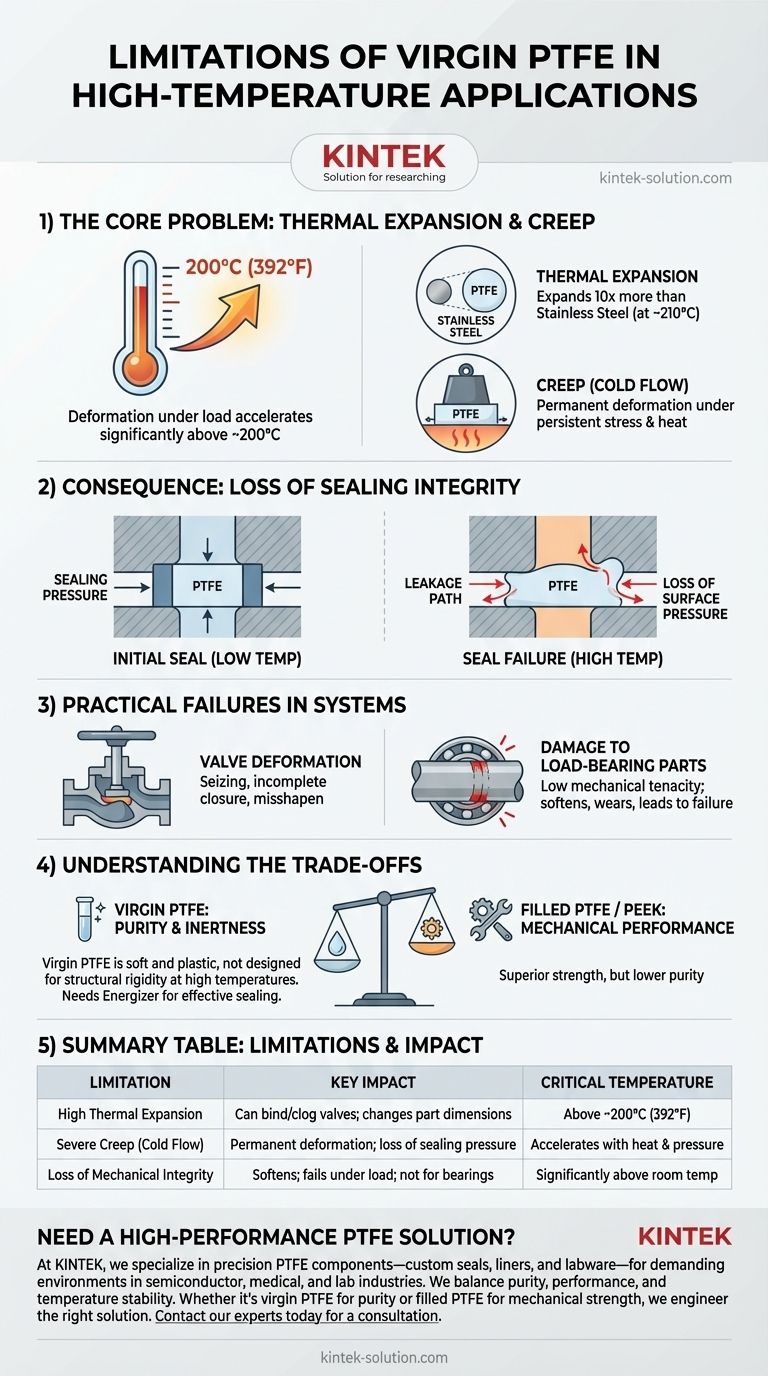
While known for its impressive heat resistance, virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has critical limitations in high-temperature applications, primarily due to its tendency to deform under load. At temperatures approaching 200°C (392°F), it experiences a dramatic rate of thermal expansion and severe "creep," leading to a loss of sealing pressure, permanent deformation, and potential mechanical failure.
The core challenge with virgin PTFE is not its melting point, but its loss of mechanical integrity at elevated temperatures. Its extreme thermal expansion and inherent softness under load are the true limiting factors that engineers must design around.

The Core Problem: Thermal Expansion and Creep
The two primary physical behaviors that limit virgin PTFE at high temperatures are its high coefficient of thermal expansion and its susceptibility to creep, also known as cold flow.
