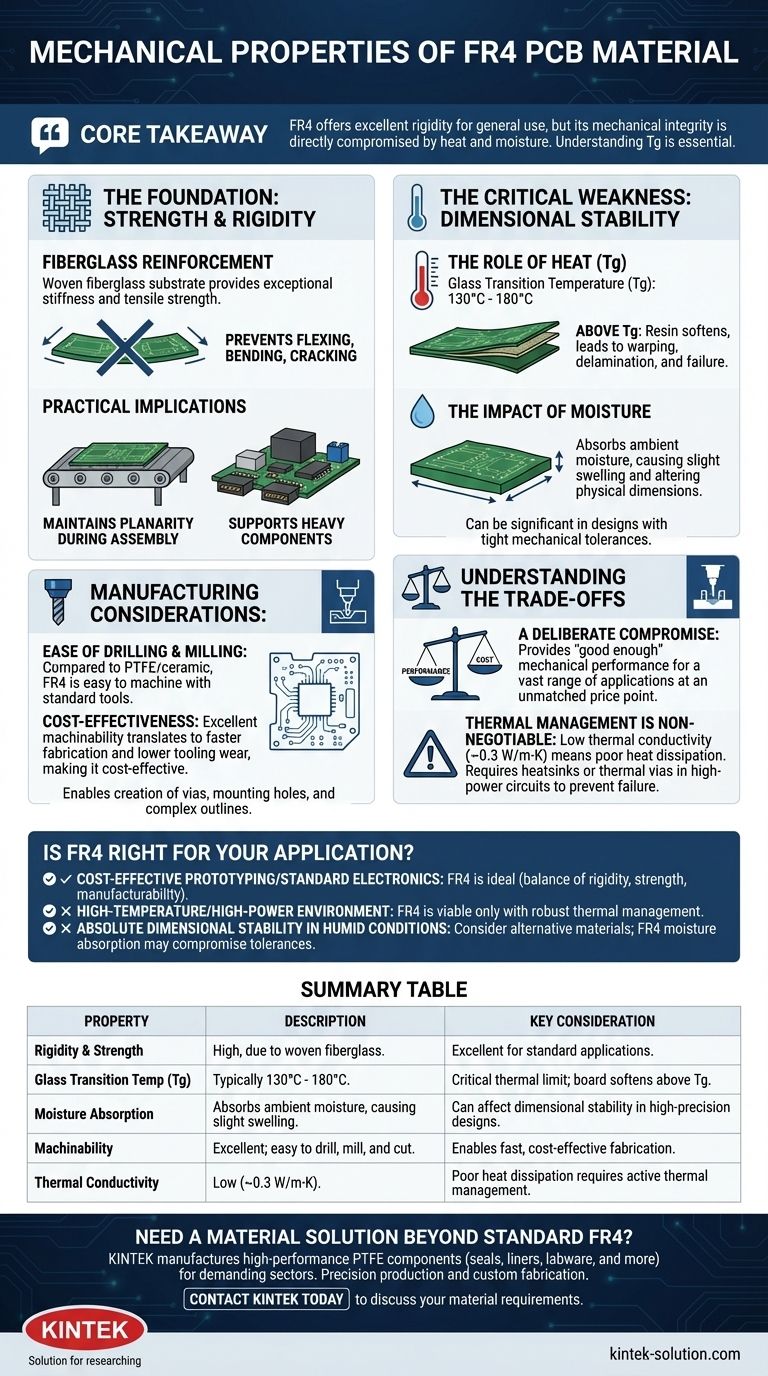
Fundamentally, FR4 is a mechanically robust and cost-effective material defined by its high rigidity and strength. This is due to its composition as a woven fiberglass cloth bonded with an epoxy resin, making it the default choice for the vast majority of standard printed circuit boards.
The core takeaway is that while FR4 offers excellent rigidity for general use, its mechanical integrity is directly compromised by heat and moisture. Understanding its thermal limits, particularly the glass transition temperature (Tg), is therefore essential to prevent mechanical failure.

