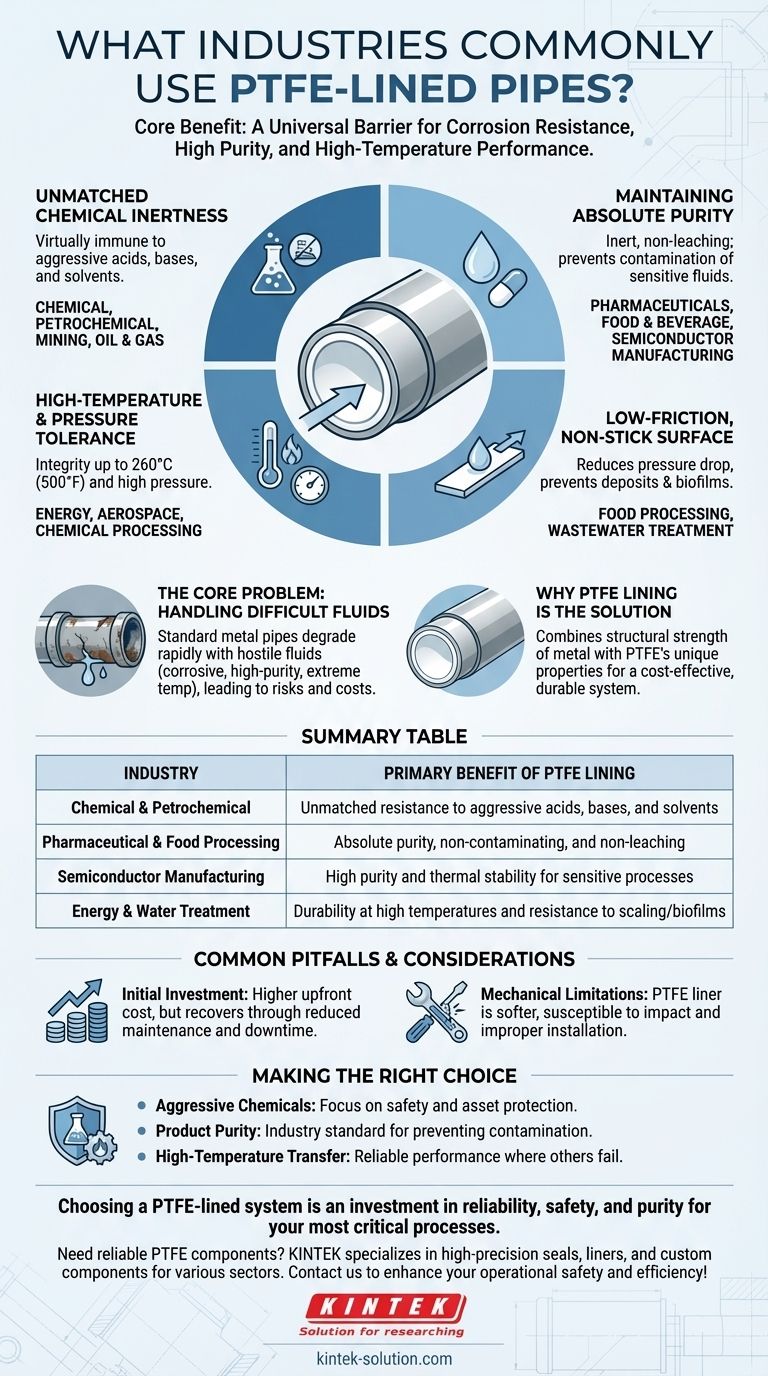
In short, PTFE-lined pipes are primarily used in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries. Their adoption extends to any sector that requires extreme corrosion resistance, high purity, and performance at high temperatures, including semiconductor manufacturing, energy, and water treatment.
The core reason for this widespread use is simple: PTFE creates a nearly universal barrier. It allows industries to safely transport highly aggressive or sensitive fluids through standard piping systems without the risk of corrosion or contamination.

The Core Problem: Handling Difficult Fluids
Many industrial processes rely on moving fluids that are hostile to conventional materials. These fluids can be highly corrosive, demand absolute purity, or exist at extreme temperatures.
Using standard metal pipes in these situations leads to rapid degradation, leaks, and potential product contamination, creating significant safety risks and operational costs.
Why PTFE Lining is the Definitive Solution
A PTFE-lined pipe combines the structural strength of a metal exterior (like carbon or stainless steel) with the unique properties of a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) interior. This creates a cost-effective system that solves the core problem of fluid handling.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. It is virtually immune to attack from aggressive acids, bases, and solvents that would quickly corrode even high-grade metal alloys.
This makes it the material of choice for the chemical, petrochemical, mining, and oil & gas industries, where equipment longevity and safety are paramount.
Maintaining Absolute Purity
In industries like pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and semiconductor manufacturing, preventing contamination is non-negotiable. Even trace amounts of leached metals or reactive byproducts can ruin a batch or an entire production run.
Because PTFE is inert and non-leaching, it ensures the fluid passing through the pipe remains in its original, pure state.
High-Temperature and Pressure Tolerance
Many chemical reactions and industrial processes occur at elevated temperatures. PTFE linings maintain their structural and chemical integrity at continuous service temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
This thermal stability makes it a reliable choice for demanding applications in the energy, aerospace, and chemical processing sectors.
Low-Friction, Non-Stick Surface
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, which is why it's famous for non-stick coatings. In a piping system, this property reduces pressure drop and helps prevent the buildup of deposits or biofilms.
This is particularly valuable in food processing and wastewater treatment, where preventing blockages and ensuring clean, efficient flow is critical.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While PTFE lining is a powerful solution, it's essential to understand its context. It represents a balance between performance and cost.
Initial Investment
PTFE-lined piping systems have a higher upfront cost compared to standard unlined steel or some basic plastic pipes. However, this initial investment is often recovered over the system's lifespan due to reduced maintenance, replacement, and downtime.
Mechanical Limitations
The steel exterior provides the mechanical strength, but the PTFE liner itself is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to damage from mechanical impact, abrasive slurries, or improper installation techniques (like over-torquing flanges). Careful handling and adherence to specifications are crucial.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right piping system depends entirely on the specific demands of the fluid you are handling.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE's near-universal chemical inertness provides the highest level of safety and long-term asset protection.
- If your primary focus is product purity: A PTFE-lined system is the industry standard for preventing contamination in pharmaceutical, food, or semiconductor applications.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature fluid transfer: PTFE's thermal stability ensures reliable performance where many plastics and even some metals would fail.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE-lined system is an investment in reliability, safety, and purity for your most critical processes.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Benefit of PTFE Lining |
|---|---|
| Chemical & Petrochemical | Unmatched resistance to aggressive acids, bases, and solvents |
| Pharmaceutical & Food Processing | Absolute purity, non-contaminating, and non-leaching |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | High purity and thermal stability for sensitive processes |
| Energy & Water Treatment | Durability at high temperatures and resistance to scaling/biofilms |
Need reliable PTFE components for your critical processes? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure your systems achieve maximum corrosion resistance, purity, and longevity—from prototype to high-volume production. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our expertise enhance your operational safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application



