Understanding Thermal Expansion
Virgin PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes far more than metals do. At around 210°C (410°F), its rate of thermal expansion can be 10 times greater than that of stainless steel.
This high expansion rate means a precisely machined PTFE component can change size significantly, potentially binding up or clogging mechanisms like valves as the system heats up.
The Impact of Creep (Cold Flow)
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress. For PTFE, this is a significant factor even at room temperature, but heat drastically accelerates the process.
Under the combined influence of heat and pressure (like in a gasket or seal), the PTFE material will slowly flow away from the point of highest stress, permanently changing its shape.
The Consequence: Loss of Sealing Integrity
In sealing applications, creep and thermal expansion work together to cause failure. An initial compressive load creates a tight seal, but as the temperature rises, the material expands and creeps.
This leads to a loss of surface pressure against the mating surfaces. When the system cools, the permanently deformed PTFE part no longer exerts the same force, resulting in leakage.
Practical Failures in High-Temperature Systems
These material properties manifest as tangible engineering problems that can compromise the safety and reliability of an entire system.
Deformation in Valves and Components
A PTFE valve seat designed for a perfect fit at room temperature can expand with heat and deform under pressure from the valve mechanism. This can cause the valve to seize, fail to close completely, or become permanently misshapen.
Damage to Load-Bearing Parts
Virgin PTFE has very low mechanical tenacity, meaning it is not inherently strong or resistant to abrasion. Using it for load-bearing parts like bushings or bearings at high temperatures is a significant risk.
The material softens with heat, increasing creep and wear, which can lead to the failure of the bearing and subsequent damage to more critical components like rotating shafts.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Virgin PTFE
Choosing any material involves weighing its benefits against its drawbacks. Virgin PTFE is selected for specific reasons, but these come with clear performance boundaries.
The Purity vs. Performance Dilemma
Virgin PTFE is often specified for its exceptional purity and chemical inertness. In industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, or semiconductor manufacturing, its clean, non-contaminating surface is non-negotiable.
The trade-off is that this purity comes at the cost of mechanical robustness. Filled grades of PTFE (containing glass, carbon, or other materials) offer vastly superior creep resistance and stability at high temperatures but are not suitable for applications where purity is the primary concern.
Inherent Softness
PTFE is fundamentally a soft polymer. This property contributes to its excellent sealing capabilities at lower temperatures but becomes a significant liability under mechanical load and heat. It is not designed to be a structurally rigid material.
Installation and Sealing Challenges
The plastic, non-elastic nature of PTFE means it does not rebound like a rubber O-ring. To maintain a seal across a wide temperature range, PTFE seals often require a separate energizer, such as a metal spring or a rubber elastomer, to provide continuous force as the PTFE itself relaxes and deforms.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To use virgin PTFE effectively, you must align its material properties with the operational demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and contamination control: Virgin PTFE is an excellent choice, but you must operate well below 200°C and keep mechanical loads to a minimum.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance at high temperatures: You should immediately consider filled grades of PTFE or an entirely different high-performance polymer like PEEK.
- If your primary focus is reliable sealing under pressure and heat: Your design must actively compensate for creep and thermal expansion, likely by incorporating spring-energized seals or other mechanisms that maintain constant pressure.
Understanding these mechanical limitations is the key to successfully leveraging virgin PTFE's exceptional chemical resistance and thermal properties.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Critical Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| High Thermal Expansion | Can bind/clog valves; changes part dimensions | Above ~200°C (392°F) |
| Severe Creep (Cold Flow) | Permanent deformation; loss of sealing pressure | Accelerates with heat & pressure |
| Loss of Mechanical Integrity | Softens; fails under load; not for bearings/bushings | Significantly above room temperature |
Need a high-performance PTFE solution that overcomes these limitations?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. We understand the critical balance between purity, performance, and temperature stability.
Whether you require the unmatched chemical purity of virgin PTFE for sensitive applications or the enhanced mechanical properties of filled PTFE compounds for high-temperature, high-load scenarios, our expertise in custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders ensures you get the right part for your specific needs.
Let's engineer a solution that ensures reliability and prevents failure in your system. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















