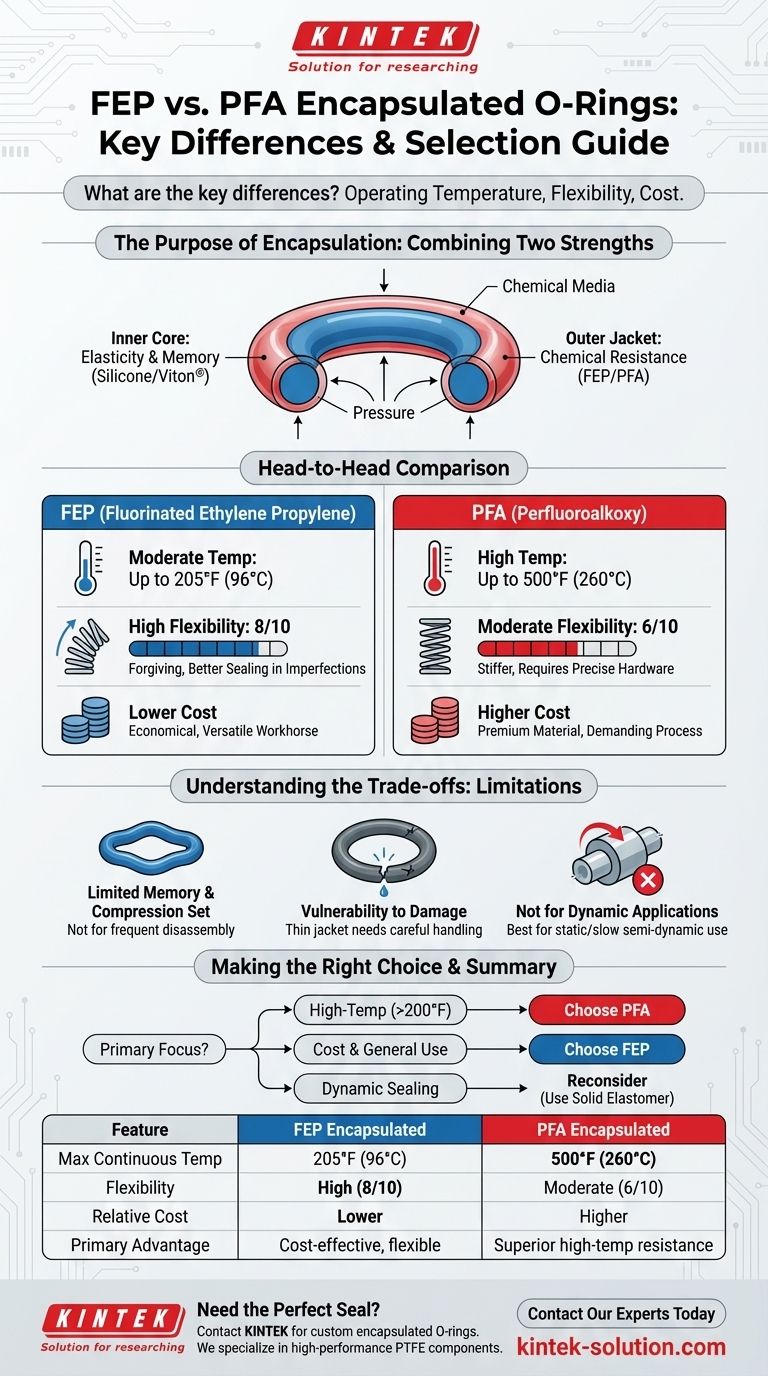
At its core, the choice between FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings comes down to three key factors: operating temperature, flexibility, and cost. PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) offers significantly higher temperature resistance but is stiffer and more expensive. FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) provides greater flexibility at a lower cost but is limited to more moderate temperature applications.
The decision is not about which material is universally better, but which specific set of trade-offs best aligns with your application's demands. PFA is the solution for high-heat environments, while FEP is the versatile, cost-effective workhorse for everything else.
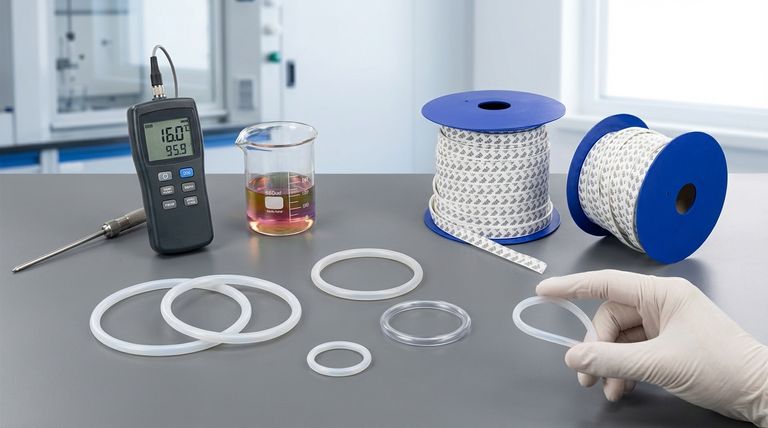

The Purpose of Encapsulation: Combining Two Strengths
Before comparing FEP and PFA directly, it's crucial to understand why encapsulated O-rings exist. They solve a fundamental engineering problem by merging the properties of two different materials.
