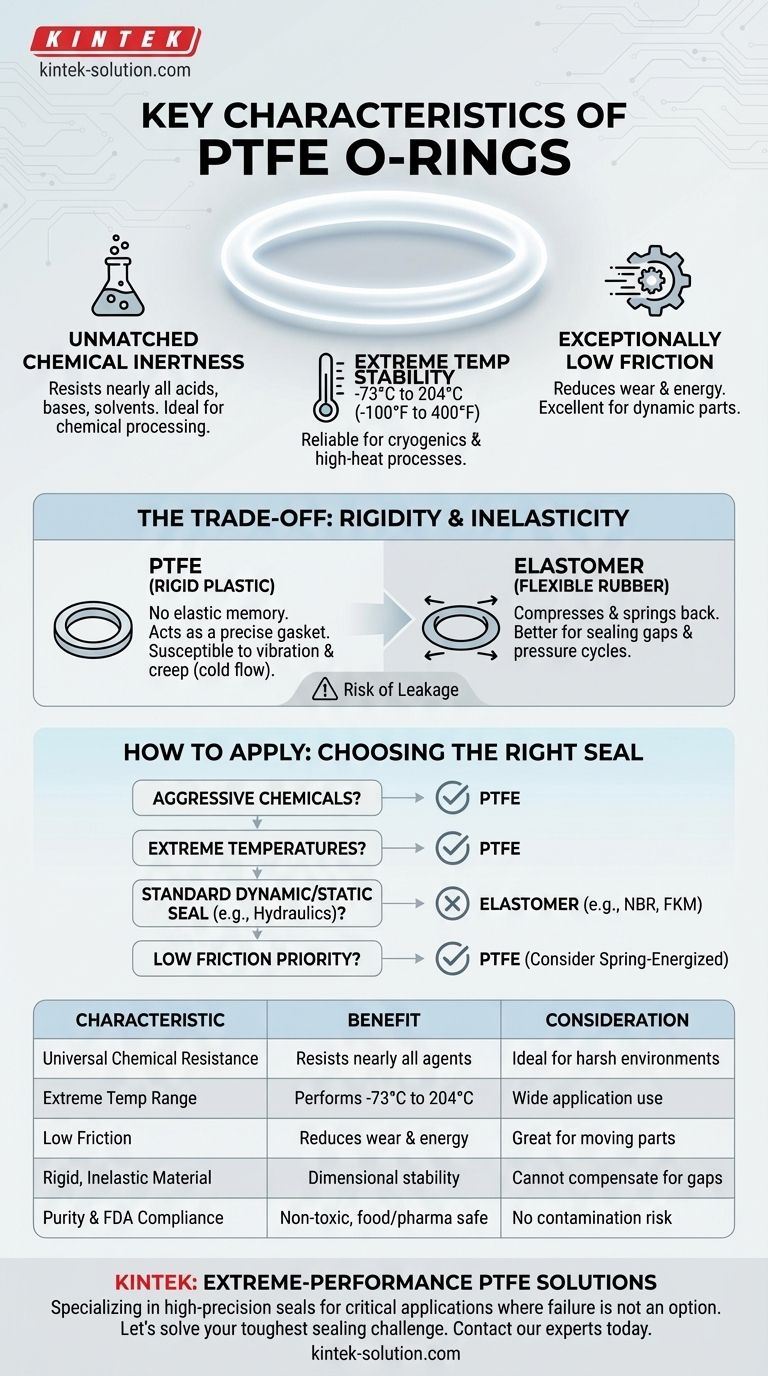
In essence, PTFE O-rings are defined by three core characteristics: their near-universal chemical resistance, an exceptionally wide operating temperature range, and an extremely low coefficient of friction. Made from the fluoropolymer polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), these white, rigid seals are engineered for extreme environments where conventional rubber O-rings would quickly fail.
The central takeaway is that PTFE O-rings are extreme-performance problem-solvers, not general-purpose seals. Their primary strength—material stability—is also the source of their primary weakness: a lack of elasticity, which fundamentally changes how they seal and where they can be used.

The Defining Strengths of PTFE
The advantages of PTFE stem directly from its stable and inert molecular structure. This makes it the material of choice when application conditions are too severe for standard elastomers.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, solvents, and fuels. This makes it invaluable for processing, chemical manufacturing, and laboratory equipment.
