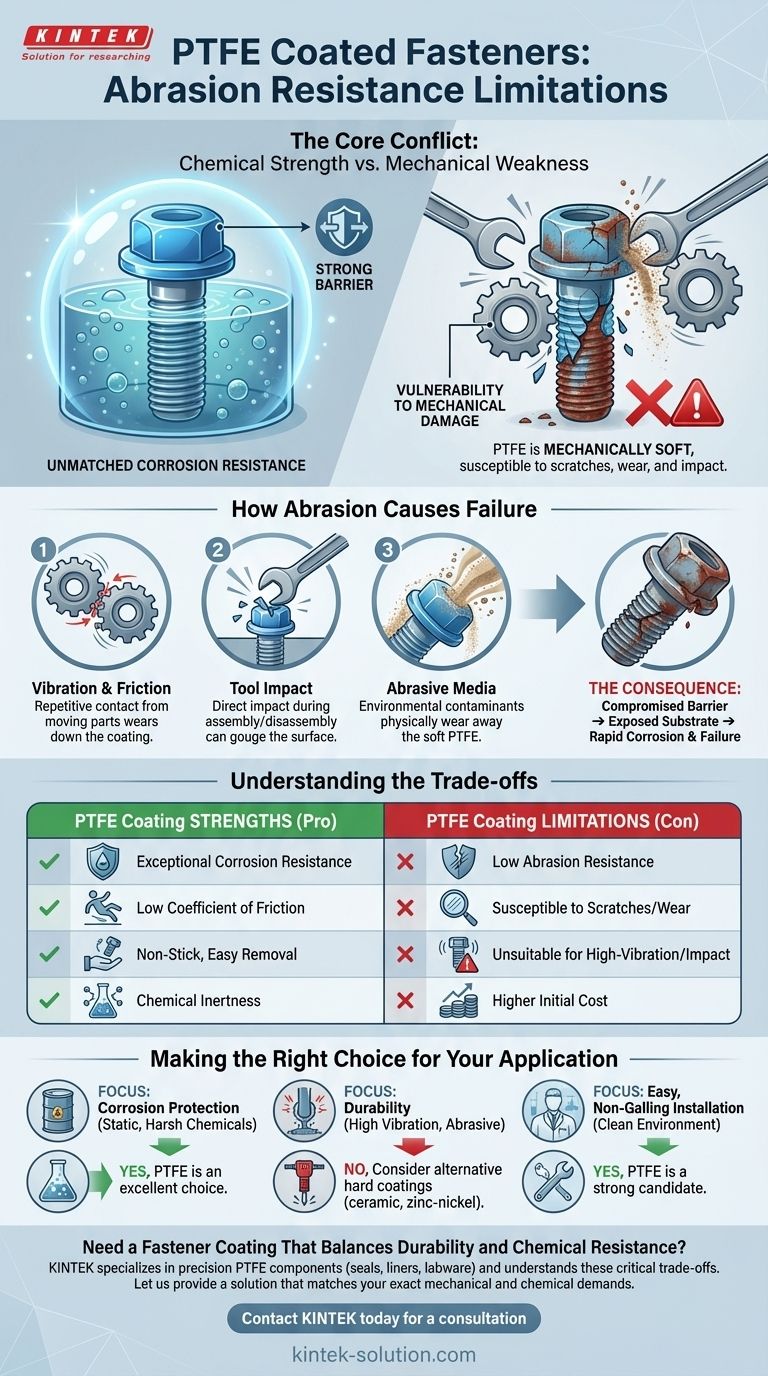
The primary limitation of PTFE-coated fasteners is their relatively low abrasion resistance. While renowned for exceptional chemical inertness and a low coefficient of friction, the PTFE coating itself is mechanically soft. This makes it susceptible to being scratched, worn, or removed by direct abrasive forces, high-contact stress, or impact.
The core takeaway is that PTFE coatings are a specialized solution, not a universal one. Their exceptional corrosion and chemical resistance come at the direct trade-off of mechanical durability, making them unsuitable for applications with significant abrasive wear.
