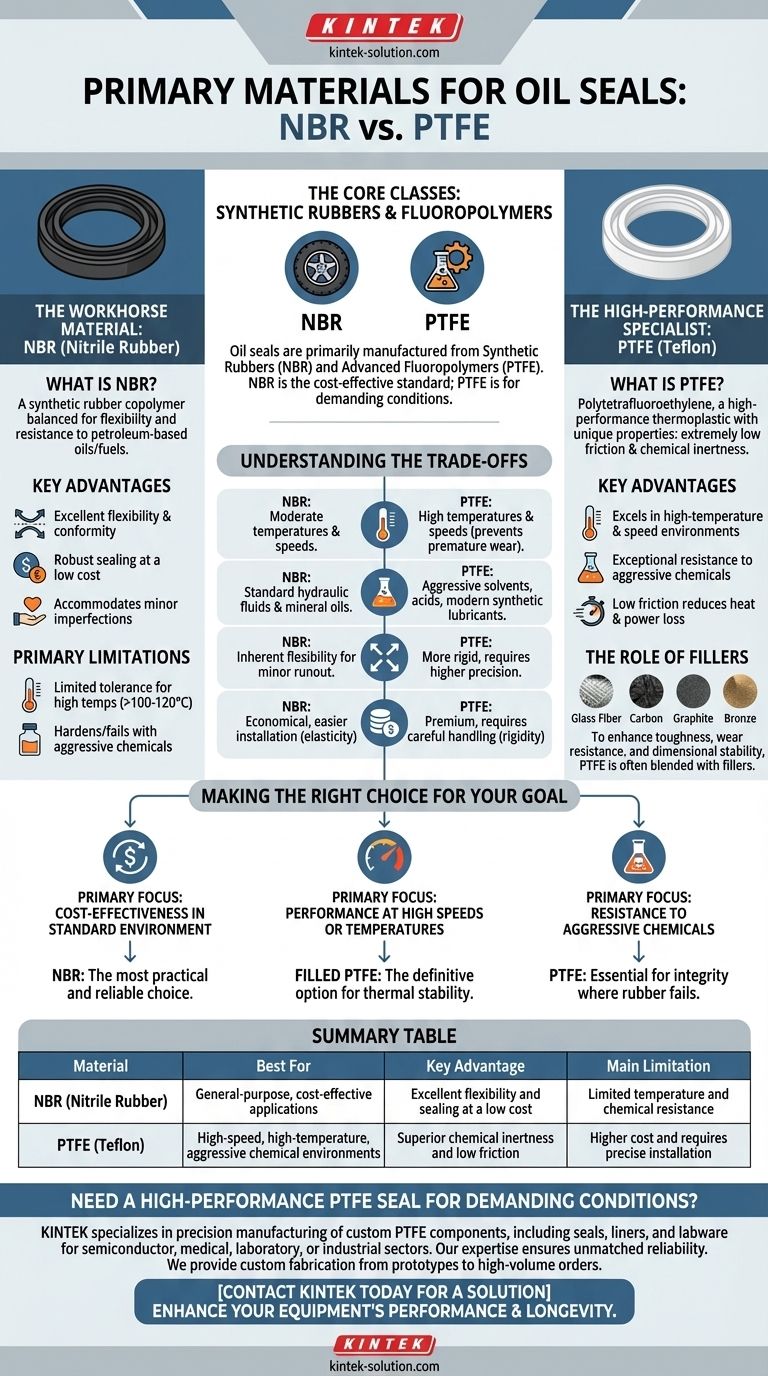
At their core, oil seals are primarily manufactured from two distinct classes of materials: synthetic rubbers, with NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) being the most common, and advanced fluoropolymers, specifically PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene). While conventional seals rely on rubber or polyurethane, PTFE represents a specialized material engineered for more demanding conditions.
The choice between oil seal materials is not a matter of which is universally "better," but which is precisely suited to your specific operational demands. NBR serves as the versatile, cost-effective standard, while PTFE is the high-performance solution for extremes in temperature, speed, or chemical exposure.

