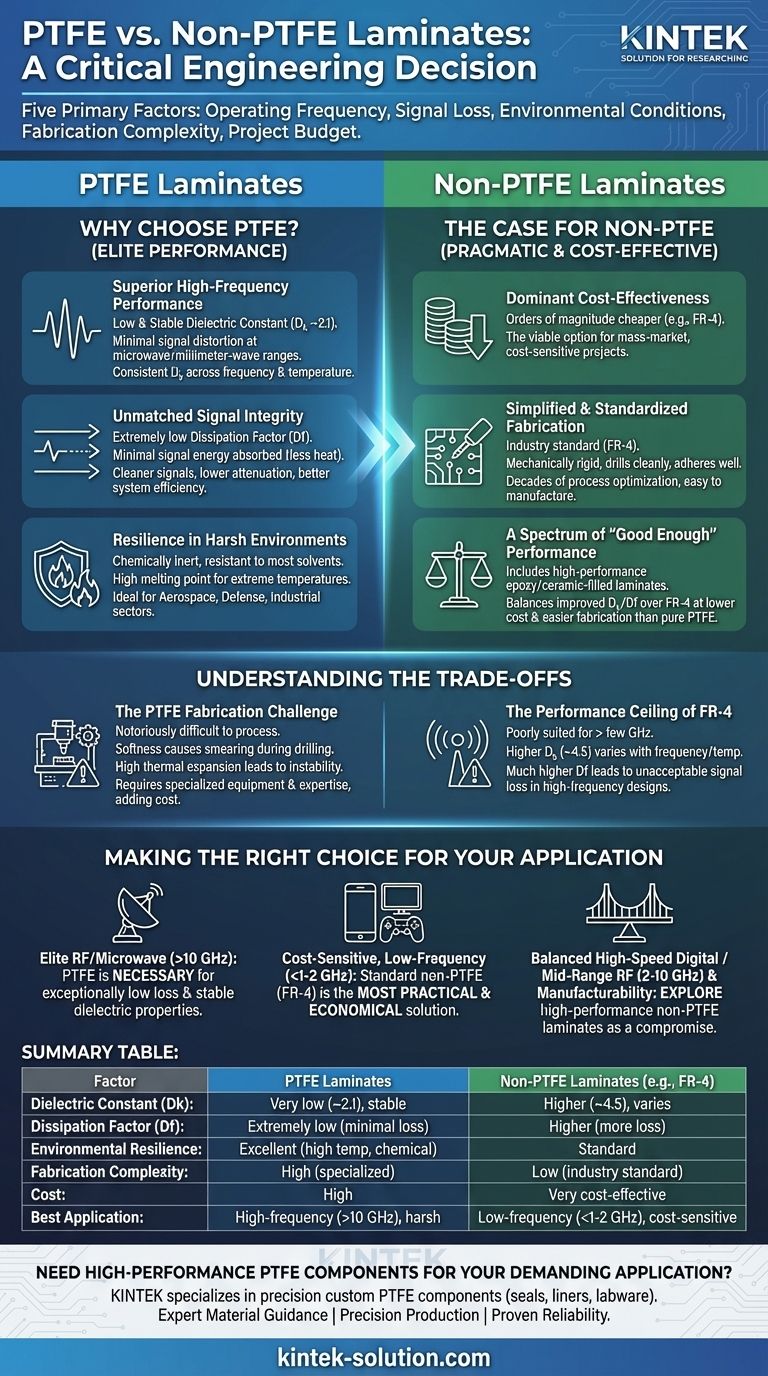
The choice between PTFE and non-PTFE laminates is a critical engineering decision that hinges on five primary factors: your application's operating frequency, your tolerance for signal loss, the environmental conditions, fabrication complexity, and your project budget. While PTFE offers supreme performance for high-frequency and harsh-environment applications, non-PTFE materials provide a more practical and cost-effective solution for a vast range of standard electronics.
The core decision is a direct trade-off: PTFE delivers superior electrical performance and environmental resilience at the cost of higher material expense and significant manufacturing challenges. Non-PTFE materials, conversely, prioritize ease of fabrication and cost-effectiveness over elite performance.

The Performance Divide: Why Choose PTFE?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known commercially as Teflon®, is a high-performance fluoropolymer. Its unique molecular structure gives it properties that are highly desirable for demanding electronic applications.
Superior High-Frequency Performance
PTFE possesses a very low and stable dielectric constant (Dk), typically around 2.1. This property is critical for high-frequency circuits, as it allows for predictable performance and minimal signal distortion as frequencies increase into the microwave and millimeter-wave ranges.
Furthermore, its Dk remains exceptionally consistent across a wide range of frequencies and temperatures, which is a key requirement for reliable device operation.
