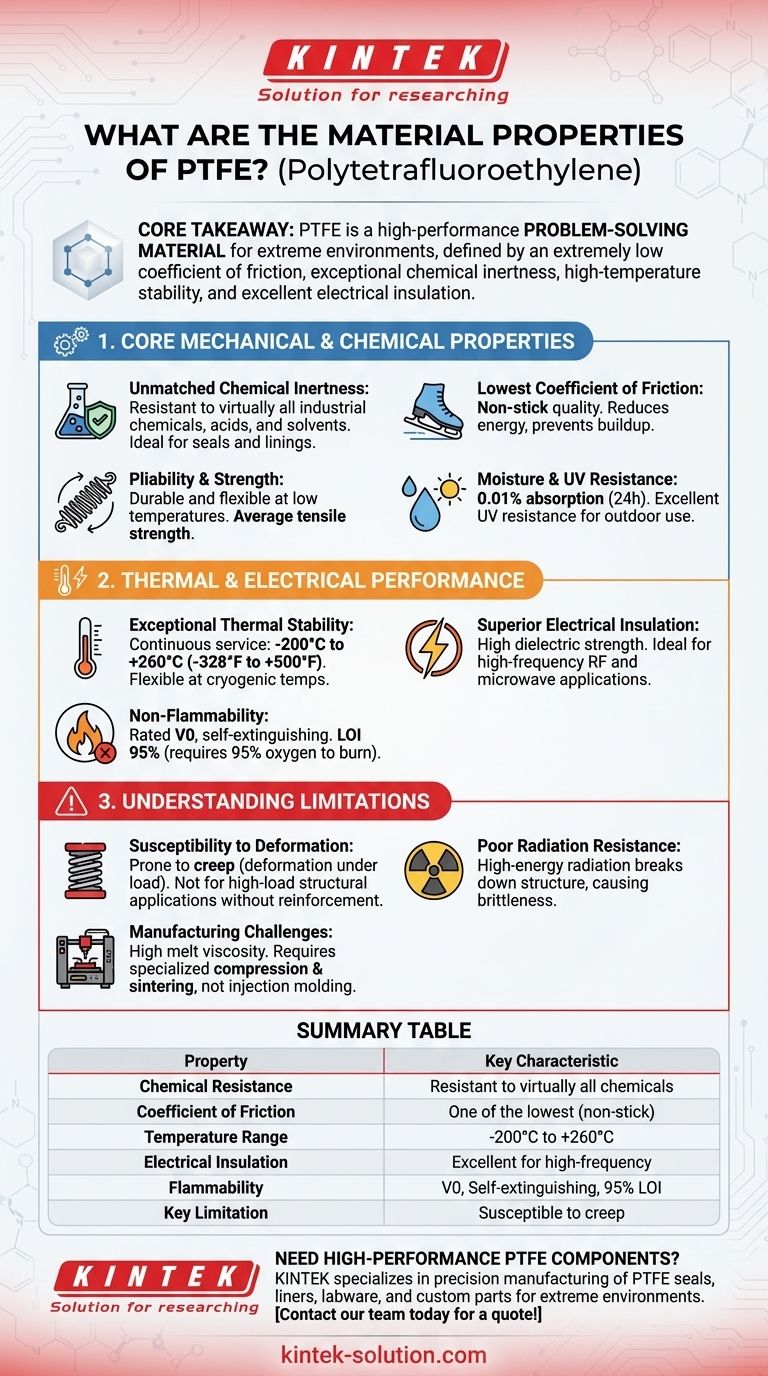
In essence, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer defined by four exceptional characteristics: an extremely low coefficient of friction, remarkable chemical inertness, high-temperature stability, and excellent electrical insulation. These properties make it a specialty material for demanding applications where other plastics would fail.
The core takeaway is that PTFE is a problem-solving material for extreme environments. Its unique combination of properties makes it invaluable for applications involving harsh chemicals, high temperatures, or low-friction surfaces, but its mechanical limitations mean it is not a universal substitute for all engineering plastics.

Core Mechanical and Chemical Properties
PTFE's molecular structure gives it a set of mechanical and chemical properties that are unmatched by most other polymers.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE has tremendous resistance to virtually all industrial chemicals and solvents, including harsh acids and bases. This makes it an ideal material for seals, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing equipment. It is often used as a protective coating against rust and corrosion.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
Of all known solid materials, PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction. This is what gives it its famous non-stick quality. In industrial settings, this property reduces energy consumption in sliding parts and prevents material buildup.
Pliability and Strength
PTFE is a durable and flexible elastomer, maintaining its pliability even at very low temperatures. While it has high flexural strength and a good strength-to-weight ratio, its tensile strength is only average compared to other engineering plastics.
Moisture and UV Resistance
The material is highly resistant to water, with a measured absorption of just 0.01% over a 24-hour period. It also exhibits excellent resistance to ultraviolet (UV) light, making it suitable for outdoor applications without degradation.
Thermal and Electrical Performance
PTFE maintains its integrity across an exceptionally wide range of temperatures and is a premier material for electrical insulation.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE offers a continuous service temperature up to +260°C (500°F), the highest among all fluoroplastics. It also retains flexibility at cryogenic temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F), making its operational range incredibly broad.
Superior Electrical Insulation
With high dielectric strength and excellent dielectric properties, PTFE is an ideal insulator. It is widely used in high-frequency applications, such as insulators in coaxial cables, connectors, and printed circuit boards (PCBs) for microwave and radio frequency engineering.
Non-Flammability
PTFE has a flammability rating of V0, meaning it self-extinguishes after the flame source is removed. Its limiting oxygen index is 95%, indicating it requires an atmosphere of 95% oxygen to burn, making it extremely non-flammable in normal air.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PTFE is a high-performance material, its limitations are critical to understand for proper application design.
Susceptibility to Deformation
The primary mechanical weakness of PTFE is its tendency to creep, or deform under load over time. This makes it unsuitable for high-load structural applications unless it is reinforced with fillers like glass fiber or carbon.
Poor Radiation Resistance
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation, such as gamma rays. Radiation can break down the polymer's molecular structure, causing it to become brittle and lose its mechanical properties.
Manufacturing Challenges
Due to its high melting point of 327°C and extremely high melt viscosity, PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like injection molding. It must be formed using specialized compression and sintering methods similar to those used in powder metallurgy.
Choosing PTFE for Your Application
Your final decision depends entirely on whether PTFE's unique strengths align with your primary design challenge.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance or high-temperature stability: PTFE is a first-class choice for seals, linings, and components in harsh industrial environments.
- If your primary focus is creating a low-friction or non-stick surface: PTFE is one of the best materials available for bearings, slide plates, and non-stick coatings.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: PTFE's excellent dielectric properties make it an ideal candidate for RF and microwave components.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load-bearing capacity: You must either use a filled grade of PTFE or consider an alternative engineering plastic to avoid failure from creep.
PTFE is a specialty polymer that solves problems that other materials simply cannot.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to virtually all industrial chemicals and solvents |
| Coefficient of Friction | One of the lowest of all solid materials (non-stick) |
| Temperature Range | Continuous service from -200°C to +260°C |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength, ideal for high-frequency applications |
| Flammability | Rated V0, self-extinguishing, with a 95% limiting oxygen index |
| Key Limitation | Susceptible to creep (deformation under sustained load) |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your exact requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise ensures your parts meet the highest standards for chemical resistance, thermal stability, and electrical performance.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, helping you solve complex challenges in extreme environments. Contact our team today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















