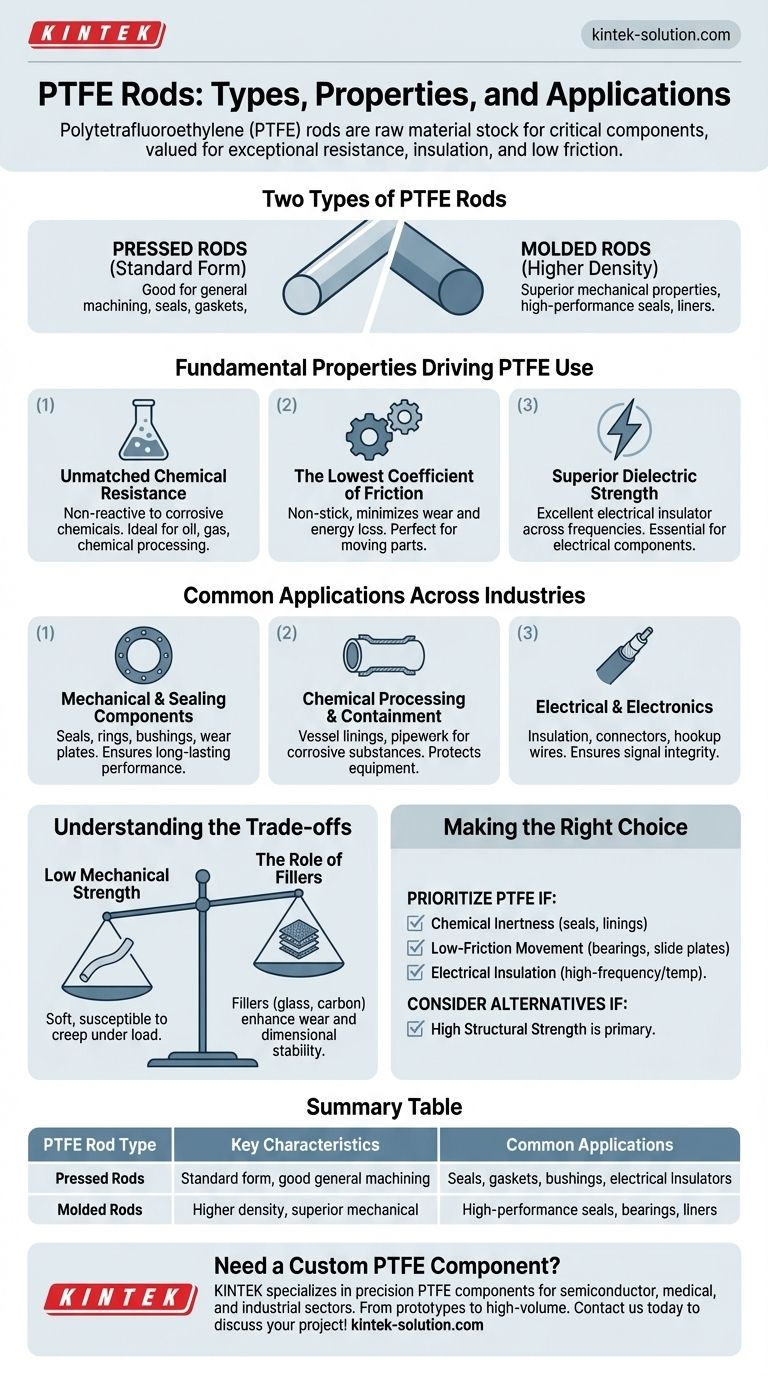
The two primary types of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) rods are pressed rods and molded rods. These forms serve as the raw material stock for manufacturing a wide range of non-standard mechanical parts and long products, particularly where exceptional chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and low friction are critical performance requirements.
At its core, the choice to use a PTFE rod is driven by the need for a component that can withstand harsh chemical environments, provide superior electrical insulation, or offer an extremely low-friction surface where conventional materials would fail.
