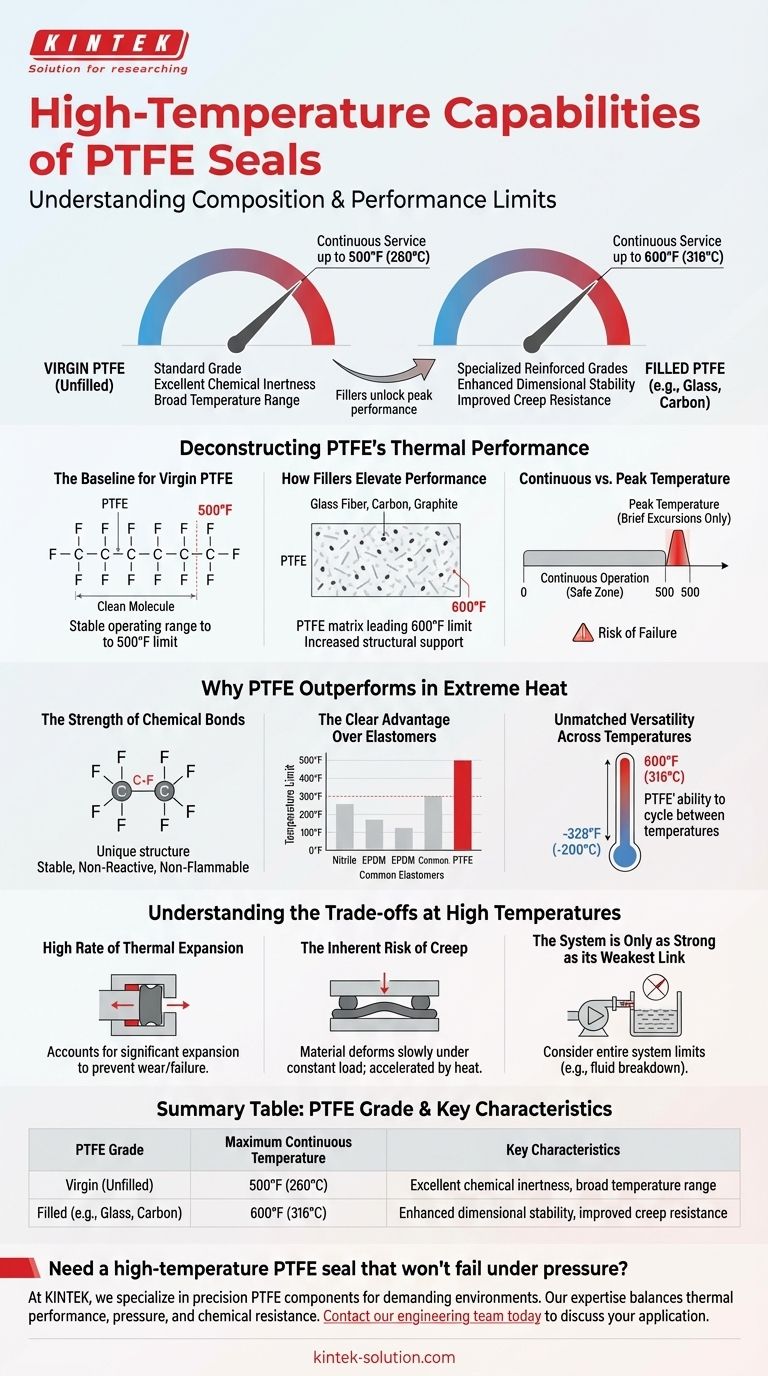
In short, the high-temperature capability of a PTFE seal depends on its composition. Standard, unfilled (virgin) PTFE is reliably rated for continuous service up to 500°F (260°C). However, specialized grades that are reinforced with fillers like glass fiber or carbon can push this continuous operating limit to as high as 600°F (316°C).
While PTFE offers exceptional thermal stability far beyond most plastics and elastomers, the true performance limit is not just a single number. It is a function of the specific PTFE grade, the duration of exposure, and the mechanical stress on the seal.

Deconstructing PTFE's Thermal Performance
Understanding the difference between PTFE grades is critical for any high-temperature application. The base polymer provides the foundation, but additives are what unlock its peak performance.
The Baseline for Virgin PTFE
Pure, unfilled PTFE is defined by its remarkable chemical inertness and a wide operating temperature range. Its upper limit for continuous use is universally recognized as 500°F (260°C).
