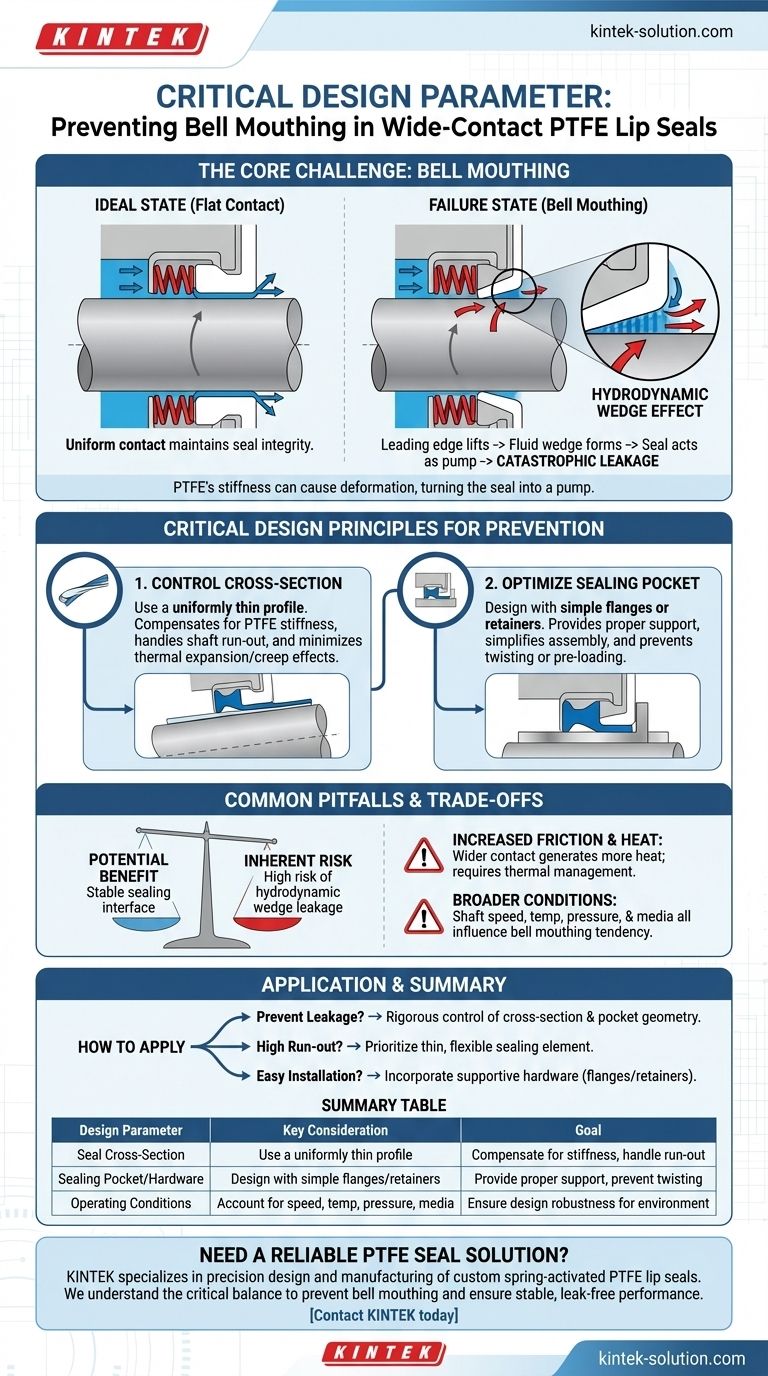
The single most critical design parameter to consider when applying a wide contact pattern to a spring-activated PTFE lip seal is the prevention of bell mouthing. This phenomenon, where the leading edge of the seal lip deforms and lifts away from the shaft, can create a hydrodynamic wedge that actively pumps fluid across the seal, resulting in catastrophic leakage rates.
The core challenge is that PTFE's inherent stiffness, while beneficial for wear resistance, makes it susceptible to deformation under load. A wide contact design must therefore be meticulously engineered to maintain a flat, stable contact pattern, preventing the seal from turning into a pump.

