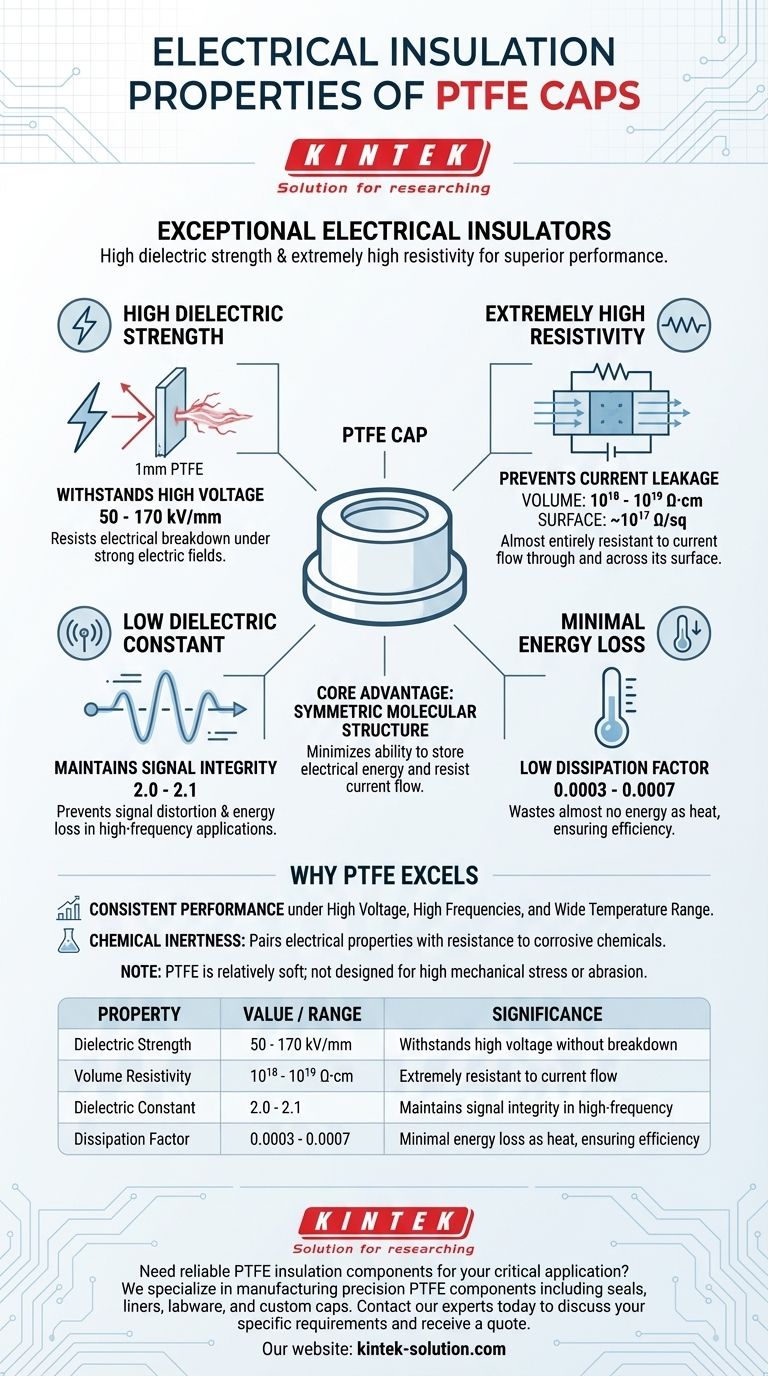
In short, PTFE caps are exceptional electrical insulators. They possess a powerful combination of high dielectric strength, meaning they resist electrical breakdown under high voltage, and extremely high volume resistivity, which prevents electrical current from flowing through them. This performance is notably stable across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies.
The core reason PTFE is a superior insulator lies in its symmetric molecular structure. This structure minimizes its ability to store electrical energy and resist current flow, making it a highly reliable choice for demanding applications, especially those involving high frequencies or harsh chemicals.

Deconstructing PTFE's Electrical Performance
To understand why PTFE is so effective, we must look at its specific, measurable properties. Each of these contributes to its overall performance as an insulator.
High Dielectric Strength (Breakdown Resistance)
Dielectric strength measures a material's ability to withstand a strong electric field without failing and allowing electricity to pass through. A higher number indicates a better insulator.
PTFE has a dielectric strength between 50 and 170 kV/mm. This is an extremely high value, meaning a 1mm thick PTFE cap can theoretically withstand up to 170,000 volts before it breaks down, providing a robust safety margin in high-voltage applications.
Extremely High Resistivity (Preventing Current Leakage)
Resistivity measures how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. For an insulator, we look at two types.
Volume resistivity, at 10¹⁸ to 10¹⁹ Ω·cm, indicates that PTFE is almost entirely resistant to current flowing through its bulk. Surface resistivity, around 10¹⁷ Ω/sq, shows it is equally resistant to current flowing across its surface. These astronomical numbers confirm its status as a top-tier insulator.
Low Dielectric Constant (Signal Integrity)
The dielectric constant indicates a material's ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. For insulation in high-frequency applications, a lower number is better because it prevents signal distortion and energy loss.
PTFE has a very low and stable dielectric constant of 2.0-2.1 across a vast frequency range (from 50 Hz to 10⁹ Hz). This makes it an ideal choice for insulating high-frequency cables and electronic components where signal purity is critical.
Minimal Energy Loss (Low Dissipation Factor)
The dissipation factor quantifies how much electrical energy is lost as heat within an insulating material when subjected to an alternating electric field.
PTFE's dissipation factor is incredibly low (0.0003 - 0.0007). This means it wastes almost no energy as heat, ensuring the efficiency and stability of the electrical system it is part of.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
No material is perfect for every situation. Understanding where PTFE excels and its potential limitations is key to using it effectively.
Where PTFE Excels
The unique combination of electrical properties makes PTFE an ideal choice in specific environments. Its performance remains consistent under high voltages, high frequencies, and a wide range of temperatures.
Crucially, these electrical properties are paired with PTFE's legendary chemical inertness. In a laboratory or industrial setting, a cap must often provide electrical insulation while being exposed to corrosive chemicals that would degrade lesser materials.
A Note on Physical Properties
While its electrical and chemical properties are world-class, it is important to remember that PTFE is a relatively soft material. It does not possess high mechanical strength or abrasion resistance compared to ceramics or certain engineering plastics. Its value is in insulation and chemical resistance, not structural integrity under high physical stress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires matching its properties to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage safety: PTFE's exceptional dielectric strength makes it a reliable barrier against electrical arcing and breakdown.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electronics: Its low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor ensure signal integrity and minimal energy loss.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh environments: The combination of elite electrical insulation and near-total chemical inertness makes PTFE a uniquely capable solution.
Ultimately, PTFE's properties make it one of the most trusted and effective insulators available for critical applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Range | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 50 - 170 kV/mm | Withstands high voltage without breakdown |
| Volume Resistivity | 10¹⁸ - 10¹⁹ Ω·cm | Extremely resistant to current flow through the material |
| Dielectric Constant | 2.0 - 2.1 | Maintains signal integrity in high-frequency applications |
| Dissipation Factor | 0.0003 - 0.0007 | Minimal energy loss as heat, ensuring efficiency |
Need reliable PTFE insulation components for your critical application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, labware, and custom caps. Our expertise ensures your parts deliver the exceptional dielectric strength, chemical inertness, and stable performance your semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial application demands—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