The Workhorse Material: NBR (Nitrile Rubber)
NBR is the most prevalent material for general-purpose oil seals and is often considered the industry standard for a wide range of applications.
What is NBR?
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber, or NBR, is a synthetic rubber copolymer. Its molecular structure provides a balanced combination of flexibility and resistance to common petroleum-based oils and fuels.
Key Advantages
The primary strengths of NBR are its excellent flexibility and robust sealing capability at a low cost. It conforms well to shaft surfaces and can accommodate minor imperfections, making it a forgiving and reliable choice.
Primary Limitations
NBR's main weakness is its limited tolerance for high temperatures (typically above 100-120°C or 212-250°F) and certain aggressive chemicals or synthetic lubricants, which can cause it to harden and fail prematurely.
The High-Performance Specialist: PTFE (Teflon)
PTFE is a high-performance thermoplastic used when the operational limits of traditional rubber seals are exceeded. It is commonly known by its DuPont brand name, Teflon.
What is PTFE?
Polytetrafluoroethylene is a fluoropolymer with unique properties, most notably its extremely low coefficient of friction and exceptional chemical inertness.
Key Advantages
PTFE seals excel in high-temperature environments, at high rotational speeds, and in applications with aggressive chemicals where NBR would degrade. Their low-friction nature reduces heat generation and power loss.
The Role of Fillers
Pure PTFE can be soft and prone to wear. To counteract this, it is often blended with fillers like glass fiber, carbon, graphite, or bronze. These additives significantly enhance the seal's toughness, wear resistance, and dimensional stability without compromising its core benefits.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct material requires a clear understanding of the environmental and mechanical stresses the seal will face.
Temperature and Speed
NBR is ideal for moderate temperatures and speeds. As heat and rotational velocity increase, the low-friction and high-temperature stability of PTFE become necessary to prevent premature wear and failure.
Chemical Resistance
For standard hydraulic fluids and mineral oils, NBR is perfectly suitable. However, for applications involving aggressive solvents, acids, or modern synthetic lubricants, PTFE's near-total chemical inertness provides far superior reliability.
Flexibility vs. Rigidity
NBR's inherent flexibility allows it to maintain a consistent seal on shafts with minor runout or surface irregularities. PTFE is much more rigid, requiring higher precision in shaft finishing and installation but providing unmatched performance under pressure and speed.
Cost and Installation
NBR seals are generally more economical and easier to install due to their elasticity. PTFE seals are a premium product and their rigidity demands more careful handling during installation to avoid damaging the sealing lip.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements should be the sole driver of your material selection.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in a standard environment: NBR is the most practical and reliable choice for general-purpose applications with moderate temperatures and speeds.
- If your primary focus is performance at high speeds or high temperatures: Filled PTFE is the definitive option, offering the low-friction and thermal stability necessary for demanding conditions.
- If your primary focus is resistance to aggressive chemicals or synthetic oils: PTFE is essential, as its chemical inertness ensures the seal's integrity and longevity where rubber compounds would fail.
Ultimately, selecting the right seal material is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts the reliability and lifespan of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Advantage | Main Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBR (Nitrile Rubber) | General-purpose, cost-effective applications | Excellent flexibility and sealing at a low cost | Limited temperature and chemical resistance |
| PTFE (Teflon) | High-speed, high-temperature, aggressive chemical environments | Superior chemical inertness and low friction | Higher cost and requires precise installation |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal for Demanding Conditions?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware. Whether your application is in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise ensures a seal that delivers unmatched reliability in extreme environments.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring a perfect fit for your specific speed, temperature, and chemical resistance requirements.
Contact KINTEK today for a solution that enhances your equipment's performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PTFE seals in terms of prototyping and production? Accelerate R&D and Ensure Elite Performance
- What are the key advantages of PTFE rotary seals over traditional rubber seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the overall operating temperature range for PTFE seals, gaskets, and O-rings? Achieve Sealing Integrity from -200°C to +260°C
- What makes PTFE stand out among materials used in sealing technology? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some common PTFE seal types used in industrial applications? Explore Solutions for Every Motion & Environment



