The Primary Risk: Understanding Bell Mouthing
Bell mouthing is the primary failure mode associated with poorly designed wide-contact PTFE seals. It is a subtle geometric change that completely undermines the seal's function.
What is Bell Mouthing?
Bell mouthing describes the condition where the front edge of the wide seal lip pivots slightly away from the shaft surface. Instead of lying flat, the contact pattern becomes angled, resembling the mouth of a bell.
This deformation occurs because the forces on the seal are not perfectly balanced across its width, often exacerbated by the material's high flexural modulus and thermal expansion.
The Hydrodynamic Wedge Effect
When bell mouthing occurs, the rotating shaft drags fluid into the tapered gap created by the lifted seal edge. This action forms a pressurized fluid film, or an oil wedge, under the lip.
Instead of sealing the fluid, the seal begins to function like a miniature hydrodynamic pump, actively transporting media to the low-pressure side and causing significant leakage.
Critical Design Principles for PTFE Seals
Preventing bell mouthing requires a holistic design approach that accounts for the unique properties of PTFE and its interaction with the surrounding hardware.
Controlling the Seal Cross-Section
The geometry of the seal element itself is paramount. Designs often incorporate a uniformly thin cross-section.
This thin profile helps compensate for the high stiffness (flexural modulus) of PTFE, allowing it to remain flexible enough to handle shaft run-out. It also minimizes the effects of thermal expansion and compressive creep, ensuring the contact pattern remains stable and controlled over time.
The Importance of the Sealing Pocket
The hardware, or sealing pocket, that houses the seal is just as critical as the seal itself. Given PTFE's plastic nature, the pocket must provide adequate support without complicating installation.
Designs with simple flanges or retainers are often preferred. They properly support the seal and simplify assembly, reducing the risk of twisting or bending the element, which could pre-load it in a way that encourages bell mouthing.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
While a wide contact pattern can offer benefits like stability, it introduces specific risks that must be carefully managed.
Potential Benefit vs. Inherent Risk
A wide contact surface can theoretically provide a more stable and robust sealing interface. However, this potential benefit is directly offset by the significantly increased risk of creating a leakage path via the hydrodynamic wedge effect.
Increased Friction and Heat
A wider contact area inherently generates more friction and heat than a narrow "knife-edge" contact pattern. This must be factored into the system's thermal management, as elevated temperatures can accelerate seal wear and material degradation.
Overlooking Broader Operating Conditions
The tendency for a seal to bell mouth is influenced by the entire application environment. Shaft speed, operating temperatures, system pressure, and the media being sealed all affect the forces and material response at the sealing interface. The design must be robust enough for the specific demands of its environment.
How to Apply This to Your Design
Your final design choices should be guided by the primary goal of your sealing application.
- If your primary focus is preventing leakage: Your design must rigorously control the seal's cross-section and pocket geometry to ensure the contact pattern on the shaft remains perfectly flat.
- If you are dealing with high shaft run-out: Prioritize a design with a thin, flexible sealing element that can conform to shaft movement without deforming into a bell mouth shape.
- If ease and reliability of installation are critical: Incorporate hardware features like flanges or simple retainers that support the seal and prevent twisting or damage during assembly.
Ultimately, a successful wide-contact PTFE seal design is achieved by managing the material's properties within a complete, well-engineered system.
Summary Table:
| Design Parameter | Key Consideration | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Seal Cross-Section | Use a uniformly thin profile | Compensate for PTFE stiffness, handle run-out |
| Sealing Pocket/Hardware | Design with simple flanges or retainers | Provide proper support, prevent twisting |
| Operating Conditions | Account for speed, temperature, pressure, media | Ensure design robustness for the specific environment |
Need a reliable PTFE seal solution for demanding applications?
KINTEK specializes in the precision design and manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom spring-activated lip seals for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance of material properties and system design to prevent failure modes like bell mouthing. Let our expertise ensure your seals deliver stable, leak-free performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom sealing requirements, from prototype to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















