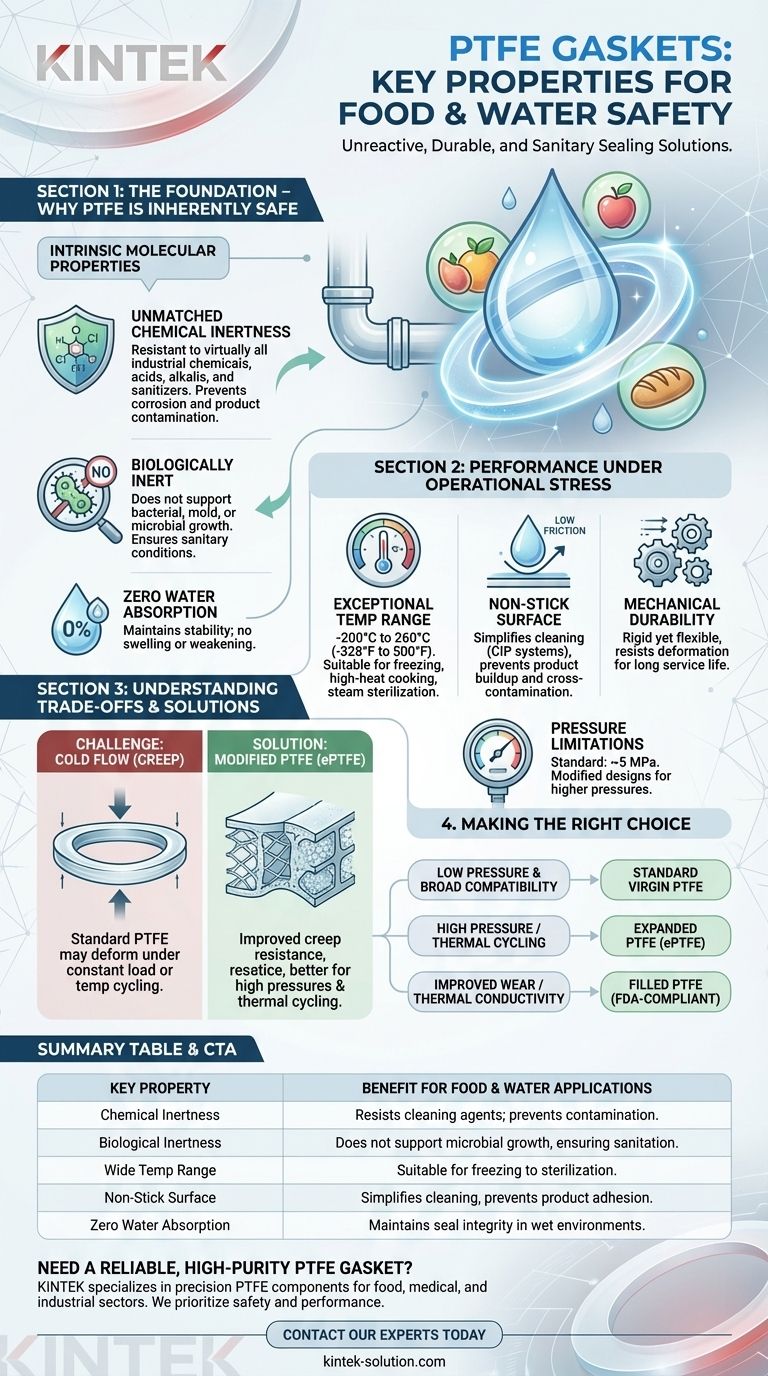
The key properties of PTFE that make it exceptionally suitable for food and water grade gaskets are its profound chemical inertness, biological inertness, wide operational temperature range, and non-stick surface. This unique combination ensures the material will not contaminate the process media, degrade from contact with food products or cleaning agents, or support microbial growth, making it a benchmark for safety and purity in sensitive applications.
The core reason PTFE is trusted for food and water contact is that it is fundamentally unreactive. It creates a stable, clean, and durable seal that neither leaches harmful substances into the product nor is compromised by it, ensuring the integrity of both the system and the media it contains.