The Foundation: Strength and Rigidity
Fiberglass Reinforcement
The mechanical backbone of FR4 is its woven fiberglass substrate. This internal structure provides exceptional stiffness and tensile strength.
This prevents the board from easily flexing, bending, or cracking under the stress of assembly and normal operation, ensuring mounted components remain secure.
Practical Implications
High rigidity is critical for maintaining the planarity of the board. This is vital during automated assembly processes like solder reflow, where a flat surface ensures reliable connections.
It also means FR4 can support heavy components and connectors without significant physical distortion, contributing to the long-term reliability of the final product.
The Critical Weakness: Dimensional Stability
The Role of Heat (Tg)
FR4 does not have a melting point, but it has a glass transition temperature (Tg), typically ranging from 130°C to 180°C.
Above this temperature, the epoxy resin softens, and the material rapidly loses its rigidity and structural integrity. This can lead to board warping, delamination, and mechanical failure.
The Impact of Moisture
FR4 has a tendency to absorb moisture from the environment. This absorption can cause the material to swell slightly, altering its physical dimensions.
For most applications, this is negligible. However, in designs with extremely tight mechanical tolerances, this can become a significant factor.
Manufacturing Considerations: Machinability
Ease of Drilling and Milling
Compared to more exotic substrates like PTFE or ceramic-filled materials, FR4 is relatively easy to machine.
Standard tools can be used to drill, mill, and cut it with high precision. This property is crucial for creating vias, mounting holes, and complex board outlines.
Cost-Effectiveness
The excellent machinability of FR4 directly translates to faster fabrication times and lower tooling wear. This is a primary driver of its position as the industry's most cost-effective rigid PCB material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Performance vs. Cost
FR4 represents a deliberate compromise. It provides "good enough" mechanical performance for an enormous range of applications at an unmatched price point. Materials with higher thermal stability or lower moisture absorption come at a significant cost premium.
Thermal Management is Non-Negotiable
You cannot evaluate FR4's mechanical properties without considering its thermal limitations. Its low thermal conductivity (~0.3 W/m·K) means it dissipates heat poorly.
Without proper thermal management like heatsinks or thermal vias in high-power circuits, localized hot spots can easily push sections of the board past their Tg, leading to catastrophic mechanical failure.
Is FR4 Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right material requires aligning its mechanical properties with the demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective prototyping or standard consumer electronics: FR4 is the ideal choice, offering a superb balance of rigidity, strength, and manufacturability.
- If your project operates in a high-temperature or high-power environment: FR4 is viable only if you implement a robust thermal management strategy to keep the board temperature safely below its Tg rating.
- If your design demands absolute dimensional stability in humid conditions: You should consider alternative materials, as FR4's tendency to absorb moisture may compromise tight mechanical tolerances.
Understanding these foundational properties allows you to leverage FR4's strengths while designing around its limitations.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Rigidity & Strength | High, due to woven fiberglass reinforcement. | Excellent for standard applications and component support. |
| Glass Transition Temp (Tg) | Typically 130°C - 180°C. | Critical thermal limit; board softens and loses integrity above Tg. |
| Moisture Absorption | Absorbs ambient moisture, causing slight swelling. | Can affect dimensional stability in high-precision designs. |
| Machinability | Excellent; easy to drill, mill, and cut with standard tools. | Enables fast, cost-effective fabrication of complex boards. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (~0.3 W/m·K). | Poor heat dissipation requires active thermal management in high-power circuits. |
Need a material solution that goes beyond standard FR4?
While FR4 is excellent for many applications, projects demanding extreme thermal stability, minimal moisture absorption, or custom fabrication require a specialized partner.
KINTEK manufactures high-performance PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer precision production and custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet the toughest mechanical and environmental demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific material requirements and get a solution engineered for your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Conductive Glass Substrate Cleaning Rack
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















