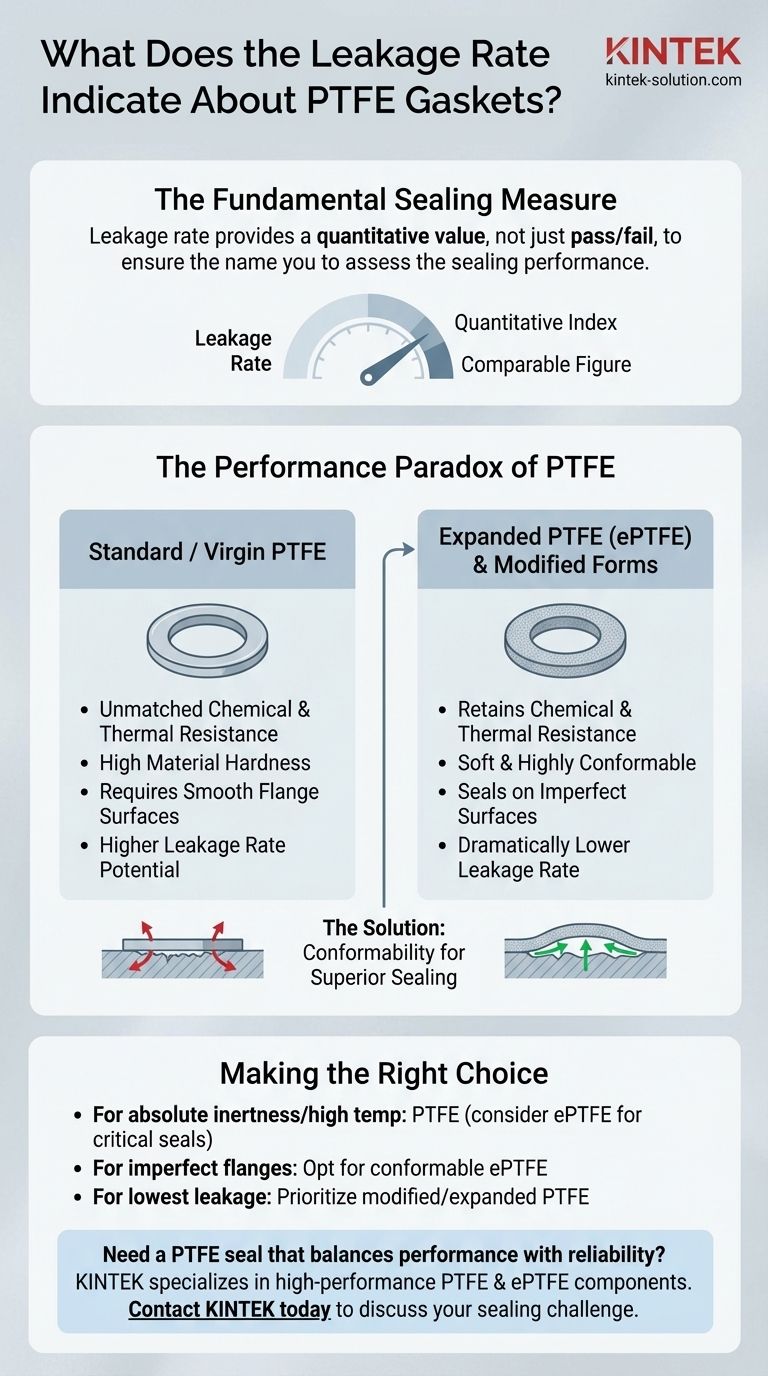
Leakage rate is a fundamental measure of a gasket's sealing performance. It provides a quantitative value that assesses how well a gasket can prevent a fluid or gas from escaping a sealed joint, making it a critical parameter for selection. For Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets, this rate is particularly important as it highlights a key trade-off between the material's exceptional resistances and its physical sealing characteristics.
