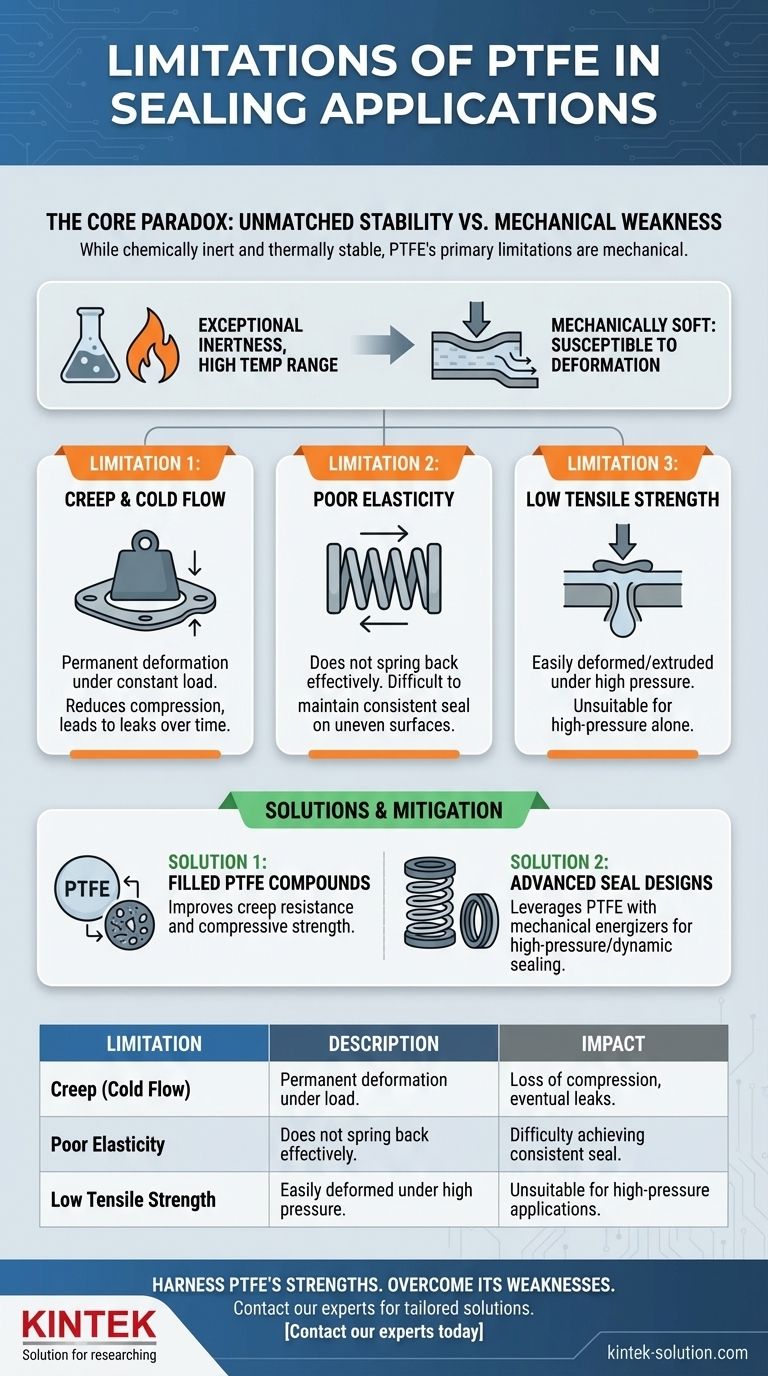
While Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for its chemical and thermal stability, its primary limitations in sealing applications are mechanical. In its pure, or "virgin," form, PTFE is susceptible to creep (cold flow) under pressure, has poor elasticity which makes consistent compression difficult, and possesses low tensile strength, making it unsuitable for high-pressure environments on its own.
The central challenge with PTFE is not its chemical resistance or temperature range, but its inherent mechanical softness. Understanding this distinction is critical to using it effectively, as its weaknesses can be overcome through material compounding and intelligent seal design.

The Core Paradox of PTFE
PTFE is a material of extremes. Its most celebrated properties are also intrinsically linked to its greatest weaknesses as a sealing material.
