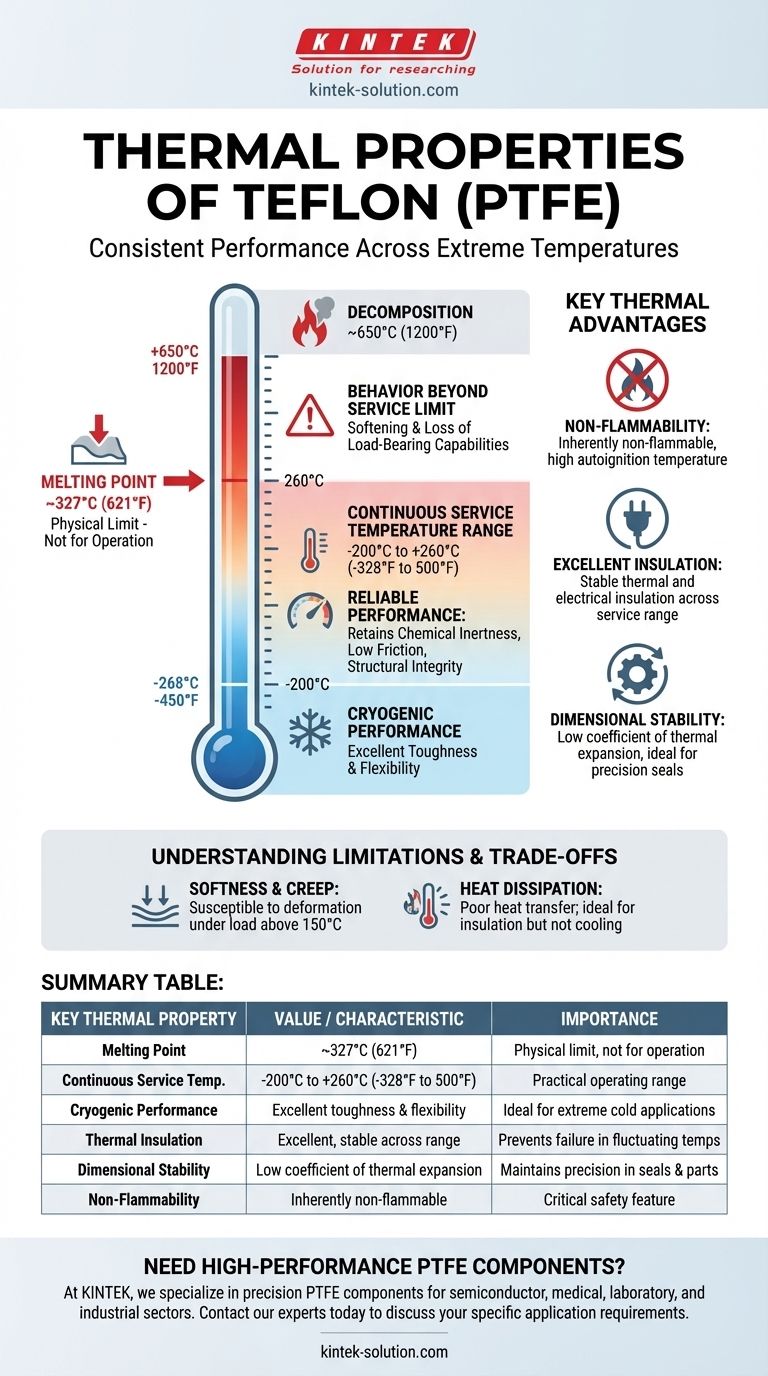
The primary thermal properties of Teflon (PTFE) are its high melting point of approximately 327°C (621°F) and its exceptionally wide continuous service temperature range, from as low as -200°C (-328°F) up to +260°C (500°F). Within this range, it maintains its other signature properties, such as chemical inertness and a very low coefficient of friction.
The true value of PTFE isn't just its high melting point, but its remarkable ability to retain its unique combination of non-stick, low-friction, and chemically inert characteristics across an enormous spectrum of temperatures, from cryogenic lows to significant heat.

