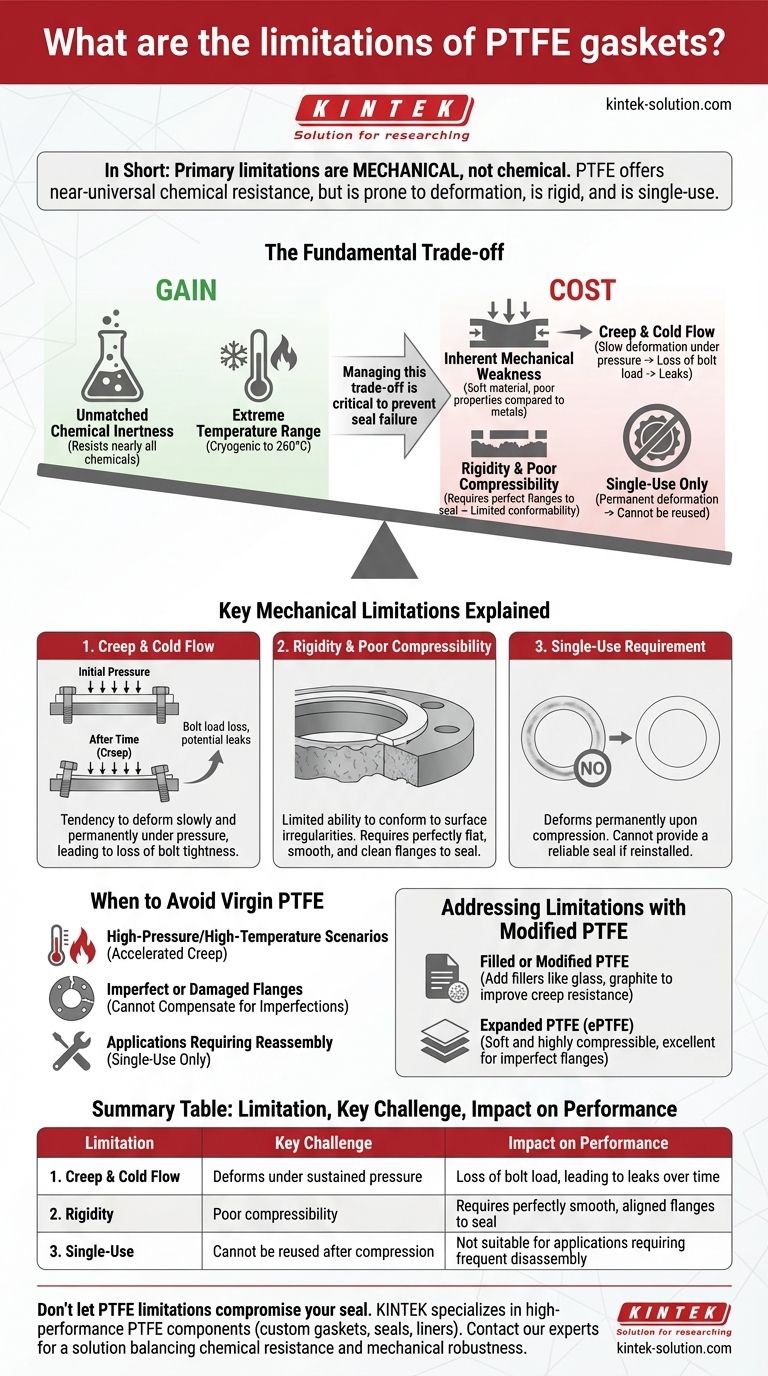
In short, the primary limitations of PTFE gaskets are mechanical, not chemical. While they offer near-universal chemical resistance, pure PTFE gaskets are prone to deformation under pressure (a phenomenon known as creep and cold flow), are relatively rigid, and require smooth, perfectly aligned flange surfaces to create a reliable seal. They are also a single-use component and cannot be reused after installation.
The core challenge with PTFE gaskets is managing a critical trade-off: you gain unparalleled chemical and temperature resistance at the cost of mechanical robustness. Understanding and planning for its inherent weaknesses, like creep and rigidity, is essential to prevent seal failure.

