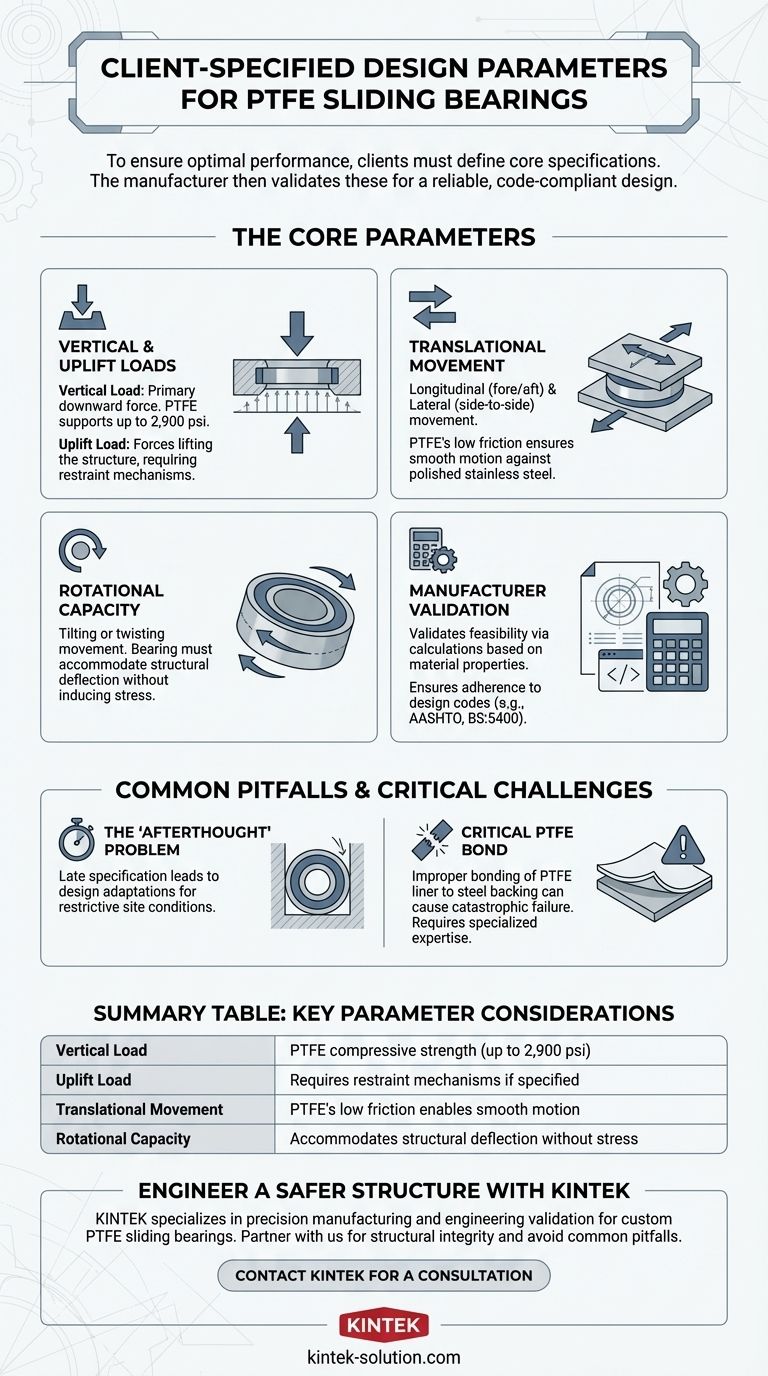
When specifying PTFE sliding bearings, clients must provide a precise set of design parameters to ensure the component meets the unique demands of the structure. These core specifications include the expected vertical load, required longitudinal and lateral movement, any potential uplift loads, and the degree of rotation the bearing must accommodate. A manufacturer uses this data to design a custom bearing and verify its feasibility through engineering calculations.
The client's role is to define the external forces and movements the bearing must endure. However, the success of the component hinges on the manufacturer's ability to translate those specifications into a reliable design that accounts for material properties and critical, often overlooked, production challenges.

The Core Design Parameters Explained
To engineer a functional and safe PTFE bearing, a manufacturer requires a clear definition of the operational demands. These parameters form the blueprint for the entire design.
