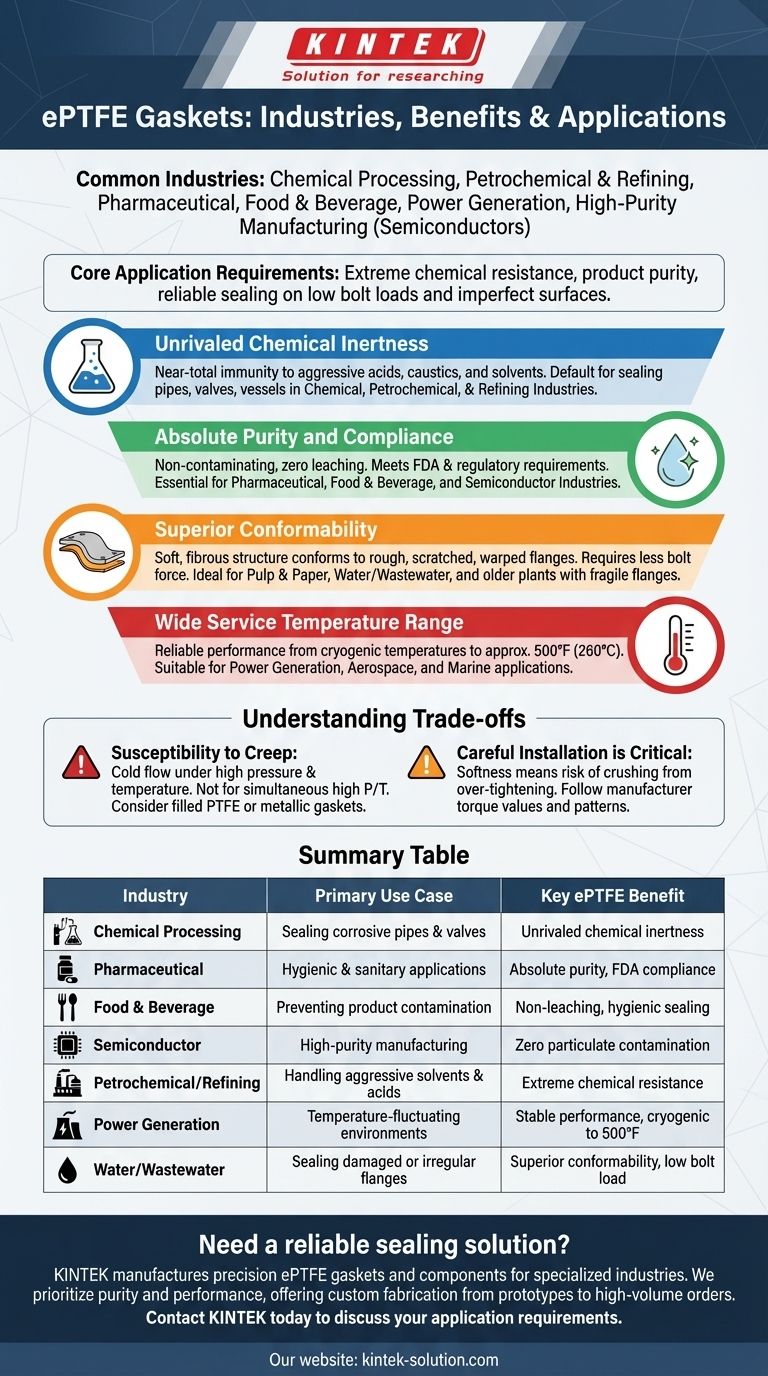
In short, ePTFE gaskets are used in virtually any industry that handles aggressive chemicals, requires absolute purity, or needs a reliable seal on less-than-perfect surfaces. The most common industries include chemical processing, petrochemical and refining, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, power generation, and high-purity manufacturing such as semiconductors.
The specific industry is less important than the application requirements. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is chosen when the priority is extreme chemical resistance, product purity, and a reliable seal under low bolt loads, especially on fragile or irregular flange surfaces.

