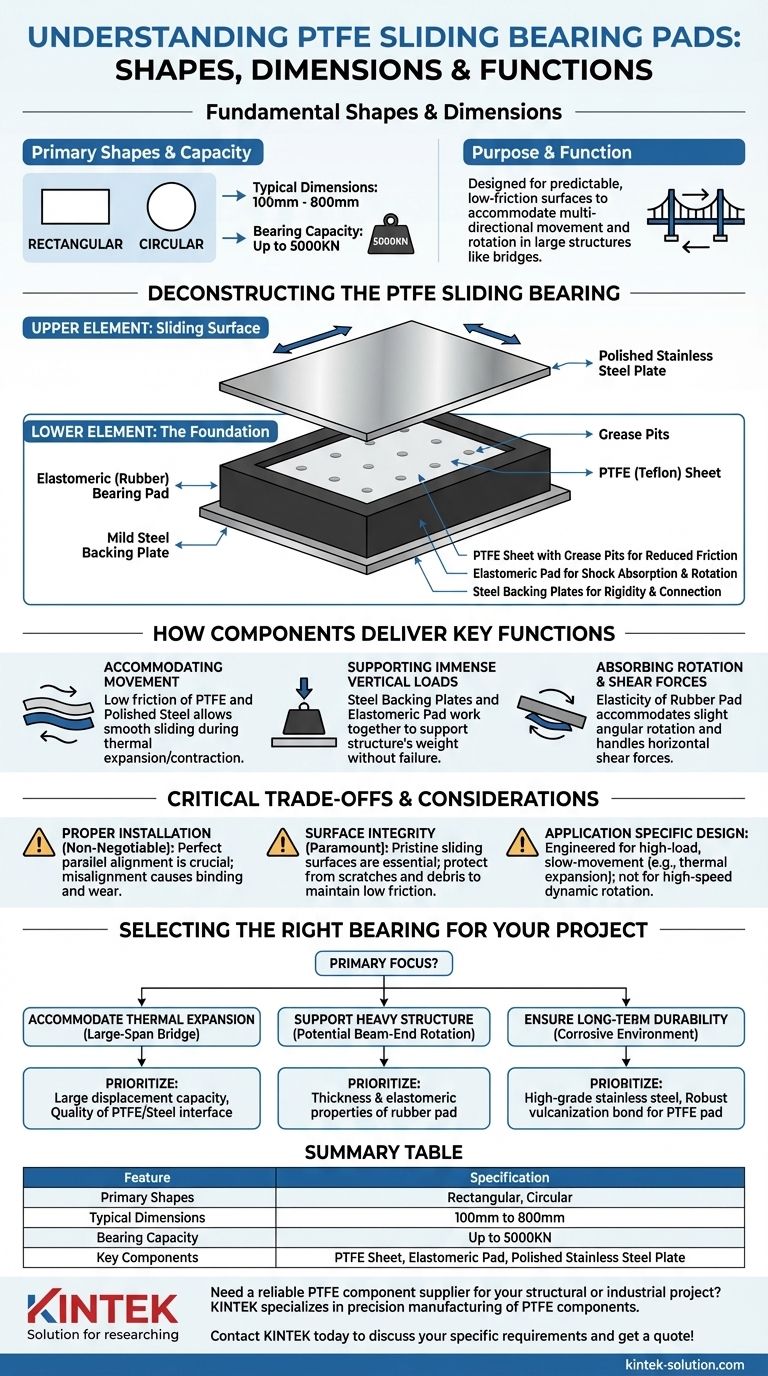
At their most fundamental level, PTFE sliding bearing pads are produced in two primary shapes: rectangular and circular. Their dimensions typically range from 100mm to 800mm, designed to handle immense structural loads with a bearing capacity that can reach up to 5000KN.
The simplicity of these shapes—rectangles and circles—belies a sophisticated function. They are designed not for aesthetic reasons, but to provide a predictable, low-friction surface that accommodates the multi-directional movement and rotation inherent in large structures like bridges.
