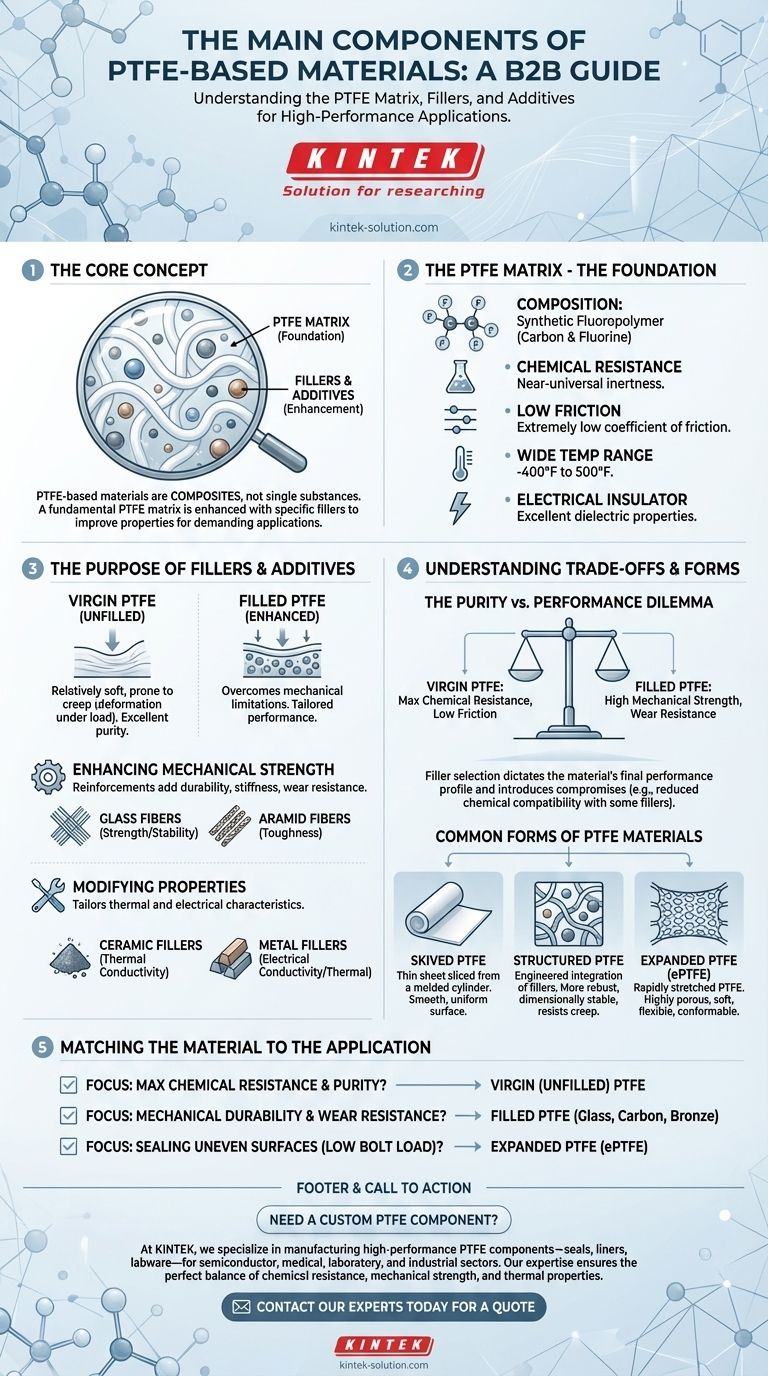
At its core, a PTFE-based material is a composite system, not a single substance. It consists of a fundamental PTFE matrix—the source of its famous chemical inertness and low friction—which is then enhanced with specific fillers and additives to improve its physical properties for demanding applications.
The central concept to grasp is that while pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides the foundational chemical resistance and non-stick surface, it is often too soft for structural use. Fillers are strategically added to overcome these mechanical limitations, creating a range of materials tailored for specific performance needs.

The Foundation: The PTFE Matrix
What is PTFE?
Polytetrafluoroethylene, or PTFE, is a synthetic fluoropolymer. It is composed of only two elements: carbon and fluorine.
The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong. This molecular stability is the source of PTFE's most valued characteristics.
The Source of Its Properties
This powerful carbon-fluorine bond gives the PTFE matrix its well-known attributes. These include near-universal chemical resistance, an extremely low coefficient of friction, and a wide operating temperature range (typically -400°F to 500°F).
It is also an excellent electrical insulator, making it a critical material in electronics and high-voltage applications.
The Purpose of Fillers and Additives
Pure, or "virgin," PTFE is relatively soft and prone to deforming under load (a phenomenon known as "creep"). Fillers are added directly into the PTFE matrix to counteract these weaknesses.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength
Reinforcements are added to significantly improve durability, stiffness, and wear resistance. Common reinforcements include glass fibers, which add strength and stability, and aramid fibers, known for their exceptional toughness.
Modifying Thermal and Electrical Properties
While pure PTFE is an electrical insulator, its properties can be modified. Ceramic fillers can be used to improve thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat more effectively in applications like seals and bearings.
Conversely, metal fillers (like bronze or stainless steel) can be added to make the material more electrically conductive or to further enhance thermal conductivity and compressive strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PTFE-based material is always an exercise in balancing competing properties. The addition of fillers, while beneficial, introduces necessary compromises.
The Purity vs. Performance Dilemma
Virgin PTFE offers the absolute highest chemical resistance and lowest coefficient of friction. However, it has the lowest mechanical strength.
Adding a filler like glass fiber dramatically increases wear resistance and reduces deformation under load. The trade-off is a slight reduction in chemical compatibility; for instance, glass-filled PTFE is not recommended for use with strong alkalis or hydrofluoric acid.
Filler Selection is Critical
The choice of filler dictates the material's final performance profile. A carbon-filled compound has good wear properties and chemical resistance, while a bronze-filled compound offers much higher thermal conductivity but is unsuitable for corrosive environments.
Understanding the service conditions—the chemicals, temperatures, and mechanical loads involved—is paramount to selecting the correct filler system.
Common Forms of PTFE Materials
The way these components are processed also defines the final material. For sealing applications, PTFE materials often fall into three classifications.
Skived PTFE
This is a thin sheet of material that is "skived," or sliced, from a large molded cylinder of PTFE. It is often pure or very lightly filled and provides a smooth, uniform sealing surface.
Structured PTFE
In this form, fillers are integrated into the PTFE matrix in a specific, engineered way. This creates a more robust and dimensionally stable material that resists creep and cold flow far better than simpler compounds.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
This material is created by rapidly stretching pure PTFE, which creates a strong but highly porous, soft, and flexible structure. ePTFE is exceptionally conformable, making it ideal for sealing damaged, irregular, or fragile flanges where a hard gasket would fail.
Matching the Material to the Application
Ultimately, the components are chosen to match a specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical resistance and purity: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability and wear resistance: A filled PTFE with glass, carbon, or bronze is required.
- If your primary focus is sealing uneven surfaces under low bolt load: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) provides the best conformability.
Understanding that PTFE-based materials are engineered composites of a polymer matrix and functional fillers empowers you to select the precise solution for your technical challenge.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE Matrix | Foundation | Chemical inertness, low friction, electrical insulation |
| Fillers (e.g., Glass, Carbon) | Reinforcement | Increases wear resistance, strength, and stiffness |
| Additives (e.g., Bronze) | Property Modification | Enhances thermal/electrical conductivity |
Need a custom PTFE component tailored to your exact requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensures you get a solution that perfectly balances chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal properties for your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















