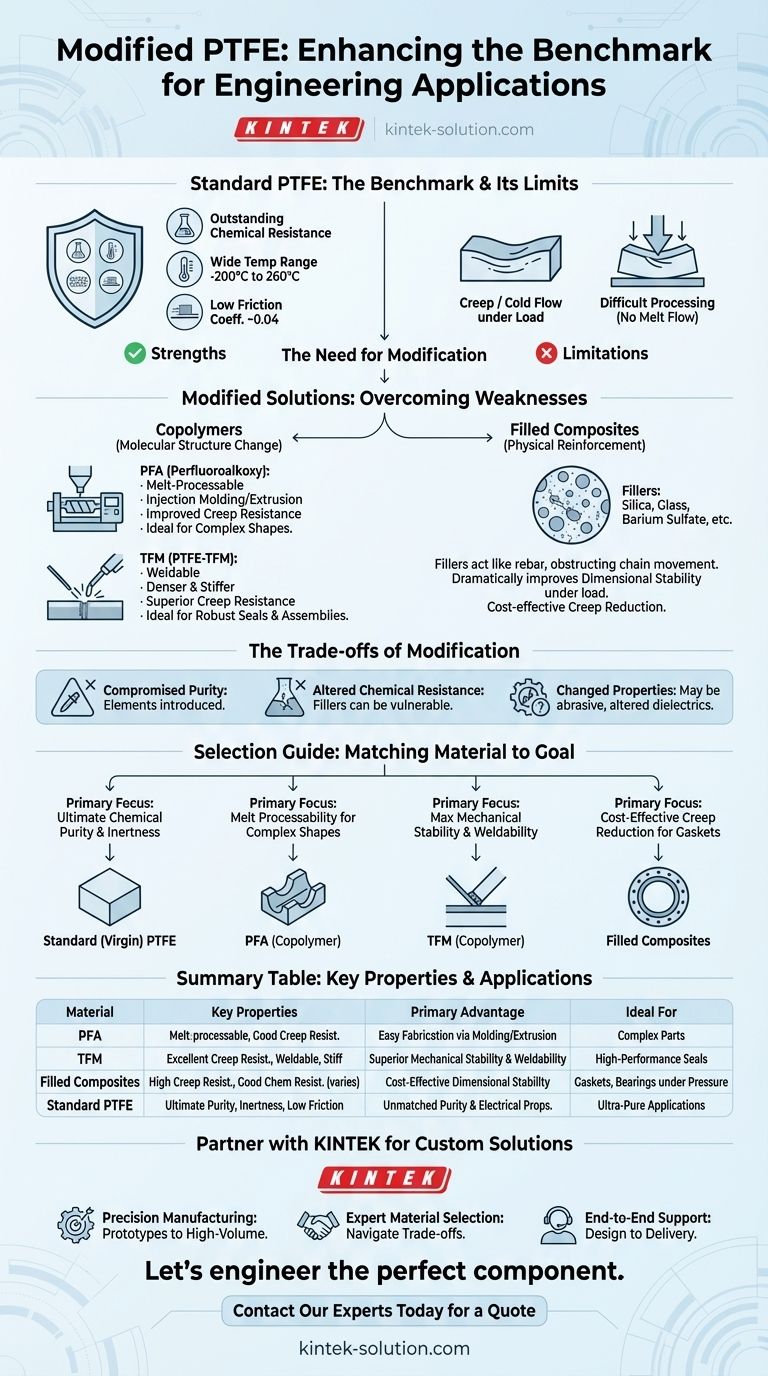
The primary modified versions of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) fall into two main categories: copolymers, such as PFA and TFM, which alter the polymer's molecular structure, and filled composites, which blend standard PTFE with inorganic materials. These modifications are specifically engineered to overcome the inherent weaknesses of pure PTFE, primarily its tendency to deform under load (creep) and its difficult processing requirements, while retaining its exceptional chemical resistance and temperature range.
The core reason to choose a modified PTFE is to gain specific mechanical or processing advantages that standard PTFE lacks. While virgin PTFE offers unmatched chemical purity and inertness, modified versions provide crucial enhancements like creep resistance, weldability, and melt processability for demanding engineering applications.

Why Modify a Near-Perfect Material?
To understand the value of modified PTFE, we must first appreciate the profile of the standard material. It is a benchmark for performance, but not without its limitations.
The Strengths of Standard PTFE
Standard, or virgin, PTFE is a semi-crystalline polymer renowned for a unique combination of properties. It has a very high melting point of 327°C and an extremely wide service temperature range, from -200°C to 260°C.
Its chemical resistance is outstanding, making it inert to nearly all acids, alkalis, and solvents. Furthermore, it possesses an exceptionally low coefficient of friction (around 0.04) and excellent electrical insulation properties.
The Inherent Limitations of Standard PTFE
Despite its strengths, standard PTFE has two significant drawbacks for certain applications.
The first is creep, also known as cold flow. Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE will slowly deform. This makes it unsuitable for high-load gaskets or structural components.
