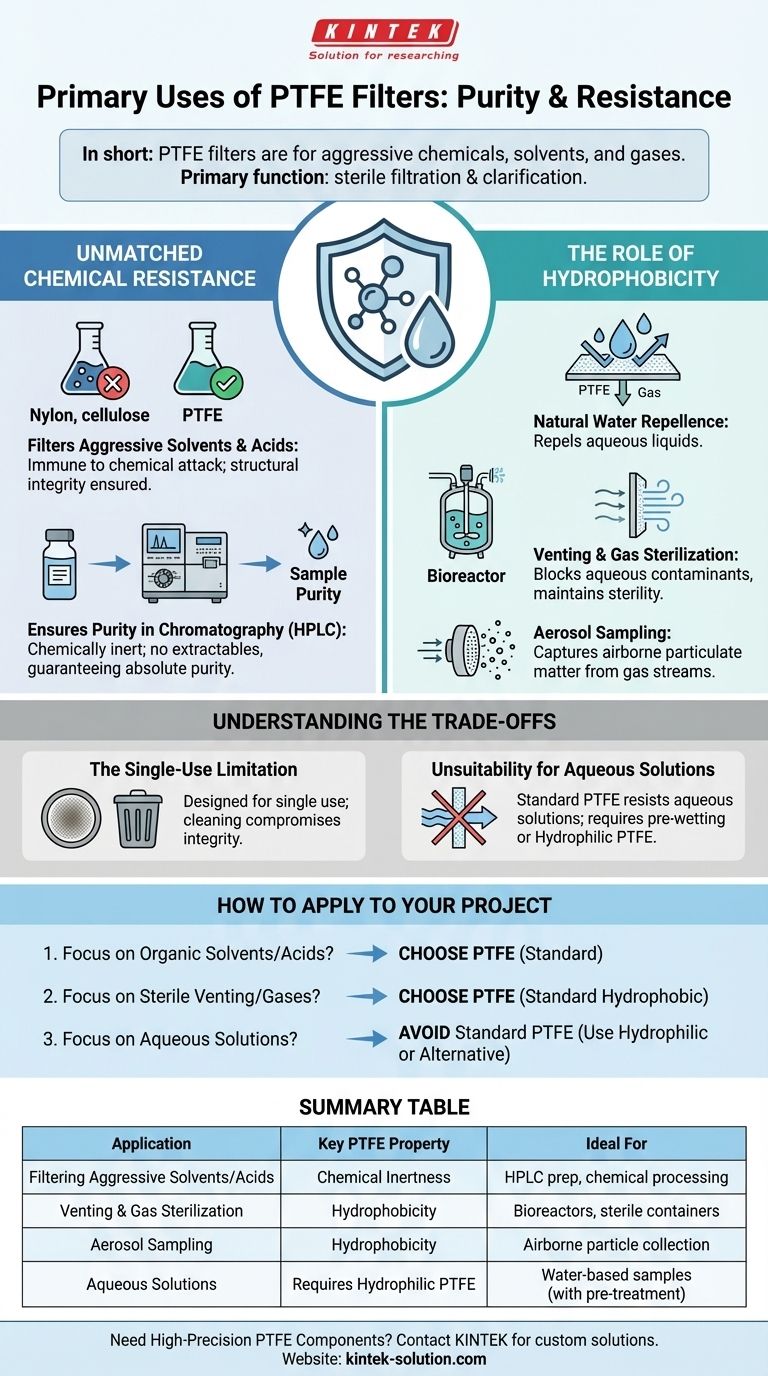
In short, PTFE filters are used for applications involving aggressive chemicals, solvents, and gases. Their primary function is to provide sterile filtration and clarification for substances that would degrade or corrode other filter materials, such as in HPLC sample preparation, venting, and aerosol sampling.
The defining characteristic of a PTFE filter is its extreme chemical inertness. This allows it to handle the most corrosive acids and aggressive solvents without breaking down or contaminating the sample, ensuring absolute purity in critical laboratory and industrial processes.

The Core Principle: Unmatched Chemical Resistance
The fundamental reason PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is chosen for specific filtration tasks is its non-reactive nature. It can withstand a wider range of chemicals than almost any other filter membrane.
Filtering Aggressive Solvents and Acids
PTFE is virtually immune to chemical attack. This makes it the default choice for filtering samples containing strong acids, bases, or aggressive organic solvents that would dissolve materials like nylon or cellulose.
This property ensures the structural integrity of the filter itself, preventing filter failure and sample loss during the process.
Ensuring Purity in Chromatography (HPLC)
In sensitive analytical techniques like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), sample purity is paramount. Even trace amounts of contaminants can compromise results.
Because PTFE filters are chemically inert, they do not leach extractables into the solvent or sample. This guarantees that the only substances being analyzed are from the original sample, not the filter itself.
The Role of Hydrophobicity
PTFE is naturally hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. This property is not a bug; it's a feature that makes it exceptionally useful for gas and air filtration applications.
Venting and Gas Sterilization
Hydrophobic PTFE membranes allow gases to pass through freely while effectively blocking aqueous liquids and aerosols.
This is ideal for sterile venting of containers or bioreactors. Air can move in and out, but airborne bacteria or water-based contaminants are prevented from entering, maintaining the sterility of the contents.
Aerosol Sampling
The same hydrophobic property allows PTFE filters to be used for collecting airborne particles. A gas stream is pulled through the filter, which captures the particulate matter for later analysis while allowing the air to pass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PTFE filters are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them correctly.
The Single-Use Limitation
PTFE filters are typically designed for single use. Their structure can trap particulates permanently, and attempting to clean them with harsh methods can compromise the membrane's integrity, making reuse unreliable.
Unsuitability for Aqueous Solutions
Because standard PTFE is hydrophobic, it will resist the flow of water-based (aqueous) solutions. Attempting to filter pure water or dilute aqueous samples will result in very slow flow rates or complete blockage.
For these applications, you must either pre-wet the filter with an alcohol (like methanol or isopropanol) or use a specially treated hydrophilic PTFE filter designed specifically for water-based samples.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of filter membrane must align directly with the chemical nature of your sample.
- If your primary focus is filtering organic solvents, strong acids, or aggressive chemical mixtures: PTFE is the safest and most reliable choice to ensure both filter integrity and sample purity.
- If your primary focus is sterile venting or filtering gases: The natural hydrophobicity of a standard PTFE filter makes it the ideal material for blocking moisture and aqueous contaminants.
- If your primary focus is filtering water-based solutions: Avoid standard PTFE unless you use a pre-wetting procedure; otherwise, choose a hydrophilic PTFE or an alternative membrane like nylon or PVDF.
Ultimately, selecting a PTFE filter is a decision to prioritize chemical compatibility and purity above all else.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key PTFE Property | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Filtering Aggressive Solvents/Acids | Chemical Inertness | HPLC sample prep, chemical processing |
| Venting & Gas Sterilization | Hydrophobicity | Bioreactors, sterile containers |
| Aerosol Sampling | Hydrophobicity | Airborne particle collection, environmental monitoring |
| Aqueous Solutions | Requires Hydrophilic PTFE | Water-based samples (with pre-treatment) |
Need a PTFE filter that guarantees purity and chemical resistance for your critical application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including filters, seals, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require standard filters or custom-fabricated solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders, our commitment to precision ensures your processes remain uncontaminated and reliable.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific filtration challenge and discover the right PTFE solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