Unmatched Signal Integrity
Signal loss is a major concern in high-speed digital and RF circuits. PTFE exhibits an extremely low dissipation factor (Df), also known as loss tangent.
A low Df means that very little of the signal's energy is absorbed and converted to heat by the laminate material. This results in cleaner signals, lower attenuation over distance, and better overall system efficiency.
Resilience in Harsh Environments
PTFE is chemically inert and resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. It also has an impressively high melting point and can operate reliably at temperatures that would degrade most other laminates.
This makes it the default choice for applications in aerospace, defense, and industrial sectors where exposure to extreme temperatures or corrosive substances is expected.
Practical Realities: The Case for Non-PTFE
While PTFE is the peak performer, the vast majority of electronic devices do not require such extreme capabilities. This is where non-PTFE laminates, most commonly FR-4, become the pragmatic choice.
Dominant Cost-Effectiveness
The most significant advantage of non-PTFE laminates like FR-4 (a glass-reinforced epoxy) is cost. It is orders of magnitude cheaper than PTFE-based materials, making it the only viable option for mass-market consumer electronics and cost-sensitive projects.
Simplified and Standardized Fabrication
FR-4 and other rigid non-PTFE laminates are the industry standard. Decades of process optimization have made them incredibly easy to manufacture. They are mechanically rigid, drill cleanly, and adhere well to copper, simplifying the entire circuit board production process.
A Spectrum of "Good Enough" Performance
The "non-PTFE" category includes more than just basic FR-4. There are many high-performance epoxy and ceramic-filled hydrocarbon laminates (from manufacturers like Rogers or Isola) that bridge the performance gap.
These materials offer improved Dk and Df characteristics over FR-4 at a lower cost and with easier fabrication than pure PTFE, providing a balanced option for many applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material requires acknowledging the downsides of each option. The benefits of one material are often the direct weaknesses of the other.
The PTFE Fabrication Challenge
Working with PTFE is notoriously difficult. Its softness can cause smearing during drilling, and its high coefficient of thermal expansion can lead to dimensional instability and plated through-hole reliability issues. Specialized equipment and expertise are required to process it successfully, adding to the overall cost.
The Performance Ceiling of FR-4
Standard FR-4 is poorly suited for applications above a few gigahertz. Its dielectric constant is higher (around 4.5) and, more importantly, it varies significantly with frequency and temperature. Its dissipation factor is also much higher, leading to unacceptable signal loss in high-frequency designs.
The Budget vs. Performance Equation
Ultimately, the decision is an economic one. You must determine if the performance gains offered by PTFE justify the substantial increase in both material cost and manufacturing complexity. Over-engineering a design with PTFE when a high-performance non-PTFE material would suffice is a common and costly mistake.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Consulting with your PCB fabricator early in the design process is always advised. They can provide crucial insight into the practical challenges and costs associated with your material choice.
- If your primary focus is elite RF/microwave performance (>10 GHz): PTFE is the necessary choice for its exceptionally low loss and stable dielectric properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, low-frequency electronics (<1-2 GHz): Standard non-PTFE materials like FR-4 are the most practical and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is a balance of high-speed digital or mid-range RF performance (2-10 GHz) and manufacturability: Explore high-performance non-PTFE laminates that offer a compromise between the two extremes.
Choosing the right laminate is about deliberately matching the material's capabilities to the precise requirements of your project.
Summary Table:
| Factor | PTFE Laminates | Non-PTFE Laminates (e.g., FR-4) |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant (Dk) | Very low (~2.1), stable with frequency/temp | Higher (~4.5), varies with frequency/temp |
| Dissipation Factor (Df) | Extremely low (minimal signal loss) | Higher (more signal loss) |
| Environmental Resilience | Excellent (high temp, chemical resistance) | Standard |
| Fabrication Complexity | High (requires specialized processes) | Low (industry standard, easy to manufacture) |
| Cost | High | Very cost-effective |
| Best Application | High-frequency RF/Microwave (>10 GHz), harsh environments | Low-frequency (<1-2 GHz), cost-sensitive consumer electronics |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Demanding Application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for industries where performance and reliability are non-negotiable. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we understand the critical balance between material properties and manufacturability.
We offer:
- Expert Material Guidance: Leverage our deep knowledge of PTFE and other high-performance polymers.
- Precision Production: From custom prototypes to high-volume orders, we ensure every component meets your exact specifications.
- Proven Reliability: Trusted by specialized industries for durable, chemically resistant, and high-temperature solutions.
Let's discuss how our PTFE expertise can enhance your product's performance and reliability. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