The Foundation: Why PTFE is Inherently Safe
To understand PTFE's role in food and beverage processing, we must first look at its intrinsic molecular properties. It is a fluoropolymer, a large molecule made of a carbon backbone completely shielded by fluorine atoms, which creates an incredibly stable and non-reactive material.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry. This makes PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) resistant to virtually all industrial chemicals, including the aggressive cleaning and disinfecting agents used in food processing.
It will not corrode or degrade when exposed to acidic substances like citrus or vinegar, alkaline solutions, or sanitizing chemicals. This prevents the gasket itself from breaking down and contaminating the product.
Biologically Inert by Nature
PTFE is biologically inert, meaning it does not provide a nutrient source for bacteria, mold, or other microorganisms to grow. This is a critical feature for preventing contamination in food and water systems.
Because the material itself does not support microbial life, it helps maintain the sanitary conditions required in these industries.
Zero Water Absorption
A simple but vital property is that PTFE does not absorb water. The gasket's dimensions and physical properties remain stable and predictable, even when fully submerged or in high-humidity environments.
This stability prevents the seal from swelling or weakening over time, ensuring long-term performance and preventing leaks.
Performance Under Operational Stress
Beyond its inherent safety, a gasket material must perform reliably under the mechanical and thermal stresses of a working environment. PTFE excels here as well.
Exceptional Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its integrity and flexibility across an extremely broad temperature spectrum, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
This makes it suitable for a vast range of applications, from cryogenic freezing processes to high-heat cooking, pasteurization, and steam sterilization cycles, without becoming brittle or degrading.
The "Non-Stick" Advantage
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a signature non-stick or non-adhesive surface.
In practice, this means food products are less likely to stick to the gasket surface. This quality simplifies cleaning processes, such as Clean-in-Place (CIP) systems, and reduces the risk of product buildup that could lead to contamination.
Mechanical Durability
While flexible, PTFE is also a rigid and durable material capable of creating and holding a seal under typical process pressures. It resists deformation and provides a long service life, reducing the need for frequent replacement and system downtime.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every scenario. Being objective about PTFE's limitations is key to using it correctly.
The Challenge of Cold Flow (Creep)
Standard, or virgin, PTFE has a tendency to exhibit "creep" or "cold flow." This is a slow deformation that can occur over time when the gasket is under constant compressive load, potentially leading to a loss of sealing pressure.
This is most relevant in applications with high pressures or significant temperature cycling, where the gasket may not fully return to its original shape.
The Role of Fillers and Modification
To counteract creep, manufacturers produce modified or expanded PTFE (ePTFE). These versions incorporate FDA-compliant fillers (like silica or glass microspheres) or are processed to have a different physical structure.
These enhancements dramatically improve creep resistance, making them better suited for more demanding applications while retaining the core chemical and thermal properties of virgin PTFE.
Pressure Limitations
While durable, standard PTFE gaskets have pressure limitations, often cited around 5 MPa (725 psi). For high-pressure systems, a modified or mechanically supported gasket design may be necessary to ensure a reliable, long-term seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct type of PTFE gasket depends entirely on the specific demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical compatibility in a low-pressure system: Standard virgin PTFE is often the most effective and suitable choice.
- If your application involves high pressure, thermal cycling, or delicate flanges: Consider expanded PTFE (ePTFE), which provides a robust seal with less compressive force and has excellent resistance to creep.
- If you need to improve wear resistance or thermal conductivity: A filled PTFE gasket using an FDA-compliant filler might be the optimal solution.
By understanding these core properties and trade-offs, you can confidently specify PTFE as a safe, reliable, and high-performance sealing solution for your food and water systems.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Food & Water Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists all cleaning agents & process media; prevents contamination. |
| Biological Inertness | Does not support microbial growth, ensuring sanitary conditions. |
| Wide Temp Range (-200°C to 260°C) | Suitable for freezing, cooking, pasteurization, and sterilization. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents product adhesion; simplifies cleaning (e.g., CIP systems). |
| Zero Water Absorption | Maintains dimensional stability and seal integrity in wet environments. |
Need a reliable, high-purity PTFE gasket for your application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize safety and performance, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and ensure the integrity of your food, water, or sensitive process systems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation



