The Fundamental Trade-off of PTFE
To understand the limitations, we must first acknowledge why PTFE is chosen. Its strengths are exceptional, but they come with equally significant mechanical downsides.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive materials used in industry. It is resistant to nearly all chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents.
This material also performs exceptionally well across a vast temperature range, from cryogenic levels up to 260°C (500°F), making it a default choice for extreme environments.
The Inherent Mechanical Weakness
The very molecular structure that makes PTFE so chemically inert also results in a relatively soft material with poor mechanical properties compared to metals or even some elastomers. This softness is the root cause of its primary limitations.
Key Mechanical Limitations Explained
The practical failures of PTFE gaskets almost always trace back to one of three mechanical issues.
Creep and Cold Flow
Creep is the tendency of a material to deform slowly and permanently over time when subjected to long-term stress, like the pressure from bolted flanges.
Cold flow is a similar phenomenon where the material deforms under pressure, even at ambient or elevated temperatures.
For a gasket, this means it will slowly thin out after installation, causing the bolts to lose their tightness (bolt load). This loss of pressure can ultimately lead to a leak.
Rigidity and Poor Compressibility
Virgin PTFE is not a flexible, forgiving material. It has limited ability to compress and conform to surface irregularities.
If your flange surfaces have even minor scratches, pitting, or are slightly warped, a rigid PTFE gasket may not be able to fill those gaps, creating a direct leak path from the start.
Requirement for Consistent Pressure
Because it is not highly compressible, a PTFE gasket requires perfectly even and consistent pressure across its entire surface to seal effectively.
Improper bolt tightening patterns or uneven flange surfaces can create high and low-pressure spots, preventing a reliable seal and potentially leading to failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Avoid Virgin PTFE
These limitations make virgin PTFE the wrong choice for certain common industrial scenarios.
High-Pressure and High-Temperature Scenarios
The combination of high pressure and high temperature significantly accelerates creep. In these applications, a virgin PTFE gasket is likely to lose its seal integrity over time.
Imperfect or Damaged Flanges
Never use a standard PTFE gasket on flanges that are not perfectly flat, smooth, and clean. A more compressible gasket material is required to compensate for surface imperfections.
Applications Requiring Reassembly
PTFE gaskets are one-time use only. Once compressed, they deform permanently and will not provide a reliable seal if reinstalled. If your application requires frequent disassembly, choose a different gasket type.
Addressing Limitations with Modified PTFE
To overcome these weaknesses, manufacturers offer filled or modified PTFE. By adding fillers like glass, graphite, or silica, they can dramatically improve the gasket's resistance to creep and cold flow. Another solution, expanded PTFE (ePTFE), is engineered to be soft and highly compressible, making it excellent for sealing imperfect flanges.
Making the Right Gasket Choice
To select the correct material, you must weigh the chemical environment against the mechanical demands of the joint.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance in a low-pressure system with perfect flanges: Virgin PTFE is an excellent and often necessary choice, provided you control the installation carefully.
- If you are dealing with high pressures, high temperatures, or thermal cycling: A filled PTFE or a composite gasket (like a spiral wound gasket with a PTFE filler) is a much safer and more reliable option.
- If your flange surfaces are old, uneven, or have minor damage: A highly compressible material like expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is the superior choice to ensure a tight, long-lasting seal.
Ultimately, successful sealing is achieved by matching the gasket's properties to the specific demands of your application, not just its chemical compatibility.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Challenge | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Creep & Cold Flow | Deforms under sustained pressure | Loss of bolt load, leading to leaks over time |
| Rigidity | Poor compressibility | Requires perfectly smooth, aligned flanges to seal |
| Single-Use | Cannot be reused after compression | Not suitable for applications requiring frequent disassembly |
Don't let PTFE limitations compromise your seal. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom gaskets, seals, and liners. We can help you select the right material—from virgin PTFE to modified or expanded PTFE (ePTFE)—to ensure reliable performance in your semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial application. Contact our experts today for a custom solution that balances chemical resistance with mechanical robustness.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















