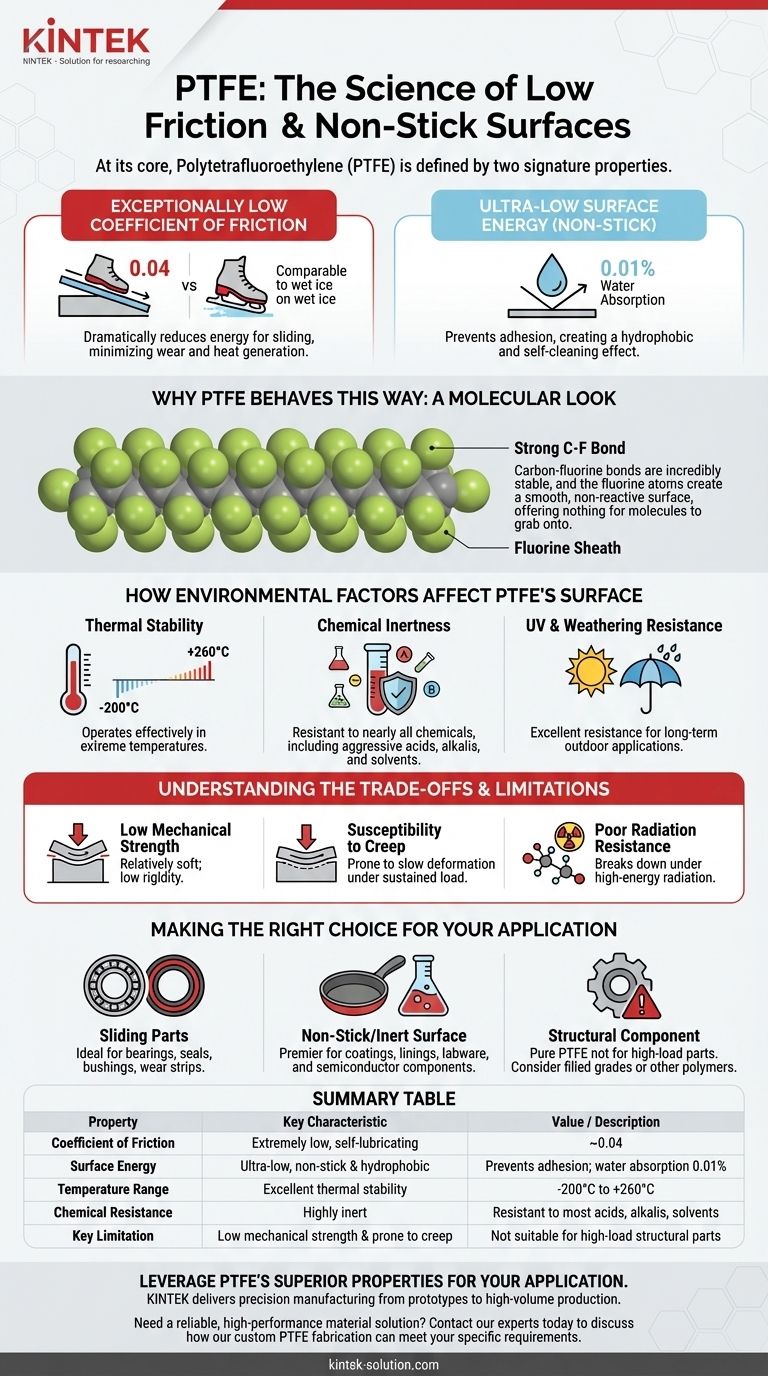
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is defined by two signature properties: an exceptionally low coefficient of friction and an ultra-low surface energy. This unique combination makes it one of the most slippery and non-stick solid materials known, stemming directly from its stable and non-reactive molecular structure.
The defining characteristic of PTFE is its dual nature: it offers elite performance in low-friction, high-temperature, and chemically aggressive environments, but this comes at the direct cost of low mechanical strength and rigidity. Understanding this trade-off is the key to using it effectively.