At this temperature, it retains its core mechanical properties and does not degrade, making it a default choice for applications that exceed the capabilities of common elastomers.
How Fillers Elevate Performance
To push beyond the 500°F baseline, manufacturers add fillers to the PTFE matrix. Common fillers include glass fiber, carbon, and graphite.
These reinforcing agents do not melt at these temperatures. They provide a supportive structure within the polymer, which improves dimensional stability, increases resistance to creep (deformation under load), and allows the seal to function effectively up to 600°F (316°C).
Continuous vs. Peak Temperature
The temperature ratings provided are for continuous operation. This is the temperature a seal can withstand for its entire service life without significant loss of sealing ability or mechanical integrity.
While a seal might survive brief excursions above its rated limit, sustained operation at excessive temperatures will inevitably lead to premature failure.
Why PTFE Outperforms in Extreme Heat
PTFE’s thermal stability is not an accident; it is a direct result of its unique molecular structure. This gives it a significant advantage over nearly all other sealing materials.
The Strength of Chemical Bonds
PTFE is composed of a long chain of carbon atoms, each completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and stable.
This structure makes the material highly non-reactive and resistant to the thermal degradation that breaks down other polymers. It is also why PTFE is non-flammable.
The Clear Advantage Over Elastomers
Most common elastomers, like Nitrile or EPDM, begin to degrade, harden, and crack at temperatures well below 300°F (150°C).
Even high-performance elastomers struggle to approach the thermal limits of standard PTFE, making PTFE the superior choice for high-heat environments like steam, petroleum processing, or aerospace applications.
Unmatched Versatility Across Temperatures
PTFE's capabilities extend to both ends of the temperature spectrum. It remains functional at cryogenic temperatures as low as -328°F (-200°C).
This makes it one of the few materials suitable for applications that experience extreme temperature fluctuations, as it can cycle between deep cold and high heat without losing its properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs at High Temperatures
Using PTFE near its thermal limit requires careful engineering. Its unique properties can become liabilities if not properly managed in the design phase.
The High Rate of Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a significantly higher coefficient of thermal expansion than metals. As the temperature rises, a PTFE seal will expand considerably.
Seal gland and hardware design must account for this expansion to prevent the seal from becoming over-compressed, which can cause excessive friction, wear, and eventual failure.
The Inherent Risk of Creep
Even with fillers, all PTFE is susceptible to creep, also known as cold flow. This is the tendency of the material to slowly deform over time when under a constant load.
High temperatures accelerate this process. In a high-pressure, high-temperature application, an improperly designed seal can slowly extrude from its groove, compromising its ability to seal effectively.
The System is Only as Strong as its Weakest Link
A PTFE seal may be rated for 500°F, but the other components in the system may not be. For example, many hydraulic fluids begin to oxidize and break down at temperatures below 200°F.
The seal's temperature capability must always be considered within the context of the entire system's thermal limitations.
Selecting the Right PTFE Seal for Your Application
Choosing the correct material is a matter of matching the seal's capabilities to the specific demands of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is operating consistently up to 500°F (260°C): A standard, unfilled (virgin) PTFE grade will provide excellent thermal performance and broad chemical resistance.
- If you need to push the limit towards 600°F (316°C): You must specify a filled PTFE compound, such as one with glass fiber or carbon, to provide the required thermal stability.
- If your application involves high pressure combined with high temperature: A filled grade is essential, and you must work with your seal provider to ensure the hardware design properly manages thermal expansion and prevents extrusion.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between the material grade and your specific operating conditions is the key to leveraging PTFE's remarkable thermal capabilities.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Grade | Maximum Continuous Temperature | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin (Unfilled) | 500°F (260°C) | Excellent chemical inertness, broad temperature range |
| Filled (e.g., Glass, Carbon) | 600°F (316°C) | Enhanced dimensional stability, improved creep resistance |
Need a high-temperature PTFE seal that won't fail under pressure?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between thermal performance, pressure, and chemical resistance.
Whether you need a standard solution or a custom-fabricated seal for a prototype or high-volume order, our expertise ensures a reliable component designed for your specific operating conditions.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your application and get a solution that performs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main chemical resistance properties of PTFE-coated O-rings? Uncover the True Role of the Coating
- What are the primary characteristics of PTFE seals? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Conditions
- How do FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings contribute to equipment longevity? Prevent Costly Downtime with Superior Seals
- What are the advantages of PTFE-based seals? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals? Unmatched Chemical & Temperature Resistance



















