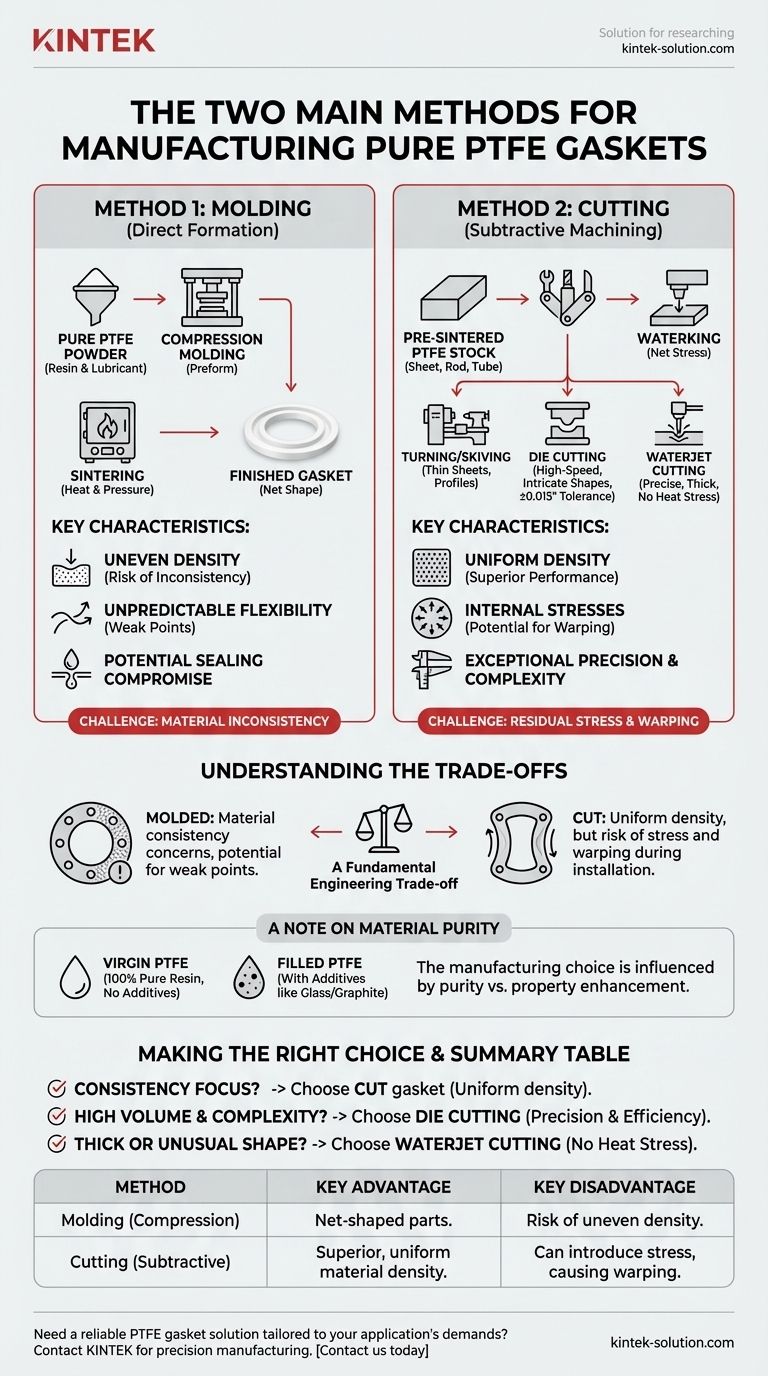
The two primary methods for manufacturing pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets are direct molding and subtractive cutting. Molding involves forming the gasket directly from raw PTFE resin powder, while cutting involves machining the gasket from a pre-made stock shape, such as a sheet or rod. Each method carries distinct implications for the final product's density, flexibility, and dimensional accuracy.
The choice between a molded and a cut PTFE gasket is a critical engineering decision. It represents a fundamental trade-off between the potential for inconsistent material density in molded parts and the risk of residual stress and warping in parts cut from stock material.

The Two Core Manufacturing Philosophies
Understanding how pure PTFE gaskets are made begins with recognizing two distinct approaches: starting with raw powder versus starting with a solid block of material.