The second is processability. Standard PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt techniques like injection molding. Instead, it must be compressed and sintered, a slower and more restrictive manufacturing method.
Key Modified PTFE Categories
Modifications are designed to directly address the limitations of creep and processability. They are typically divided into copolymers and filled composites.
Category 1: Copolymers (PFA and TFM)
Copolymers introduce a second monomer into the polymer chain, altering its fundamental structure and properties.
PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy)
PFA was developed to make a fluoropolymer with properties similar to PTFE but with a critical difference: it is melt-processable.
This allows PFA to be fabricated using conventional techniques like injection molding and extrusion, opening up a much wider range of complex part geometries. It also offers improved creep resistance compared to standard PTFE.
TFM (PTFE-TFM)
TFM is another modified copolymer designed for enhanced performance. It is a denser and stiffer material than standard PTFE.
Its key advantages are significantly improved creep resistance and the ability to be welded. This makes it a superior choice for applications requiring robust sealing and the fabrication of complex assemblies.
Category 2: Filled Composites
This approach involves mechanically blending inorganic filler materials into the PTFE matrix. The fillers act as a reinforcing agent, much like rebar in concrete.
The Role of Inorganic Fillers
Fillers physically obstruct the movement of PTFE polymer chains, which is the mechanism of creep. This results in a material with dramatically improved dimensional stability under load.
While the PTFE matrix provides the primary chemical resistance and low-friction surface, the fillers add the required mechanical backbone.
Common Fillers and Their Impact
Various fillers are used to target specific properties. Common examples include silica, glass microspheres, and barium sulfate.
Each of these significantly reduces creep while largely maintaining the extreme chemical resistance of the base PTFE, making filled PTFE a standard choice for demanding gasketing applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While modified versions solve key problems, introducing new materials into the PTFE matrix is not without consequences.
Compromised Chemical Purity
The most significant trade-off is purity. Copolymers and fillers introduce different chemical elements and structures. For ultra-high-purity applications, such as in the semiconductor or pharmaceutical industries, only virgin PTFE may be acceptable.
Altered Chemical Resistance
The filler material itself may not share PTFE's near-universal chemical inertness. For example, glass-filled PTFE could be attacked by hydrofluoric acid or strong hot caustics, even though the PTFE matrix itself would be unaffected.
Changes in Mechanical and Electrical Properties
Fillers increase hardness and stiffness but can also make the material more abrasive. They can also alter the excellent dielectric properties of pure PTFE, which must be considered in electrical insulation applications.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Choosing between standard and modified PTFE requires a clear understanding of your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical purity and inertness: Stick with standard (virgin) PTFE for its unmatched performance in this area.
- If your primary focus is melt processability for complex shapes: PFA is the definitive choice, offering PTFE-like properties in an easily moldable form.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical stability and weldability: TFM provides superior creep resistance and stiffness for the most demanding sealing and structural roles.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective creep reduction for gaskets: A filled PTFE composite offers a robust and economical solution for reliable sealing under pressure.
By understanding these targeted modifications, you can select a material precisely engineered to meet your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Modified PTFE Type | Key Properties | Primary Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| PFA (Copolymer) | Melt-processable, good creep resistance, high temp/chemical resistance | Easy fabrication via injection molding/extrusion | Complex parts requiring PTFE-like properties |
| TFM (Copolymer) | Excellent creep resistance, weldable, stiff, dense | Superior mechanical stability and weldability | High-performance seals and complex assemblies |
| Filled Composites | High creep resistance, good chemical resistance (varies by filler) | Cost-effective dimensional stability under load | Gaskets, bearings, and seals under pressure |
| Standard (Virgin) PTFE | Ultimate chemical purity, inertness, low friction | Unmatched chemical purity and electrical properties | Ultra-pure applications (semiconductor, pharmaceutical) |
Need a Custom PTFE Solution?
Choosing the right fluoropolymer is critical to your project's success. Whether you require the unmatched purity of virgin PTFE, the processability of PFA, the mechanical strength of TFM, or the cost-effectiveness of a filled composite, KINTEK has the expertise to guide you.
Why Partner with KINTEK?
- Precision Manufacturing: We specialize in the custom fabrication of high-quality PTFE components—from prototypes to high-volume production runs—ensuring precision and reliability for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
- Expert Material Selection: Our team will help you navigate the trade-offs to select the optimal material (PTFE, PFA, TFM, or filled composite) for your specific application requirements, including chemical resistance, temperature stability, and mechanical load.
- End-to-End Support: From design consultation to final delivery, we are committed to providing solutions that enhance your product's performance and durability.
Let's engineer the perfect component for your needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE balls particularly suitable for high-performance applications? Key Properties & Selection Guide
- What are the overall advantages of using PTFE balls in fluid management systems? Enhance Reliability & Efficiency
- How do the chemical properties of PTFE balls influence their performance? Unmatched Durability in Harsh Environments
- What factors determine the different grades of PTFE balls available? Select the Right Grade for Your Application
- How do PTFE balls contribute to reduced maintenance costs? Extend Component Life and Cut Downtime



