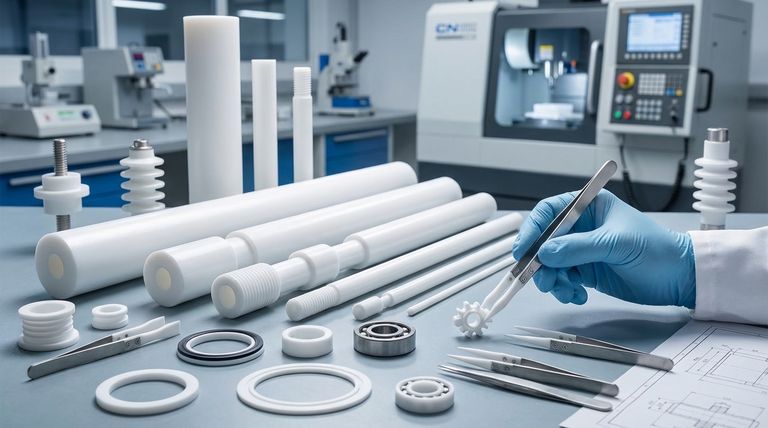

The Fundamental Properties Driving PTFE Use
To understand the applications of PTFE rods, one must first understand the material's three defining characteristics. These properties make it a go-to choice for demanding engineering challenges.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is famously non-reactive. It can handle continuous exposure to a vast range of corrosive and reactive chemicals without degrading.
This makes it an essential material for components used in the oil and gas, petrochemical, and chemical processing industries.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any known solid material, giving it its well-known "non-stick" quality.
This property is crucial for applications involving moving parts, such as bearings, gears, slide plates, and dynamic seals, as it minimizes wear and energy loss.
Superior Dielectric Strength
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. It maintains its insulating properties across a wide range of frequencies and temperatures.
This makes it invaluable for manufacturing insulating parts in electrical components, from simple seat electricity components to high-frequency coaxial cables.
Common Applications Across Industries
PTFE rods are machined into finished parts that serve critical functions in numerous sectors. The specific application determines the final component's design, but the underlying material benefits remain the same.
Mechanical and Sealing Components
This is the most common use for machined PTFE rods. The material is ideal for creating seals, gaskets, rings, and bushings.
Its ability to resist chemicals and provide a low-friction surface ensures a long-lasting, effective seal in pumps, valves, and other equipment. Wear-resistant plates and bearings are also common.
Chemical Processing and Containment
Due to its chemical inertness, PTFE is used to create linings for vessels and pipework that handle highly corrosive substances.
This protects the structural material of the equipment (typically steel) from chemical attack, extending the life and safety of the installation.
Electrical and Electronics
The dielectric properties of PTFE make it a first-choice material for electrical insulation.
It's used in computer hookup wires, complex connectors, and other components where signal integrity and insulation are paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Low Mechanical Strength
Standard, unfilled PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to creep and deformation under sustained load.
For this reason, it is generally not used for high-load structural components unless its other properties are absolutely necessary.
The Role of Fillers
To counteract its mechanical weaknesses, PTFE is often blended with other materials, creating "Filled PTFE."
Additives like glass, carbon, or bronze can significantly enhance its wear resistance, reduce creep, and improve dimensional stability, making it suitable for more demanding mechanical roles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE means you are prioritizing a specific set of performance characteristics. Use these guidelines to determine if it fits your project.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness: PTFE is the industry standard for seals, gaskets, and linings in aggressive chemical environments.
- If your primary focus is low-friction movement: It is an excellent choice for bearings, slide plates, and non-stick surfaces where minimal resistance is required.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: PTFE provides exceptional dielectric performance, especially for high-frequency or high-temperature applications.
- If your primary focus is high structural strength: Standard PTFE is likely unsuitable; investigate a filled grade or a different engineering polymer entirely.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE means prioritizing its unique combination of chemical, frictional, and electrical properties for challenges that other materials cannot solve.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Rod Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pressed Rods | Standard form, good for general machining | Seals, gaskets, bushings, electrical insulators |
| Molded Rods | Higher density, superior mechanical properties | High-performance seals, bearings, liners for demanding environments |
Need a Custom PTFE Component?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your parts meet exact specifications for chemical resistance, low friction, and electrical insulation.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