Vertical and Uplift Loads
The vertical load is the primary downward force, or weight, the bearing must support. PTFE's excellent compressive strength, capable of handling pressures up to 2,900 psi, makes it ideal for this purpose.
Conversely, uplift loads are forces that could potentially lift the superstructure off the bearing. The design must include mechanisms to restrain this movement if specified.
Translational Movement (Longitudinal & Lateral)
A bearing's primary function is to allow for movement. Longitudinal movement (forward and backward) and lateral movement (side-to-side) are critical specifications.
This is where PTFE excels. It has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid, especially when sliding against a polished stainless steel plate, allowing for smooth, low-resistance motion.
Rotational Capacity
Structures are not entirely rigid. Rotation refers to the slight twisting or tilting movement the bearing must permit as the superstructure deflects or adjusts under various conditions. The bearing must be designed to accommodate this pivot without inducing stress.
From Specification to Reality: The Manufacturer's Role
Receiving the parameters is only the first step. An experienced manufacturer adds value by validating the design and ensuring its long-term viability.
Verifying Feasibility with Calculations
The manufacturer is responsible for providing calculations that prove the proposed design can safely handle the client's specified loads and movements. This is based on the known material properties of the PTFE, stainless steel, and backing plates.
Adherence to Design Codes
Designs must conform to established engineering standards. Key codes include AASHTO (American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials) and BS:5400 for global projects, or regional standards like IRC:83 (Part II) in India.
How the Components Work Together
A typical PTFE sliding bearing is a system. It consists of two steel plates, with one housing a sheet of PTFE and the other faced with a highly polished stainless steel surface. The low-friction interface between the PTFE and stainless steel allows for movement while the steel plates distribute the load.
Common Pitfalls and Real-World Constraints
The transition from a theoretical design to a physical product is where most problems arise. Understanding these challenges is key to avoiding costly errors and delays.
The "Afterthought" Problem
Bearings are frequently overlooked until late in the project timeline. This leads to rushed requests where the design must be adapted to pre-existing and often restrictive site conditions.
Physical and Installation Constraints
Late-stage specifications often reveal limitations. There may be insufficient space for the ideal portal plate size, unexpected gaps between structures, or restrictions on welding or bolting to the existing steelwork, requiring costly and complex custom solutions.
The Criticality of the PTFE Bond
The single most critical aspect of manufacturing is the bonding of the PTFE liner to its steel backing plate. This is a difficult process that requires specialized expertise.
Improper or failed bonding can cause the liner to separate, leading to rapid degradation of the bearing's performance and, in the worst-case scenario, catastrophic structural failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your specification process should be guided by your project's primary goals.
- If your primary focus is structural safety and longevity: Prioritize selecting a manufacturer with documented experience and a proven track record in bonding PTFE liners, as this is the most common point of catastrophic failure.
- If your primary focus is project efficiency and budget control: Engage the bearing manufacturer early in the design process to avoid late-stage customizations driven by unforeseen physical constraints.
- If your primary focus is performance validation: Insist on receiving detailed calculations that verify the proposed bearing design can accommodate all specified loads and movements according to established engineering codes.
A precise and early specification is the foundation for a reliable and durable structural bearing system.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Description | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Load | Primary downward force/weight | PTFE compressive strength (up to 2,900 psi) |
| Uplift Load | Force lifting structure off bearing | Requires restraint mechanisms if specified |
| Translational Movement | Longitudinal (forward/back) & lateral (side-to-side) movement | PTFE's low coefficient of friction enables smooth motion |
| Rotational Capacity | Tilting or twisting movement | Must accommodate structural deflection without inducing stress |
Engineer a Safer, More Reliable Structure with KINTEK
Specifying PTFE sliding bearings is complex, but you don't have to navigate it alone. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom sliding bearings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We go beyond simply taking your parameters. Our team provides critical engineering validation to ensure your design is feasible and adheres to relevant codes like AASHTO. Most importantly, we possess the specialized expertise required for the critical PTFE bonding process—the single most important factor in preventing catastrophic failure.
Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, partner with a manufacturer who prioritizes structural integrity.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and let us help you translate your specifications into a durable, high-performance bearing solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