Unmatched Chemical and Thermal Stability
PTFE is virtually inert, resisting attack from almost all acids, bases, and solvents. It also maintains its properties across an exceptionally wide temperature range, from cryogenic conditions (-200°C) up to 260°C (500°F).
These characteristics make it a default choice for applications involving aggressive media or extreme temperatures where other elastomers would quickly fail.
The Inherent Mechanical Weaknesses
The same molecular structure that makes PTFE chemically stable and low-friction also makes it mechanically soft. This softness is the root cause of its limitations in demanding sealing roles.
Key Mechanical Limitations Explained
When evaluating PTFE, particularly in its pure virgin state, three specific mechanical issues are paramount.
Limitation 1: Creep and Cold Flow
Creep, also known as cold flow, is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress.
Because PTFE is soft, a gasket or seal under constant bolt load or system pressure will slowly "flow" or thin out over time. This reduces the compressive force on the seal, eventually leading to a loss of sealing performance and potential leaks.
Limitation 2: Poor Compression and Elasticity
Unlike rubber or other elastomers, virgin PTFE has very poor "memory." It does not spring back to its original shape effectively after being compressed.
This makes it difficult to achieve a consistent and reliable seal, especially on surfaces that are not perfectly flat. It requires careful installation and may not adapt well to pressure or temperature fluctuations that cause flange surfaces to shift.
Limitation 3: Low Tensile Strength
Virgin PTFE can be easily deformed, stretched, or extruded through gaps when subjected to high pressure.
This makes pure PTFE rings or gaskets unsuitable for high-pressure applications. The material can be forced out of the intended sealing area, resulting in catastrophic failure of the seal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The limitations of pure PTFE are well-understood, and the industry has developed effective solutions to mitigate them. The key is knowing when to use pure PTFE versus an enhanced version.
Virgin PTFE vs. Filled PTFE
The most common solution to PTFE's mechanical weakness is the addition of fillers. Compounds are created by mixing PTFE with materials like glass fiber, carbon, graphite, or bronze.
- Filled PTFE dramatically improves creep resistance, increases compressive strength, and raises the material's pressure-handling capabilities.
- The trade-off is that fillers can sometimes slightly reduce the overall chemical resistance of the compound compared to virgin PTFE.
The Impact of Seal Design
Modern engineering uses PTFE strategically in advanced seal designs. For high-pressure or dynamic applications, you will almost never see a simple, pure PTFE O-ring.
Instead, designs like spring-energized seals or the use of PEEK back-up rings provide the mechanical strength and elasticity that PTFE lacks. This allows engineers to leverage PTFE's low friction and chemical resistance in environments it could never handle alone.
Niche Chemical Vulnerabilities
While exceptionally inert, PTFE is not completely immune. It can be attacked by highly reactive substances like molten alkali metals (e.g., sodium) and powerful fluorinating agents. These are rare exceptions but are critical to note for specialized applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE-based solution requires matching the material and design to the specific pressures, temperatures, and mechanical stresses of your system.
- If your primary focus is static, low-pressure chemical sealing: A gasket made from virgin PTFE may be a perfectly acceptable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure or dynamic sealing: You must use a filled PTFE compound or an engineered seal design that incorporates energizers or back-up rings.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability under load: Prioritize a filled PTFE material specifically compounded for low creep to ensure the seal maintains its integrity over time.
By understanding that PTFE's limitations are primarily mechanical, you can select the right grade or design to harness its exceptional properties without falling victim to its weaknesses.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Description | Impact on Sealing Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Creep (Cold Flow) | Permanent deformation under constant load. | Loss of compression and eventual leaks over time. |
| Poor Elasticity | Does not spring back effectively after compression. | Difficulty achieving a consistent seal on uneven surfaces. |
| Low Tensile Strength | Easily deformed or extruded under high pressure. | Unsuitable for high-pressure applications in pure form. |
Don't let PTFE's limitations compromise your sealing performance.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom labware. Our expertise lies in precisely compounding filled PTFE materials and designing engineered seals that overcome the inherent mechanical weaknesses of virgin PTFE. We provide solutions for the most demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Harness the chemical and thermal stability of PTFE without the mechanical drawbacks. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific sealing challenge and receive a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