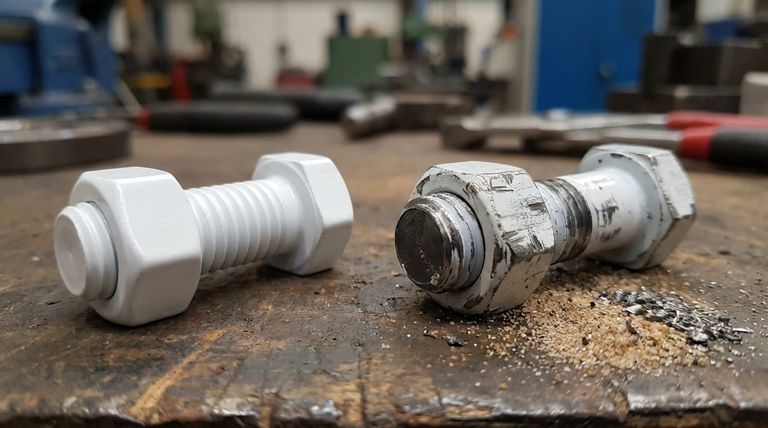

The Core Conflict: Chemical Strength vs. Mechanical Weakness
PTFE coatings solve critical problems related to corrosion and friction, but it's essential to understand that these benefits are a result of the material's unique properties, which also create its primary weakness.
Understanding PTFE's Nature
The molecular structure that gives PTFE its non-stick, low-friction characteristics also makes it a relatively soft material. Unlike hard-plating like zinc or ceramic coatings, PTFE lacks the inherent hardness to resist physical scraping or gouging effectively.
How Abrasion Causes Failure
Any direct, repetitive mechanical contact can compromise the coating. This includes friction from vibrating components, impact from tools during installation or removal, or contact with abrasive media like sand or grit in the environment.
The Consequence: A Compromised Barrier
Once the PTFE coating is scratched or worn away, the underlying metal substrate is exposed. This completely negates the primary benefit of the coating—its corrosion protection. A small breach can become the starting point for rust or chemical attack, leading to premature fastener failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a fastener coating is always a matter of balancing competing priorities. PTFE excels in specific areas but requires careful consideration of its limitations.
Pro: Unmatched Corrosion Resistance
The primary strength of PTFE is its ability to create an inert barrier. It shields the fastener from corrosive agents like moisture, chemicals, acids, and salt, ensuring a long service life in harsh environments where uncoated metal would quickly degrade.
Con: Vulnerability to Mechanical Damage
This is the direct trade-off for its chemical resilience. PTFE is not designed for high-wear applications. Environments with frequent assembly/disassembly, high vibration, or abrasive particles will quickly damage the coating.
Pro: Low Coefficient of Friction
This property provides a significant advantage by ensuring consistent and low torque values for installation. It also facilitates easy removal, preventing the galling or seizing common with other fasteners, especially stainless steel.
Con: Higher Initial Cost
Specialized coatings like PTFE are more expensive than conventional fasteners or those with simple platings like zinc. This cost must be justified by the specific environmental challenge you are trying to solve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To decide if PTFE is appropriate, you must analyze the specific demands of your environment.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection in a static, harsh chemical environment: PTFE is an excellent choice, as its primary weakness (abrasion) is not a factor.
- If your primary focus is durability in a high-vibration or mechanically abrasive setting: You should consider alternative hard coatings like ceramic, zinc-nickel, or specialized platings designed for mechanical wear.
- If you need easy, non-galling installation and removal in a clean environment: PTFE is a strong candidate, especially for applications where fasteners may need to be serviced.
Ultimately, selecting the right fastener coating requires matching its specific strengths to the precise mechanical and chemical demands of your environment.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Coating Strength | PTFE Coating Limitation |
|---|---|
| Exceptional Corrosion Resistance | Low Abrasion Resistance |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Susceptible to Scratches/Wear |
| Non-Stick, Easy Removal | Unsuitable for High-Vibration/Impact |
| Chemical Inertness | Higher Initial Cost |
Need a Fastener Coating That Balances Durability and Chemical Resistance?
PTFE coatings are ideal for harsh chemical environments, but their low abrasion resistance makes them unsuitable for high-wear applications. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) and understands these critical trade-offs. We can help you select or fabricate the perfect component for your specific needs, whether for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
Let us provide a solution that matches your exact mechanical and chemical demands. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation to discuss custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