While PTFE gaskets offer unparalleled chemical and thermal resistance, their leakage rate reveals a critical trade-off. The material's inherent hardness can lead to higher leakage unless specific types, like expanded PTFE, or improved flange surfaces are utilized.

What Leakage Rate Truly Measures
A Quantitative Sealing Index
The leakage rate is not a simple pass/fail metric. Instead, it offers a precise, comparable figure that defines a gasket's sealing ability under specific conditions.
This allows engineers and technicians to compare different gasket materials and types objectively, ensuring the chosen component meets the strict requirements of the application.
The Impact of Material Properties
A gasket’s material composition is the primary driver of its potential leakage rate. Factors like hardness, compressibility, and recovery directly influence how well the gasket conforms to the imperfections on a flange surface to create a tight seal.
The Performance Paradox of PTFE Gaskets
Unmatched Chemical and Thermal Stability
PTFE is renowned for its extraordinary material properties. It is virtually inert to all chemicals across the entire pH range (0–14) and remains stable in extreme temperatures, from cryogenic levels up to 260°C (500°F).
These characteristics, combined with low friction and non-contaminating properties, make PTFE the default choice for chemically aggressive or high-purity environments.
The Challenge of Material Hardness
Standard, or virgin, PTFE is a relatively hard material compared to other elastomers or gasket fillers. This hardness presents a mechanical challenge for sealing.
A harder material does not conform as easily to the microscopic irregularities, scratches, and waves present on typical flange surfaces.
How Hardness Can Increase Leakage
Because standard PTFE is less malleable, it requires greater compressive force (bolt load) to flow into the flange imperfections.
If the surfaces are not perfectly smooth or the load is insufficient, microscopic leak paths can remain. This results in a higher measured leakage rate compared to softer, more conformable gasket materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Standard PTFE vs. Softer Materials
In a direct comparison, a standard PTFE ring gasket will often exhibit a higher leakage rate than gaskets made from more pliable materials under the same conditions.
This is a direct consequence of its hardness and is a critical factor to consider during the design and selection phase.
The Importance of Surface Finish
To achieve an acceptable leakage rate with standard PTFE, the flange sealing surfaces must be exceptionally smooth and well-maintained. The references note that "post-process surface finish improvements" are often required to ensure a low-leakage seal.
The Solution: Modified and Expanded PTFE
To address the leakage issue, manufacturers developed different forms of PTFE. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) and other modified versions are created to be much softer and more conformable than virgin PTFE.
These advanced types retain the outstanding chemical and thermal resistance of PTFE but compress easily to fill flange imperfections, resulting in dramatically lower leakage rates even on less-than-perfect surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires balancing the material's chemical properties with its mechanical sealing performance.
- If your primary focus is absolute chemical inertness or high temperature: PTFE is an excellent candidate, but strongly consider expanded PTFE (ePTFE) for critical applications to ensure a tight seal.
- If you are sealing against imperfect or irregular flange surfaces: A standard virgin PTFE gasket is likely a poor choice; opt for a highly conformable material like expanded PTFE to prevent leakage.
- If your system requires the lowest possible leakage rate: Do not assume all PTFE is the same. Prioritize modified or expanded PTFE, which are specifically engineered for superior sealing performance.
Ultimately, understanding the leakage rate allows you to select the right type of PTFE gasket, ensuring you harness its strengths without being compromised by its inherent weaknesses.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Gasket Type | Key Characteristic | Impact on Leakage Rate | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard/Virgin PTFE | High hardness, chemical inertness | Higher (requires smooth surfaces/high load) | Chemically aggressive environments with perfect flanges |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Soft, highly conformable | Lower (seals on imperfect surfaces) | Critical seals, irregular surfaces, low-leakage requirements |
Need a PTFE seal that balances performance with reliability?
Understanding the trade-off between chemical resistance and leakage rate is key to selecting the right gasket. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE and expanded PTFE (ePTFE) components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get a seal engineered for your specific application's demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sealing challenge and discover the right PTFE solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















