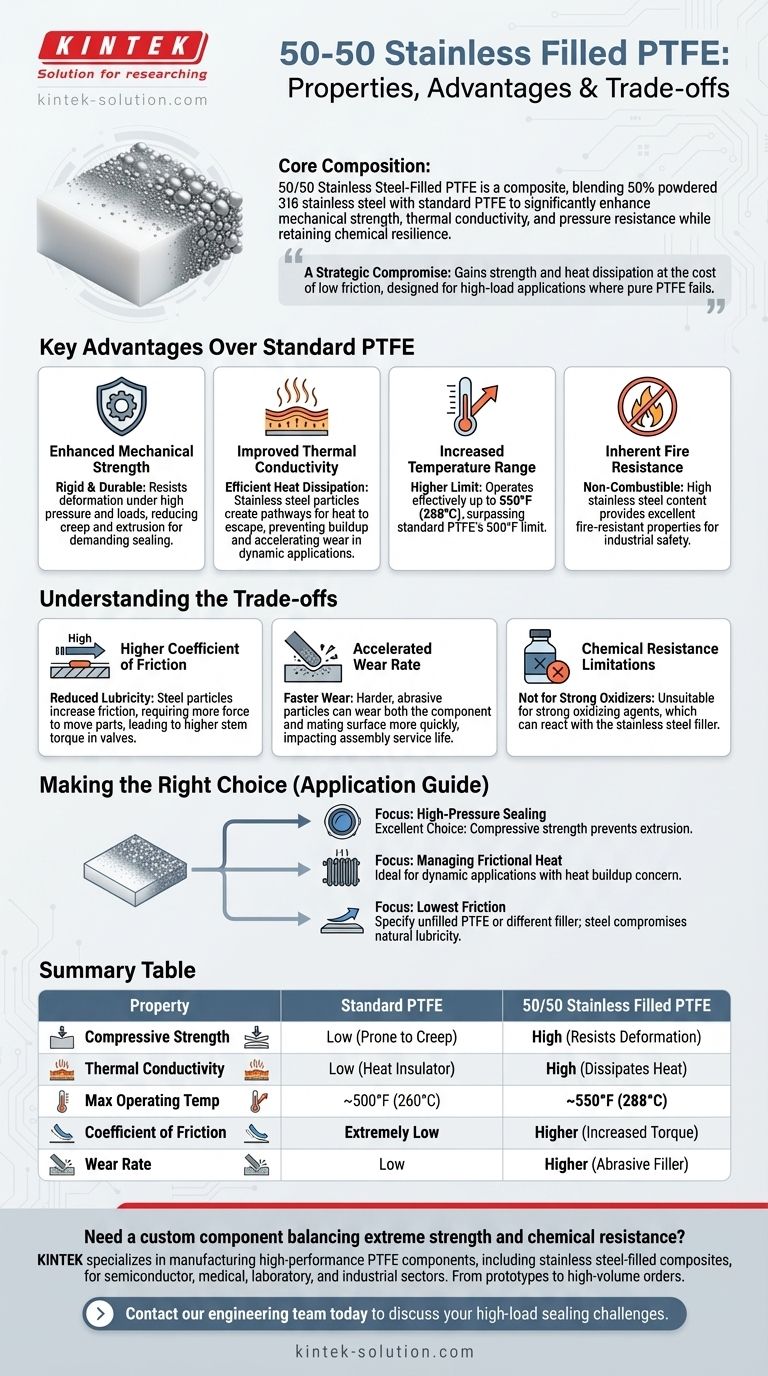
At its core, 50/50 stainless steel-filled PTFE is a composite material engineered to enhance the properties of standard Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). By blending PTFE with 50% powdered 316 stainless steel, it gains significantly improved mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and pressure resistance while retaining PTFE's excellent chemical resilience.
This material is not simply a stronger version of PTFE; it's a strategic compromise. You gain strength and heat dissipation at the cost of PTFE's famously low friction, resulting in a material designed for high-load applications where pure PTFE would fail.

Key Advantages Over Standard PTFE
The addition of stainless steel particles is a deliberate engineering choice designed to overcome the inherent limitations of unfilled PTFE, such as its tendency to deform under load (creep).
Enhanced Mechanical Strength
Unfilled PTFE is soft and can deform under pressure. The inclusion of stainless steel powder creates a much more rigid and durable composite.
This reinforcement allows the material to handle significantly higher pressures and loads without creep or extrusion, making it suitable for demanding sealing applications.
Improved Thermal Conductivity
PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator, which can be a drawback when friction generates heat. Trapped heat can accelerate wear and cause material failure.
The stainless steel particles create a pathway for heat to dissipate away from the contact surface, improving the material's stability and lifespan in dynamic applications.
Increased Temperature Range
While not a high-temperature material in the context of metals, this composite offers a notable improvement over standard PTFE.
It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 550°F (288°C), slightly higher than the typical 500°F (260°C) limit of pure PTFE.
Inherent Fire Resistance
The high concentration of non-combustible stainless steel gives the material excellent fire-resistant properties, a critical factor in certain industrial and safety applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is without its compromises. The very properties that make stainless steel-filled PTFE strong also introduce specific limitations you must consider.
Higher Coefficient of Friction
The primary trade-off is a loss of lubricity. Pure PTFE is one of the slickest materials known, but adding abrasive steel particles increases the coefficient of friction.
This means more force is required to move parts against it. In applications like valve seats, this translates directly to higher stem torque needed for operation.
Accelerated Wear Rate
Higher friction directly leads to a faster wear rate. The harder steel particles can be more abrasive to both the filled-PTFE component and the mating surface it slides against.
This is a critical design consideration, as it can impact the service life of the entire assembly, not just the seal or bearing itself.
Chemical Resistance Limitations
While overall chemical resistance remains excellent, it is not absolute. The material is specifically unsuitable for use with strong oxidizing agents, which can react with the stainless steel filler.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational demand.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure sealing: This material is an excellent choice, as its compressive strength prevents extrusion where pure PTFE would fail.
- If your primary focus is managing frictional heat: The enhanced thermal conductivity makes it ideal for dynamic applications where heat buildup is a concern.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction: You should specify unfilled PTFE or a compound with a different filler, as the steel content compromises its natural lubricity.
Ultimately, 50/50 stainless steel-filled PTFE is a specialized problem-solver for when the strength of steel and the resilience of PTFE are needed in a single component.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard PTFE | 50/50 Stainless Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | Low (Prone to Creep) | High (Resists Deformation) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (Heat Insulator) | High (Dissipates Heat) |
| Max Operating Temp | ~500°F (260°C) | ~550°F (288°C) |
| Coefficient of Friction | Extremely Low | Higher (Increased Torque) |
| Wear Rate | Low | Higher (Abrasive Filler) |
Need a custom component that balances extreme strength with chemical resistance?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including stainless steel-filled composites, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get the exact part your application demands.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss how our materials expertise can solve your high-load sealing challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















