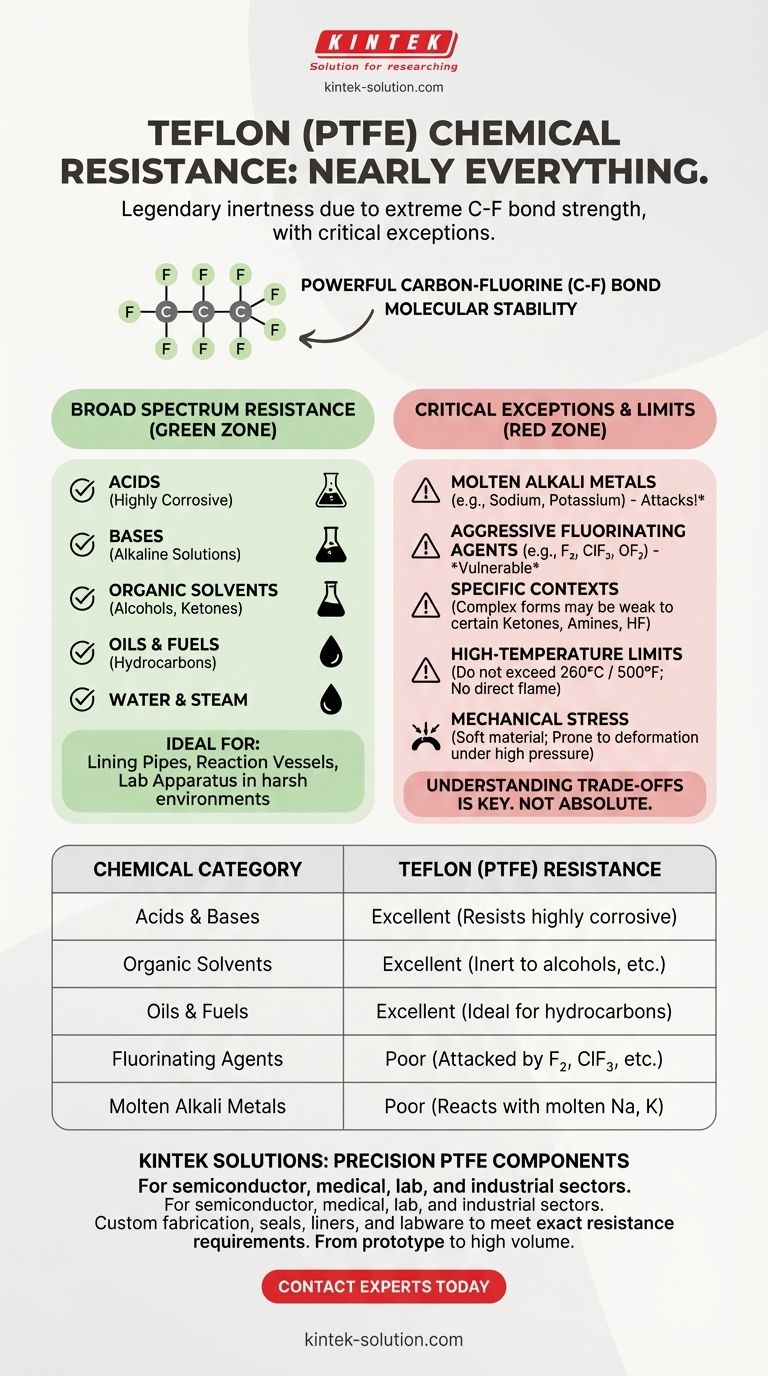
In short, Teflon is resistant to nearly everything. Its chemical inertness is legendary, making it non-reactive to a vast range of substances, including most acids, bases, alcohols, solvents, hydrocarbons, and fuels. This is why it has become a default material for use in harsh chemical environments.
The core reason for Teflon's resistance is the extreme strength of the carbon-fluorine bonds in its molecular structure. This makes it a highly reliable choice for most applications, but you must be aware of a few critical exceptions that can lead to material failure.

Why Teflon Sets the Standard for Chemical Resistance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), the chemical compound known as Teflon, is a fluoropolymer. Its unique properties are a direct result of its molecular architecture.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms, each completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry.
This powerful bond makes the molecule incredibly stable and non-reactive. It effectively creates an armor-like shell that prevents other chemicals from breaking it down.
Broad Spectrum Inertness
Because of this molecular stability, Teflon remains unaffected by the vast majority of common and aggressive chemicals.
This includes near-total resistance to:
- Acids, including highly corrosive ones.
- Bases and alkaline solutions.
- Organic solvents, alcohols, and ketones.
- Oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons.
- Water and steam.
This makes it an ideal material for lining pipes, reaction vessels, and critical laboratory apparatus in chemical processing and manufacturing.
Critical Exceptions: When Teflon Fails
No material is universally perfect. While Teflon's resistance is broad, it is not absolute. Exposure to a few specific substances, particularly under certain conditions, can cause it to degrade rapidly.
Molten Alkali Metals
Teflon will react with and be attacked by molten alkali metals, such as sodium and potassium. This is a well-documented and critical incompatibility.
Aggressive Fluorinating Agents
Teflon is vulnerable to extremely strong fluorinating agents. This is a very specific category of chemicals that includes gaseous fluorine (F₂), chlorine trifluoride (ClF₃), and oxygen difluoride (OF₂), especially at elevated temperatures and pressures.
Other Specific Contexts
In certain product forms, like encapsulated O-rings, additional weaknesses can be introduced. While pure PTFE is highly resistant, these complex products may be vulnerable to specific ketones, amines, or hydrofluoric acid (HF).
Understanding the Trade-offs Beyond Chemicals
A material's suitability also depends on its physical limitations. Simply resisting a chemical is not enough if the operating environment is too demanding.
High-Temperature Limits
While Teflon has a good service temperature range, it is not immune to heat. Most grades of Teflon should not be used above 260°C (500°F). It should never be exposed to a direct flame, which can cause it to decompose.
Mechanical Stress
Teflon is a relatively soft material. In applications involving high pressure or significant mechanical stress, it can be prone to deformation or failure. The material's physical properties must match the demands of the system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding both the strengths and the precise limitations of Teflon is key to its successful implementation.
- If your primary focus is general industrial or lab use: Teflon is an excellent and reliable default choice for handling nearly all common acids, bases, and solvents.
- If you are working with reactive metals: Immediately disqualify Teflon for any application involving molten alkali metals like sodium or potassium.
- If you operate in the specialty chemical industry: Always verify material compatibility charts when dealing with powerful fluorinating agents or other highly reactive, uncommon compounds.
Ultimately, leveraging Teflon's remarkable chemical resistance requires acknowledging the specific agents and conditions it cannot handle.
Summary Table:
| Chemical Category | Teflon (PTFE) Resistance | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Acids & Bases | Excellent | Resists highly corrosive acids and alkaline solutions. |
| Organic Solvents | Excellent | Inert to alcohols, ketones, and most solvents. |
| Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Ideal for hydrocarbon and fuel applications. |
| Fluorinating Agents | Poor | Attacked by fluorine, chlorine trifluoride, etc. |
| Molten Alkali Metals | Poor | Reacts with molten sodium, potassium. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get parts that meet your exact chemical resistance and performance requirements, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how our PTFE solutions can enhance your operational safety and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















