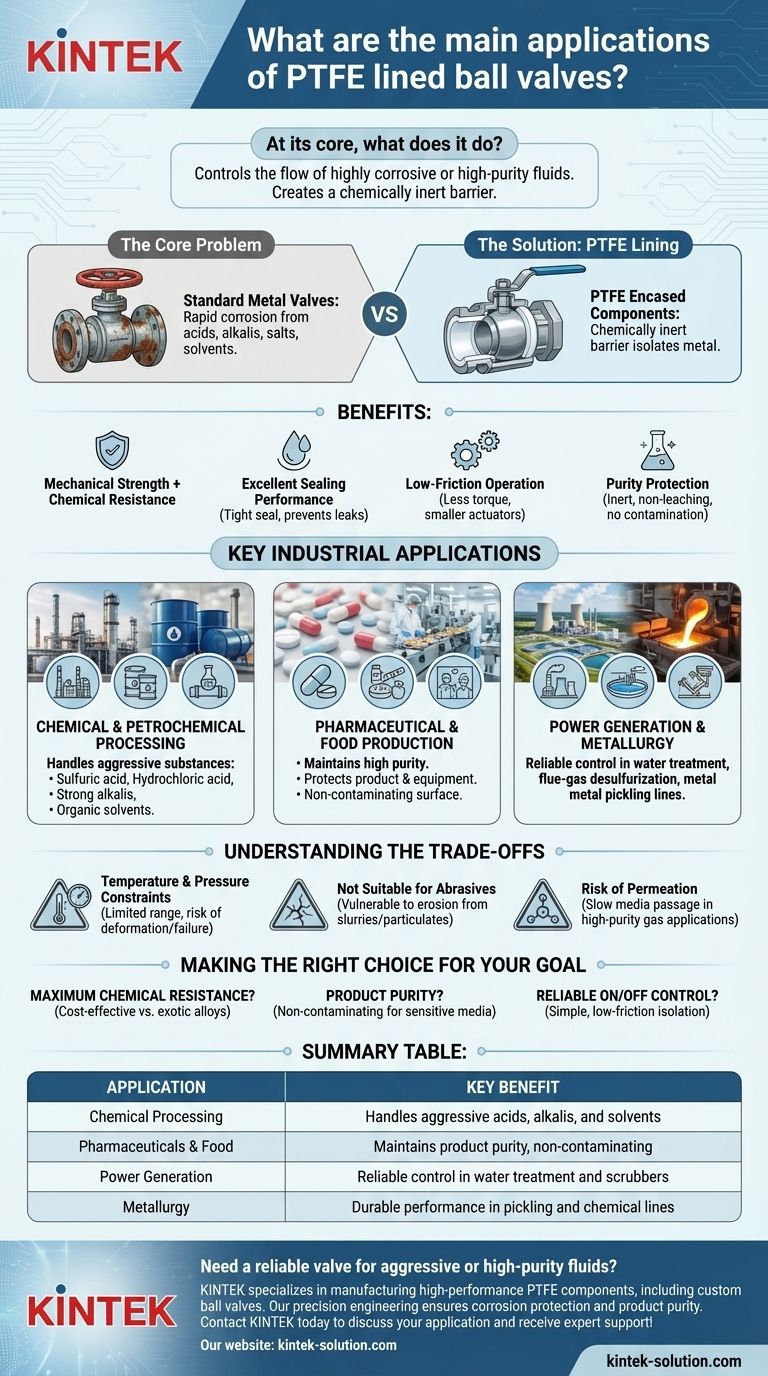
At its core, a PTFE lined ball valve is a specialized tool for controlling the flow of highly corrosive or high-purity fluids. They are most commonly used in demanding industrial applications where standard metal valves would quickly fail. Key industries include chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, power generation, and metallurgy.
The primary function of a PTFE lined ball valve is not just to control flow, but to create a chemically inert barrier within a pipeline. This protects the valve's structural components from aggressive media and prevents the process fluid from being contaminated.

The Core Problem: Handling Aggressive Media
Standard metal valves, even those made from stainless steel, face a significant challenge when handling aggressive chemicals. The constant exposure to acids, alkalis, salts, and solvents leads to rapid corrosion.
How PTFE Lining Provides a Solution
A PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) lined ball valve encases the internal metal components—the valve body, ball, and stem—in a seamless layer of chemically inert fluoroplastic. This lining acts as a robust barrier, isolating the structural metal from the corrosive fluid.
The result is a valve that combines the mechanical strength of a metal body with the superior chemical resistance of PTFE.
Key Benefits Beyond Corrosion Resistance
Beyond simple corrosion protection, the PTFE lining offers several critical operational advantages.
Excellent Sealing Performance: PTFE is a soft, pliable material that creates a tight seal around the ball, preventing leaks. This is vital for handling hazardous chemicals or valuable products.
Low-Friction Operation: PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This property means the valve requires less torque to open and close, allowing for smaller actuators and easier manual operation.
Purity Protection: In industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing, preventing contamination is paramount. Because the PTFE liner is inert and non-leaching, it ensures the purity of the medium passing through it is never compromised by metallic ions.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique properties of PTFE lined ball valves make them indispensable in several key sectors.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
This is the primary application. These valves are used to handle a wide range of aggressive substances, including sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, strong alkalis, and organic solvents that would destroy conventional valves.
Pharmaceutical and Food Production
In these high-purity industries, the goal is twofold: protect equipment and protect the product. The non-contaminating, non-reactive surface of the PTFE liner makes it ideal for processing sensitive ingredients and final products.
Power Generation and Metallurgy
These industries often use aggressive chemicals for processes like water treatment, flue-gas desulfurization, and metal pickling. PTFE lined valves provide a reliable and long-lasting solution for controlling these corrosive fluid lines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE lined valves are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to proper application.
Temperature and Pressure Constraints
PTFE has a more limited operating temperature range compared to solid metal. High temperatures can cause the liner to soften, deform, or even fail under pressure. Similarly, they are not typically specified for extremely high-pressure applications where the liner could be compromised.
Not Suitable for Abrasives
The softness that makes PTFE an excellent sealant also makes it vulnerable to abrasive media. Slurries or fluids containing hard particulates can quickly erode the liner, leading to valve failure.
Risk of Permeation
For some high-purity gas or small-molecule liquid applications, there can be a risk of the media slowly permeating through the PTFE liner over time. This is a specialized consideration but is critical in certain semiconductor or laboratory settings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting this valve type depends entirely on the specific challenge you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical resistance: A PTFE lined valve is often a more cost-effective solution than a valve made entirely from an expensive exotic alloy for handling aggressive acids and solvents.
- If your primary focus is product purity: For food, beverage, or pharmaceutical applications, the inert, non-contaminating surface of the liner is its most important feature.
- If your primary focus is reliable ON/OFF control: The simple, low-friction quarter-turn action of a ball valve, combined with the protection of PTFE, provides dependable isolation of corrosive fluid lines.
Ultimately, a PTFE lined ball valve is the definitive choice for safely controlling the flow of aggressive media where both equipment integrity and fluid purity are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Handles aggressive acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Pharmaceuticals & Food | Maintains product purity, non-contaminating |
| Power Generation | Reliable control in water treatment and scrubbers |
| Metallurgy | Durable performance in pickling and chemical lines |
Need a reliable valve for aggressive or high-purity fluids? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom ball valves, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision engineering ensures your equipment is protected from corrosion and your process fluid remains uncontaminated. From prototype to high-volume production, we deliver solutions tailored to your exact needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and receive expert support!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems



