The Core Properties: Friction and Surface Energy
PTFE's reputation is built on its unparalleled surface characteristics. These two properties work in tandem to create its unique performance profile.
Exceptionally Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, with a value of approximately 0.04. This is often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
This property means that it dramatically reduces the energy required for one surface to slide over another, minimizing wear and heat generation.
Ultra-Low Surface Energy (The "Non-Stick" Effect)
The famous non-stick quality of PTFE comes from its very low surface energy. This prevents almost any substance from adhering to its surface.
This not only creates a non-stick effect but also makes the material highly hydrophobic (water-repelling) and effectively self-cleaning. It absorbs a negligible amount of water, just 0.01% over 24 hours.
Why PTFE Behaves This Way: A Look at the Molecular Level
The source of these properties lies in PTFE's unique chemical makeup and the arrangement of its atoms.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms, each completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable.
This powerful bond is the source of PTFE's remarkable chemical inertness and thermal stability.
The Fluorine Sheath
You can visualize the fluorine atoms as creating a tight, protective "sheath" around the carbon backbone. This sheath is what other materials interact with.
Because the fluorine atoms are so tightly packed and non-reactive, they create a smooth, low-energy surface that other molecules have virtually nothing to "grab onto," resulting in both low friction and non-stick behavior.
How Environmental Factors Affect PTFE's Surface
A key advantage of PTFE is the consistency of its surface properties across a wide range of demanding conditions.
Unrivaled Thermal Stability
PTFE maintains its integrity and properties over an extremely broad temperature range, operating effectively from -200°C to +260°C (with a melting point of 327°C).
Extreme Chemical Inertness
The material is resistant to nearly all chemicals, including aggressive acids, alkalis, and solvents. This ensures its surface is not degraded or altered in corrosive environments.
Resistance to UV and Weathering
PTFE shows excellent resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and general weathering, making it suitable for long-term outdoor applications without degradation of its surface properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While its surface properties are extraordinary, PTFE is not the right choice for every application. Its limitations are just as important to understand as its strengths.
Low Mechanical Strength
The primary trade-off for PTFE's excellent friction and chemical properties is its low mechanical strength and rigidity. It is a relatively soft material.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a sustained load, PTFE is prone to "creep," or slow deformation over time. This makes it unsuitable for high-load structural components.
Poor Radiation Resistance
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation, which can break down its molecular structure and cause it to become brittle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Leveraging PTFE successfully requires aligning its unique strengths with your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is low-friction sliding parts: PTFE is an ideal choice for bearings, seals, bushings, and wear strips, especially in chemically harsh or high-temperature environments where lubrication is difficult.
- If your primary focus is a non-stick or inert surface: It is a premier material for coatings on cookware, linings for chemical vessels, and components for medical or semiconductor manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is a structural or high-load component: Pure PTFE should be avoided; consider instead filled grades of PTFE or other high-performance polymers with greater mechanical strength.
By understanding both its unparalleled surface properties and its inherent mechanical limitations, you can effectively deploy PTFE in the world's most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Value / Description |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Friction | Extremely low, self-lubricating | ~0.04 (similar to wet ice on wet ice) |
| Surface Energy | Ultra-low, non-stick & hydrophobic | Prevents adhesion; water absorption of 0.01% |
| Temperature Range | Excellent thermal stability | -200°C to +260°C |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly inert | Resistant to most acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Key Limitation | Low mechanical strength & prone to creep | Not suitable for high-load structural parts |
Leverage PTFE's Superior Properties for Your Application
PTFE's unique combination of low friction, non-stick performance, and chemical resistance makes it ideal for critical components in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, or specialized components, KINTEK delivers precision manufacturing from prototypes to high-volume production.
Need a reliable, high-performance material solution? Contact our experts today to discuss how our custom PTFE fabrication can meet your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