The Inner Core: Providing Elasticity
An encapsulated O-ring has an inner core made of an elastomer, typically Silicone or Viton® (FKM). This core provides the flexibility and "memory" necessary to maintain a tight seal under pressure.
Without this elastomeric core, a solid fluoropolymer ring would be too rigid to conform to surface imperfections, leading to leaks.
The Outer Jacket: Delivering Chemical Resistance
The inner core is seamlessly enclosed in an outer jacket of FEP or PFA. This fluoropolymer shell is what contacts the aggressive media.
This jacket provides the exceptional chemical resistance needed to protect the vulnerable inner core from acids, bases, solvents, and other harsh substances that would quickly degrade a standard rubber O-ring.
Head-to-Head Comparison: FEP vs. PFA
While both materials offer near-universal chemical inertness, their performance characteristics diverge in critical areas that dictate their use.
Temperature Resistance: The Deciding Factor
This is the most significant difference between the two materials and the primary reason to specify PFA.
PFA is engineered for high-heat services, with a maximum continuous operating temperature of up to 500°F (260°C).
FEP is suited for moderate-temperature applications, with a much lower limit of approximately 205°F (96°C).
Flexibility and Sealing Pressure
The material's flexibility directly impacts its ability to create and maintain a seal, especially in non-ideal conditions.
FEP is noticeably more flexible (rated 8 out of 10). This makes it more forgiving during installation and better at sealing in glands with minor imperfections.
PFA is significantly stiffer (rated 6 out of 10). It requires more careful handling and more precise hardware finishes to ensure a leak-free connection.
Cost Implications
As a higher-performance material, PFA comes at a premium.
PFA encapsulated O-rings are generally more expensive due to the higher material cost and more demanding manufacturing process.
FEP is the more economical option, making it the default choice when the extreme temperature resistance of PFA is not required.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Encapsulated Seals
While superior to conventional O-rings in harsh environments, encapsulated seals have inherent limitations you must consider.
Limited Memory and Compression Set
Because of their stiff outer jacket, encapsulated O-rings do not rebound as effectively as solid elastomer seals.
They are more susceptible to taking a "compression set," meaning they can become permanently deformed after being compressed for a long time. This makes them less suitable for applications that require frequent disassembly and reassembly.
Vulnerability to Damage
The thin fluoropolymer jacket is the seal's primary defense.
If this jacket is scratched or nicked during installation, the aggressive media can bypass it and attack the inner elastomeric core, leading to rapid failure. Careful handling is essential.
Not for Dynamic Applications
The rigidity and low elasticity of the jacket make encapsulated O-rings best suited for static or very slow, semi-dynamic applications.
They are not recommended for rotating shafts or high-speed reciprocating parts, where a standard high-performance elastomer seal would be a more reliable choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material prevents premature failure and ensures operational reliability. Your decision should be guided by your primary operational constraint.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature service (above 200°F / 95°C): PFA is the only appropriate choice, as FEP will fail.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and general-purpose use: FEP is the standard choice for its excellent chemical resistance and flexibility within its temperature range.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic sealing application: You should reconsider if an encapsulated O-ring is appropriate and investigate high-performance solid elastomers instead.
By matching the material's properties to your specific operating environment, you ensure reliable, long-term sealing performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | FEP Encapsulated O-Rings | PFA Encapsulated O-Rings |
|---|---|---|
| Max Continuous Temperature | 205°F (96°C) | 500°F (260°C) |
| Flexibility | High (8/10) | Moderate (6/10) |
| Relative Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Primary Advantage | Cost-effective, flexible sealing | Superior high-temperature resistance |
Need the Perfect Seal for Your Demanding Application?
Selecting the right O-ring is critical for preventing leaks and ensuring system reliability in harsh environments. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom encapsulated O-rings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We can help you navigate the trade-offs between FEP and PFA to deliver a seal that meets your exact requirements for temperature, chemical resistance, and budget.
Let's engineer your solution together. Contact our experts today for a consultation on custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for seals? Unlock Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What are the benefits of PTFE seals in terms of prototyping and production? Accelerate R&D and Ensure Elite Performance
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals? Unmatched Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- What are the two temperature extremes discussed for PTFE seals? Maximize Performance from Cryogenic to High-Heat



















