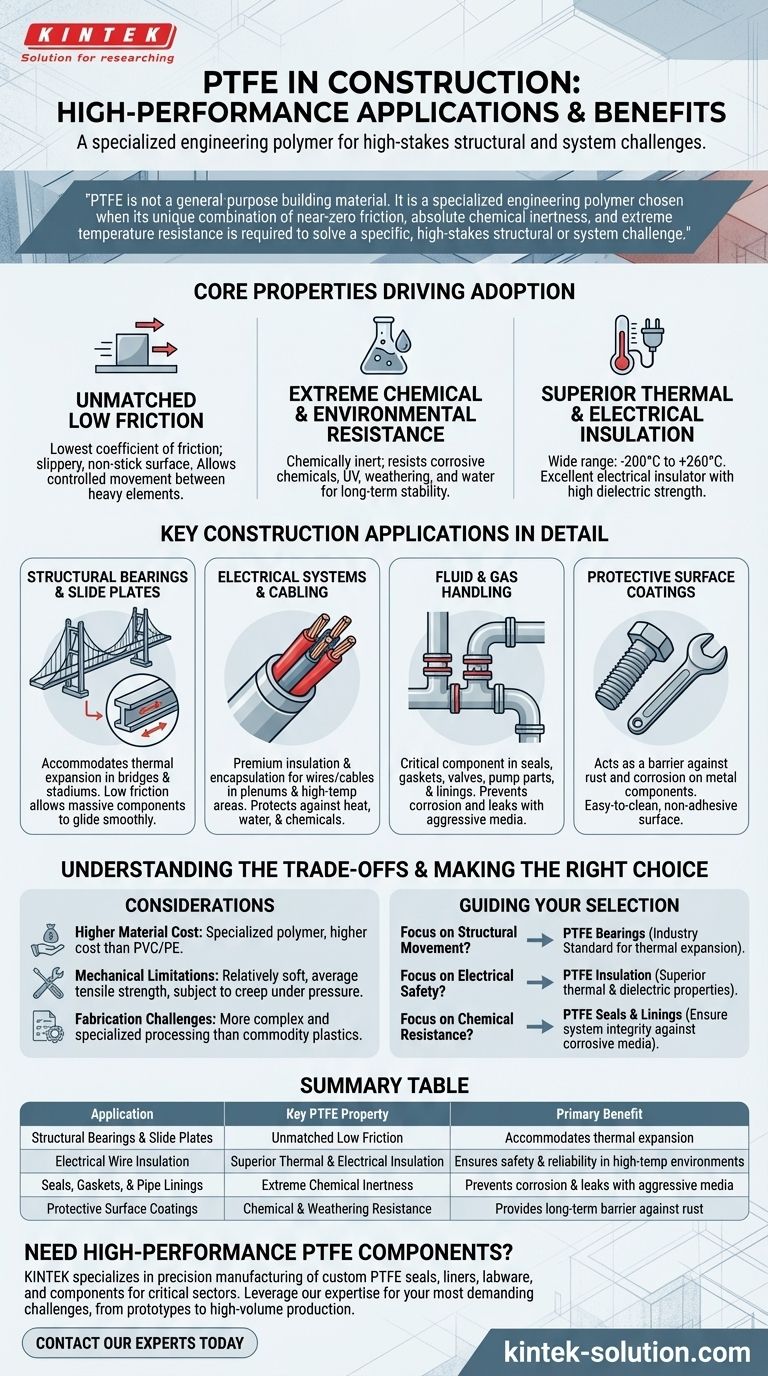
In modern construction, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance problem solver. This fluoropolymer is specified for critical applications where conventional materials would fail, including structural slide bearings for bridges, high-temperature electrical wire insulation, corrosion-proof coatings, and chemically resistant seals, gaskets, and pipes. Its value comes from a unique combination of extreme durability and functional properties.
PTFE is not a general-purpose building material. It is a specialized engineering polymer chosen when its unique combination of near-zero friction, absolute chemical inertness, and extreme temperature resistance is required to solve a specific, high-stakes structural or system challenge.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE Adoption
To understand where PTFE excels, you must first understand its fundamental characteristics. Its use is almost always a direct result of one of three superior properties that common plastics and metals cannot match.