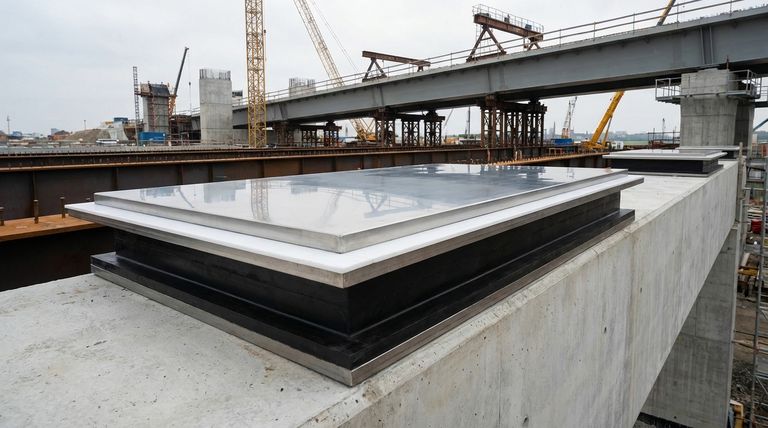

Deconstructing the PTFE Sliding Bearing
To understand why these simple shapes are so effective, you must first understand the components. A typical PTFE sliding bearing is not a single piece of material but a precisely engineered assembly.
The Lower Element: The Foundation
The base of the bearing consists of a thick elastomeric (rubber) bearing pad. This component is crucial for absorbing shock and allowing for slight rotational movements at the connection point.
A sheet of PTFE (Teflon) is bonded into a recess on top of this rubber pad. This recess prevents the PTFE from spreading under extreme pressure. The surface of the PTFE often includes "grease pits" or dimples to retain lubricant, further reducing friction.
The Upper Element: The Sliding Surface
The upper element features a highly polished stainless steel plate. This plate is designed to slide effortlessly across the PTFE surface of the lower element.
Both the rubber pad and the stainless steel plate are typically bonded to mild steel backing plates. These backing plates provide overall rigidity and serve as the connection points for welding the bearing to the larger structure.
How These Components Deliver Key Functions
The effectiveness of a PTFE bearing comes from how these distinct materials work together to solve specific engineering challenges.
Accommodating Movement (The Core Purpose)
The primary function is to create a sliding plane. As a structure like a bridge expands and contracts due to temperature changes, the polished stainless steel plate slides smoothly across the PTFE surface.
This is possible because the combination of PTFE and polished steel has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any two solid materials, allowing movement under immense pressure.
Supporting Immense Vertical Loads
While the PTFE provides the sliding surface, the vertical load is transferred through the entire assembly. The robust steel backing plates and the high-strength elastomeric pad work in concert to support the structure's weight without failing.
Absorbing Rotation and Shear Forces
The elasticity of the rubber pad is critical. It allows the bearing to accommodate slight angular rotation from the beam or girder it supports. It also deforms to handle horizontal shear forces, providing flexibility to the structural connection.
Critical Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly effective, the performance of PTFE bearings is contingent on several critical factors that can be points of failure if overlooked.
Proper Installation is Non-Negotiable
The upper and lower elements must be perfectly parallel and aligned. Any misalignment can cause binding, uneven pressure, and premature wear, compromising the bearing's function.
Surface Integrity is Paramount
The low-friction properties depend entirely on the pristine condition of the two sliding surfaces. During transport and installation, the PTFE and polished steel must be protected from scratches, dirt, and construction debris, which can dramatically increase friction.
Design is Specific to Application
These bearings are engineered for high-load, slow-movement applications like thermal expansion. They are not suitable for high-speed or continuously dynamic rotational applications where other types of mechanical bearings would be required.
Selecting the Right Bearing for Your Project
The shape and dimensions you choose are directly tied to the specific forces and movements your structure must handle.
- If your primary focus is accommodating thermal expansion in a large-span bridge: You require a bearing with a large displacement capacity, making the overall dimension and the quality of the PTFE/steel interface critical.
- If your primary focus is supporting a heavy structure with potential for beam-end rotation: The thickness and elastomeric properties of the underlying rubber pad are as important as the PTFE sliding surface itself.
- If your primary focus is ensuring long-term durability in a corrosive environment: Prioritize bearings that use high-grade stainless steel plates and a robust vulcanization bond for the PTFE pad.
Understanding that a PTFE bearing is an assembly of specialized components is the key to specifying the correct solution for your project's unique demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Primary Shapes | Rectangular, Circular |
| Typical Dimensions | 100mm to 800mm |
| Bearing Capacity | Up to 5000KN |
| Key Components | PTFE Sheet, Elastomeric Pad, Polished Stainless Steel Plate |
Need a reliable PTFE component supplier for your structural or industrial project?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom parts for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures the quality and performance your critical applications demand.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