Deconstructing PTFE's Thermal Performance
Understanding PTFE requires looking beyond a single melting point. Its performance is defined by its behavior across a wide temperature range, making it suitable for some of the most demanding environments.
The Melting Point: A Physical Limit
PTFE's crystalline melting point is consistently measured at ~327°C (621°F). This is the physical temperature at which the material transitions from a solid to a viscous gel.
It is critical to note that this is not a practical operating temperature. Well before it reaches this point, its mechanical properties will have degraded significantly.
The Continuous Service Temperature: The Practical Range
The most important metric for any real-world application is the continuous service temperature, which is -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
Within this vast range, PTFE reliably maintains its structural integrity and its other valuable properties, including exceptional chemical resistance and lubricity.
Performance at Cryogenic Temperatures
PTFE is a standout performer in extreme cold. Unlike many polymers that become brittle, it retains a high degree of toughness and flexibility even at temperatures approaching absolute zero (-268°C or -450°F).
This makes it an ideal material for seals, gaskets, and components used in cryogenics and aerospace applications.
Behavior Beyond the Service Limit
Pushing PTFE above its 260°C service limit introduces risk. As it approaches its melting point, it softens considerably and loses its load-bearing capabilities.
At much higher temperatures, around 650°C (1200°F), it undergoes depolymerization, breaking down its fundamental structure.
Key Properties Influenced by Temperature
PTFE's thermal stability ensures its other defining characteristics remain consistent, making it a highly reliable material.
Non-Flammability
PTFE is inherently non-flammable. It has a high autoignition temperature and does not support combustion, which is a critical safety feature in electrical, automotive, and industrial applications.
Thermal and Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent thermal and electrical insulator. Crucially, these insulating properties are maintained consistently across its entire service temperature range, preventing failure in electronics or components exposed to fluctuating temperatures.
Dimensional Stability
PTFE has a low coefficient of thermal expansion compared to many other polymers. This means it expands and contracts less when subjected to temperature changes, making it ideal for precision seals, gaskets, and components where tight tolerances are essential.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging PTFE's limitations is key to using it effectively and safely.
Service Temperature vs. Melting Point
The most common point of confusion is mistaking the melting point for the usable temperature limit. For any application involving mechanical stress or load, you must design for the 260°C (500°F) maximum service temperature, not the 327°C melting point.
Softness and Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft material. At the upper end of its temperature range (above 150°C), it becomes more susceptible to "creep," a slow deformation that occurs when under a constant load. This must be factored into the design of load-bearing parts.
Heat Dissipation
As a thermal insulator, PTFE does not transfer or dissipate heat well. In applications where heat removal is necessary, this can be a significant drawback. Conversely, this same property makes it ideal for insulating components from a heat source.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision depends entirely on the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature mechanical parts: Use 260°C (500°F) as your absolute limit and account for increased material softness and potential creep under load.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic or extreme cold environments: PTFE is an excellent choice, as it retains its toughness and flexibility where other materials fail.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation across a wide temperature range: PTFE offers highly stable and reliable performance.
- If your primary focus is non-stick coatings (e.g., cookware): The 260°C (500°F) limit explains why very high searing heat can damage the coating, even though the pan itself is unharmed.
PTFE is defined by its consistent performance in environments where other materials would fail.
Summary Table:
| Key Thermal Property | Value / Characteristic | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | ~327°C (621°F) | Physical limit, not for operation |
| Continuous Service Temp. | -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Practical operating range |
| Cryogenic Performance | Excellent toughness & flexibility | Ideal for extreme cold applications |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, stable across range | Prevents failure in fluctuating temps |
| Dimensional Stability | Low coefficient of thermal expansion | Maintains precision in seals & parts |
| Non-Flammability | Inherently non-flammable | Critical safety feature |
Need high-performance PTFE components that can handle extreme temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your parts deliver reliable performance, whether in cryogenic conditions or high-temperature environments.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing the material properties you depend on.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















