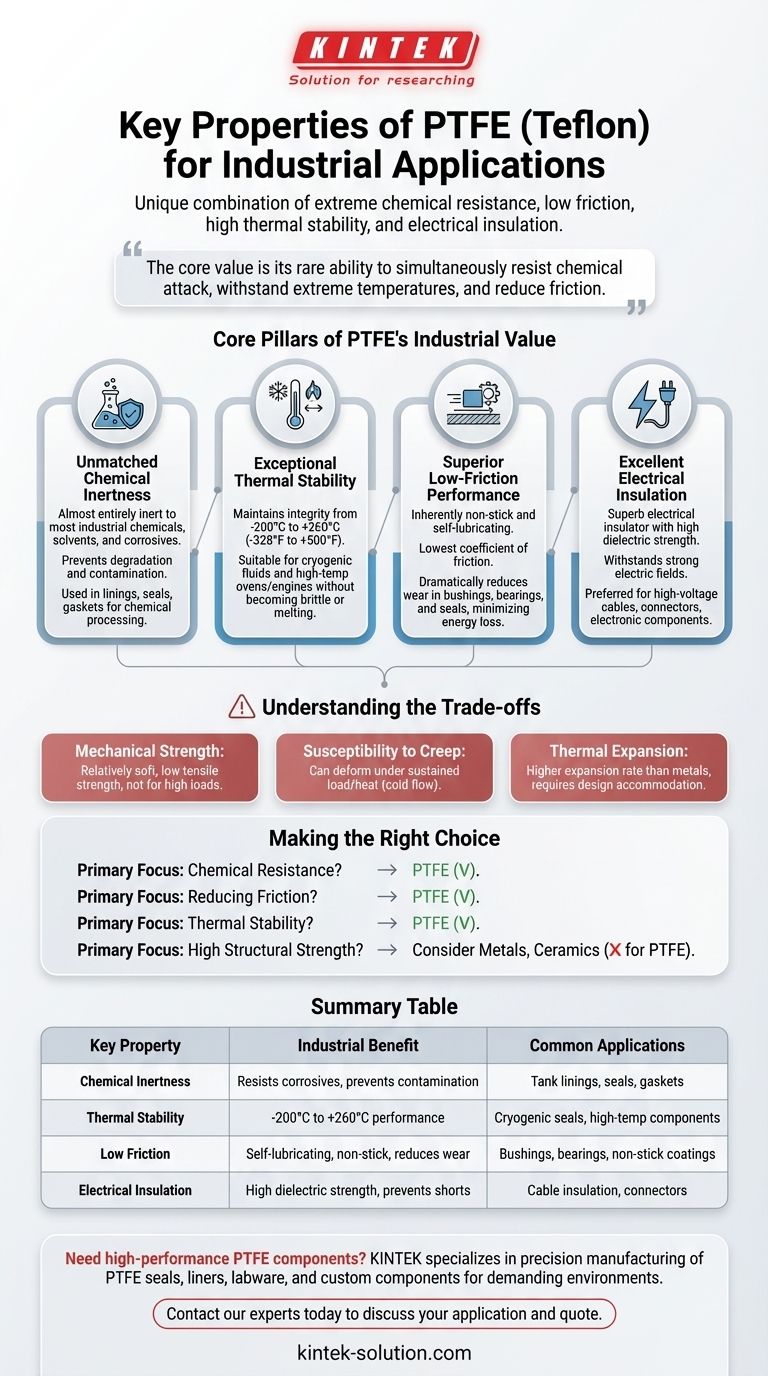
In industrial material science, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, is selected for its unique combination of properties. Its suitability stems from four primary characteristics: extreme chemical resistance, a very low coefficient of friction, high thermal stability across a wide temperature range, and excellent electrical insulation.
The core value of PTFE in an industrial setting is not any single property, but its rare ability to simultaneously resist chemical attack, withstand extreme temperatures, and reduce mechanical friction where most other materials would fail.
