate directly into tangible limitations in real-world engineering scenarios.
Limitations in High-Load Scenarios
Because of its softness and tendency to creep, pure PTFE is a poor choice for high-load applications.
For example, shaft bearings or load-bearing bushings made from pure PTFE can deform and fail under the consistent pressure of their operation.
Reduced Seal Reliability
In applications like ball valve seats or gaskets, PTFE's weaknesses can compromise reliability.
A scratch on a sealing surface can create a leak path, and its high coefficient of thermal expansion means temperature changes can cause it to expand or contract more than surrounding parts, potentially breaking the seal.
The Inherent Need for Reinforcement
To overcome these mechanical shortfalls, PTFE is frequently enhanced with fillers.
Materials like carbon fiber, glass, or graphite are mixed into the PTFE base. These fillers act as a reinforcing matrix, dramatically improving creep resistance, stiffness, and abrasion resistance without completely sacrificing its low-friction properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing PTFE is a classic engineering trade-off. You are selecting a material for its elite surface characteristics, not its mechanical prowess.
The Friction vs. Strength Dilemma
The fundamental trade-off is accepting low mechanical strength to gain world-class chemical inertness and an extremely low coefficient of friction.
If your application demands high strength, PTFE is likely the wrong starting point unless a heavily reinforced composite version is considered.
Processing and Machining Challenges
PTFE's unique properties also make it difficult to work with. It is effectively unweldable because it does not melt into a liquid state when heated.
This, combined with its softness, can make precision machining challenging and drive up the cost and lead time for custom components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To decide if PTFE is appropriate, you must weigh its benefits against its mechanical limitations for your specific use case.
- If your primary focus is extremely low friction or broad chemical resistance: PTFE is an excellent candidate, but you must use a filled grade for any application involving sustained pressure or abrasion.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load or structural integrity: Pure PTFE is unsuitable. You should consider other high-strength engineering polymers or metals.
- If your primary focus is a reliable, long-lasting seal under pressure: Be cautious with pure PTFE due to creep. A filled PTFE or an entirely different sealing material may provide better long-term performance.
Ultimately, understanding that pure PTFE is a specialized surface material—not a structural one—is the key to using it effectively.
Summary Table:
| Mechanical Disadvantage | Practical Consequence | Common Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Strength & Softness | Deforms under load; not a structural material | Use filled/reinforced PTFE grades |
| Poor Creep Resistance (Cold Flow) | Permanent deformation under sustained pressure | Reinforcement with carbon, glass, or graphite |
| Insufficient Abrasion Resistance | Wears down quickly in moving parts | Filled PTFE composites improve wear life |
Don't let PTFE's mechanical limitations compromise your design.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We overcome PTFE's inherent weaknesses by expertly utilizing filled and reinforced composites to enhance creep resistance, strength, and durability for your specific application.
Whether you need a custom prototype or high-volume production, we deliver precision-engineered solutions that perform reliably under pressure.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our advanced PTFE components can meet your exact requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