Unlike elastomers that swell, soften, or degrade upon chemical exposure, PTFE maintains its integrity and sealing capability.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE O-rings perform reliably across a vast temperature spectrum, typically from -73°C to 204°C (-100°F to 400°F), with some grades capable of even wider ranges.
This stability allows them to be used in cryogenic applications as well as high-temperature processes where materials like Nitrile or EPDM would become brittle or melt.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This "slippery" characteristic is ideal for dynamic applications involving sliding or rotating parts.
This property reduces wear on moving components, minimizes heat generation from friction, and lowers the energy required to operate machinery.
Purity and Compliance
Because it is an inherently pure and non-toxic material, PTFE is often compliant with FDA standards for food and beverage contact.
This, combined with its chemical inertness, makes it a preferred choice for pharmaceutical, medical, and food processing applications where contamination is not an option.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rigidity and Sealing Method
The most critical factor to understand about PTFE is that it is a rigid plastic, not a flexible rubber. This creates significant trade-offs that limit its use as a direct replacement for elastomeric O-rings.
The Challenge of Inelasticity
Standard O-rings are made from elastomers, which are compressed during installation to create a constant "squeeze" that actively seals a gap. They are flexible and spring back, like a rubber band.
PTFE, with a hardness of 60-65 Shore D, is rigid and has almost no elasticity. It does not compress to seal; it acts as a precise-fitting gasket. This means it cannot easily compensate for surface imperfections, pressure fluctuations, or thermal expansion differences.
Risk of Leakage
Because a PTFE O-ring does not have the "elastic memory" of rubber, it is more susceptible to leakage in applications with vibration, pressure cycles, or any movement that could create a microscopic gap.
The seal relies entirely on the initial tight fit and the system pressure energizing the seal, rather than inherent material compression.
Potential for Creep
Under a constant load (compression), especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE is subject to creep, or "cold flow." This is a slow, permanent deformation.
While elastomers can take a "compression set," they still retain some elasticity. PTFE, once it deforms, does not spring back, which can lead to a loss of seal over time.
Installation Difficulties
The rigidity of PTFE makes installation more challenging. Unlike a rubber O-ring that can be easily stretched over a part, a solid PTFE O-ring can be broken or permanently deformed if stretched even slightly. This often necessitates special seal designs (like scarf cuts) or glands designed for easier installation.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing a PTFE O-ring requires carefully matching its unique properties to the demands of your application. It is rarely the default choice, but often the only choice.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals: PTFE is almost certainly the right material, provided you can ensure a precise fit and stable operating pressures.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: PTFE is an excellent candidate for both cryogenic and high-heat static applications.
- If your primary focus is a standard dynamic or static seal (e.g., hydraulics): A standard elastomer like NBR, FKM (Viton™), or EPDM is a better, more reliable, and more cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in a dynamic system: PTFE is a superior option, but you may need to consider a spring-energized PTFE seal to compensate for its lack of elasticity.
Ultimately, select PTFE when its chemical and thermal resistance is a necessity, not just a preference.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Benefit | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Universal Chemical Resistance | Resists nearly all acids, bases, and solvents. | Ideal for chemical processing and labs. |
| Extreme Temperature Range | Performs from -73°C to 204°C (-100°F to 400°F). | Suitable for cryogenics and high-heat processes. |
| Extremely Low Friction | Reduces wear and energy consumption in dynamic systems. | Excellent for sliding or rotating parts. |
| Rigid, Inelastic Material | Maintains dimensional stability under load. | Cannot compensate for gaps or vibration like rubber. |
| Purity & FDA Compliance | Non-toxic and suitable for food, pharma, and medical use. | Ensures no contamination in sensitive applications. |
Need a PTFE Seal for Extreme Conditions?
PTFE O-rings are critical for applications where chemical resistance, temperature extremes, and purity are non-negotiable. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We understand that a standard O-ring won't work when failure is not an option. Our expertise ensures you get a PTFE seal that is precisely engineered for your specific environment, whether you need a prototype or high-volume production.
Let's solve your toughest sealing challenge together. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