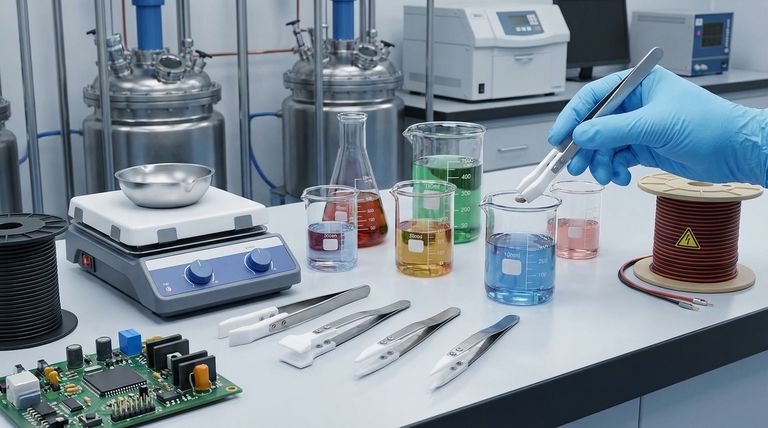

The Core Pillars of PTFE's Industrial Value
To understand why PTFE is a cornerstone material in demanding applications, we must look at how its intrinsic properties solve specific engineering challenges.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is almost entirely inert, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents.
This property makes it indispensable for components that handle aggressive substances, such as linings for pipes and tanks, seals, and gaskets in the chemical processing industry. It prevents both material degradation and contamination of the process media.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE maintains its integrity and performance across an exceptionally broad temperature range, typically cited from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
This allows it to be used in applications involving cryogenic fluids as well as high-temperature environments like industrial ovens or engine components without becoming brittle or melting.
Superior Low-Friction Performance
With one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, PTFE is inherently non-stick and self-lubricating.
This is critical for dynamic applications involving moving parts. Using PTFE for bushings, bearings, and seals dramatically reduces wear and tear, minimizes energy loss, and eliminates the need for external lubricants that could fail or cause contamination.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is a superb electrical insulator with a high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand a strong electric field without breaking down.
This characteristic makes it a preferred material for insulating high-voltage cables, connectors, and other electronic components, preventing electrical shorts and ensuring signal integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its limitations compared to other materials like metals or engineered ceramics.
Mechanical Strength and Rigidity
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It does not possess the high tensile strength or rigidity of metals. It is not suitable for applications that require significant load-bearing or structural support on its own.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a sustained compressive load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can be subject to "creep" or cold flow. This means it may slowly deform over time, which must be accounted for in the design of static seals and gaskets.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than most metals. Designs must accommodate this tendency to expand and contract with temperature changes to avoid component failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material depends entirely on the primary challenge you need to solve. Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: PTFE is a premier choice for linings, seals, and components in highly corrosive or pure environments.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: Use PTFE for self-lubricating bushings, low-friction bearings, and non-stick surface coatings.
- If your primary focus is thermal stability: Select PTFE for components that must perform reliably in both cryogenic and high-temperature applications.
- If your primary focus is high structural strength: You should consider metals, ceramics, or reinforced grades of PTFE to meet significant load requirements.
Ultimately, PTFE's power lies in its capacity to provide reliable performance under conditions that cause other materials to corrode, melt, or seize.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Industrial Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosive chemicals, prevents contamination | Chemical tank linings, seals, gaskets |
| Thermal Stability | Performs from -200°C to +260°C | Cryogenic seals, high-temperature components |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Self-lubricating, non-stick, reduces wear | Bushings, bearings, non-stick coatings |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength, prevents shorts | High-voltage cable insulation, connectors |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your specific industrial challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. Whether you require standard parts or custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—we deliver solutions that leverage PTFE's unique properties to ensure reliability in the most demanding semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial environments.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and receive a custom solution quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