Unmatched Low Friction
PTFE has the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid material. This means it offers an incredibly slippery, non-stick surface.
This property is not just for convenience; it is a critical engineering function. It allows for controlled, predictable movement between heavy structural elements.
Extreme Chemical and Environmental Resistance
PTFE is almost completely chemically inert. It is unaffected by the vast majority of corrosive chemicals, acids, and bases.
This makes it an ideal material for protective coatings, seals, and pipes that handle aggressive media. Furthermore, it exhibits outstanding resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and water, ensuring long-term stability in exposed environments.
Superior Thermal and Electrical Insulation
PTFE maintains its integrity and flexibility across an exceptionally wide temperature range, from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
It is also an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. This combination makes it indispensable for high-performance wiring in demanding conditions where heat and potential chemical exposure are concerns.
Key Construction Applications in Detail
These core properties translate directly into specific, high-value applications across the construction industry.
Structural Bearings and Slide Plates
In large structures like bridges and stadiums, materials expand and contract with temperature changes. PTFE slide plates and bearings are placed between structural elements to accommodate this movement without building up destructive stress.
The material's low friction allows massive concrete and steel components to glide smoothly over one another, ensuring the structural integrity of the entire project.
Electrical Systems and Cabling
Safety and reliability are paramount in electrical systems. PTFE is used as a premium insulation and encapsulation for electrical wires and data cables, especially in plenums or high-temperature environments.
Its resistance to heat, water, and chemicals protects the wiring from degradation, preventing short circuits and ensuring long-term operational safety.
Fluid and Gas Handling
Within a building's mechanical systems, PTFE serves as a critical component in seals, gaskets, valves, and pump parts. It is also used to line hoses and pipes for gas or chemical transport.
Its chemical inertness guarantees that it will not corrode or degrade when in contact with process fluids, preventing leaks and ensuring system purity and longevity.
Protective Surface Coatings
PTFE can be applied as a coating on metal components or even construction tools. This layer acts as a barrier, providing excellent protection against rust and corrosion.
Its non-adhesive, easy-to-clean surface also adds functional value in certain architectural and industrial applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its performance is exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its limitations.
Higher Material Cost
PTFE is a specialty polymer, and its cost is significantly higher than that of common construction plastics like PVC or polyethylene. Its use must be justified by a clear performance requirement that other materials cannot meet.
Mechanical Limitations
While durable, PTFE is a relatively soft material with average tensile strength compared to engineering metals. It is not used as a primary load-bearing structural element itself. It can also be subject to "creep"—a slow deformation under sustained pressure—which is useful for seals but must be accounted for in bearing design.
Fabrication Challenges
Processing PTFE into finished components is more complex and specialized than for many commodity plastics. This can impact the cost and availability of custom parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting PTFE is about matching its specific strengths to the most critical demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is structural movement: PTFE bearings and slide plates are the industry standard for managing thermal expansion in bridges and large buildings.
- If your primary focus is electrical safety in harsh conditions: Its superior thermal and dielectric properties make PTFE insulation a critical choice for high-performance cabling.
- If your primary focus is long-term chemical resistance: Use PTFE for seals, gaskets, and pipe linings to ensure system integrity against corrosive media.
Ultimately, PTFE is specified not as a general-purpose plastic, but as a specialized engineering solution where performance, safety, and long-term reliability are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key PTFE Property Utilized | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Bearings & Slide Plates | Unmatched Low Friction | Accommodates thermal expansion in bridges & large buildings |
| Electrical Wire Insulation | Superior Thermal & Electrical Insulation | Ensures safety & reliability in high-temperature environments |
| Seals, Gaskets, & Pipe Linings | Extreme Chemical Inertness | Prevents corrosion & leaks with aggressive media |
| Protective Surface Coatings | Chemical & Weathering Resistance | Provides long-term barrier against rust and degradation |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical construction project?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, and other components. Our expertise is crucial for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors where material performance is non-negotiable. We can help you leverage PTFE's unique properties to solve your most demanding engineering challenges, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure the integrity of your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