Why ePTFE Is a Go-To Sealing Solution
Expanded PTFE is a unique material created by expanding standard PTFE, resulting in a fibrous, porous microstructure. This structure gives it exceptional properties that make it invaluable for critical sealing applications across many sectors.
Unrivaled Chemical Inertness
The primary reason for ePTFE's widespread use is its near-total immunity to chemical attack. It can handle the most aggressive acids, caustics, and solvents without degrading.
This makes it the default choice for sealing pipes, valves, and vessels in the chemical, petrochemical, and refining industries, where contact with corrosive media is constant.
Absolute Purity and Compliance
Standard PTFE is inherently pure and non-contaminating. The manufacturing process for ePTFE maintains this purity, ensuring it does not leach chemicals or particulates into the process media.
This property is non-negotiable in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and semiconductor industries. Here, product purity is paramount, and ePTFE meets stringent FDA and other regulatory requirements for hygienic and sanitary conditions.
Superior Conformability
The soft, fibrous structure of ePTFE allows it to conform easily to rough, scratched, or warped flange surfaces. It creates a tight seal with much less bolt force than is required for many other gasket types.
This is a significant advantage in pulp & paper, water & wastewater treatment, and older manufacturing plants. It's ideal for sealing fragile flanges made of glass, plastic, or ceramic, which could crack under the high torque required for other gaskets.
Wide Service Temperature Range
ePTFE performs reliably across a broad temperature spectrum, from cryogenic temperatures up to approximately 500°F (260°C).
This stability makes it suitable for applications in power generation facilities, aerospace components, and marine applications that experience significant temperature fluctuations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly versatile, ePTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly and avoiding failure.
Susceptibility to Creep
The most significant limitation of PTFE-based materials is creep, also known as cold flow. Under the combined forces of bolt load and high temperature, the material can slowly deform and "flow" out of the flange, leading to a loss of seal.
This makes pure ePTFE unsuitable for applications involving very high pressures and high temperatures simultaneously. For these services, filled PTFE or metallic gaskets are often a better choice.
Careful Installation is Critical
The softness that makes ePTFE so conformable also makes it susceptible to damage from over-tightening. Applying excessive torque can crush the gasket's fibrous structure, compromising its sealing ability.
It is essential to follow manufacturer-specified torque values and use proper installation patterns to ensure a reliable, long-lasting seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right gasket material comes down to the specific demands of your service conditions.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: ePTFE is one of the safest and most reliable choices available.
- If your primary focus is product purity and hygiene: ePTFE is an industry standard for pharmaceutical and food processing applications.
- If you need to seal fragile or damaged equipment flanges: The low-stress sealing capability of ePTFE is a significant advantage.
- If you are dealing with high-pressure, high-temperature steam or gas: You should evaluate filled PTFE or alternative materials designed specifically to resist creep.
Ultimately, understanding the unique combination of chemical inertness and mechanical conformability is the key to deploying ePTFE gaskets effectively.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use Case | Key ePTFE Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Sealing corrosive pipes & valves | Unrivaled chemical inertness |
| Pharmaceutical | Hygienic & sanitary applications | Absolute purity, FDA compliance |
| Food & Beverage | Preventing product contamination | Non-leaching, hygienic sealing |
| Semiconductor | High-purity manufacturing processes | Zero particulate contamination |
| Petrochemical/Refining | Handling aggressive solvents & acids | Extreme chemical resistance |
| Power Generation | Temperature-fluctuating environments | Stable performance from cryogenic to 500°F |
| Water/Wastewater | Sealing damaged or irregular flanges | Superior conformability with low bolt load |
Need a reliable sealing solution for aggressive chemicals, high purity requirements, or challenging flange surfaces?
KINTEK manufactures precision ePTFE gaskets and components specifically designed for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, industrial, and other specialized industries. We prioritize material purity and performance while offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application requirements and discover how our ePTFE expertise can solve your toughest sealing challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