Method 1: Molding (Direct Formation)
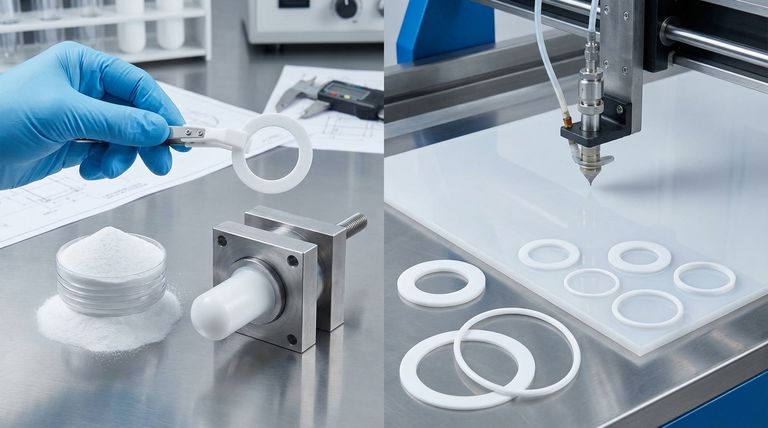
Molding, specifically compression molding, builds the gasket from the ground up. The process involves taking pure PTFE powder (sometimes referred to as suspended material), often mixed with a lubricant, and pressing it into a mold or "preform."
This preformed shape is then heated under pressure in a process called sintering. This fuses the PTFE particles into a solid, finished gasket, creating the final part in its net shape.
Method 2: Cutting (Subtractive Machining)
The second approach is to cut or machine gaskets from a large, pre-sintered piece of PTFE stock, like a sheet, rod, or tube. This is a subtractive process where material is removed to achieve the final shape.
Several cutting techniques are used, each suited for different requirements:
- Turning/Skiving: A process where a thin layer of material is "shaved" or cut from a rotating PTFE rod or cylinder to create thin sheets or specific circular gasket profiles.
- Die Cutting: A high-speed method where a sharp, custom-shaped die is used to punch gaskets from a PTFE sheet. It is highly efficient for producing exact, complex shapes in high volumes.
- Waterjet Cutting: This technique uses a high-pressure stream of water to cut through the PTFE material. It is exceptionally precise and ideal for cutting very thick gaskets (up to 6 inches) without introducing heat stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither manufacturing method is perfect; each has inherent advantages and disadvantages that affect the final gasket's performance in an application.
The Challenge with Molded Gaskets
The primary concern with molded gaskets is material consistency. The molding process can result in uneven density throughout the part.
This inconsistency can lead to poor or unpredictable flexibility and create weak points, potentially compromising the gasket's sealing capability under pressure.
The Challenge with Cut Gaskets
Gaskets cut from stock material, especially via turning or skiving, generally have a more uniform density, which is a significant performance advantage.
However, the machining process can introduce internal stresses into the material. This can cause the finished gasket to warp or curve, which may complicate installation and prevent a proper, even seal on the flange surface.
Precision and Complexity
Modern cutting methods offer exceptional precision. Die cutting can achieve tight tolerances of ±0.015 inches and is excellent for intricate designs.
Waterjet cutting provides similar precision and repeatability, with the added benefit of handling very thick materials without heat distortion, which is a common issue with other cutting methods.
A Note on Material Purity
The user's question specifies "pure" PTFE gaskets, which corresponds to what is known as Virgin PTFE. This grade is made from 100% pure PTFE resin with no additives.
It's important to distinguish this from Filled PTFE, which includes additives like glass or graphite to enhance properties like wear resistance or reduce deformation under load. The manufacturing choice can sometimes be influenced by whether the material is virgin or filled.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the manufacturing method's strengths to your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is material consistency and predictable sealing: Choose a gasket that has been cut from a high-quality, stress-relieved sheet or rod to ensure uniform density.
- If your primary focus is a high volume of complex, identical parts: Die cutting offers an excellent balance of precision and cost-efficiency at scale.
- If your primary focus is a very thick gasket or an unusual shape: Waterjet cutting provides the most reliable precision and avoids introducing heat-related stress into the material.
Ultimately, understanding the origin of your gasket is key to ensuring its reliability in your system.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process Description | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molding (Compression) | Forms gasket directly from PTFE powder via sintering. | Creates net-shaped parts. | Risk of uneven density and weak points. |
| Cutting (Subtractive) | Machines gasket from pre-made PTFE sheet/rod. | Superior, uniform material density. | Can introduce stress, causing warping. |
Need a reliable PTFE gasket solution tailored to your application's demands?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom gaskets for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether your priority is the material consistency of a cut gasket or the design flexibility of a molded part, our experts will guide you to the optimal solution. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring performance and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your project and receive a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















