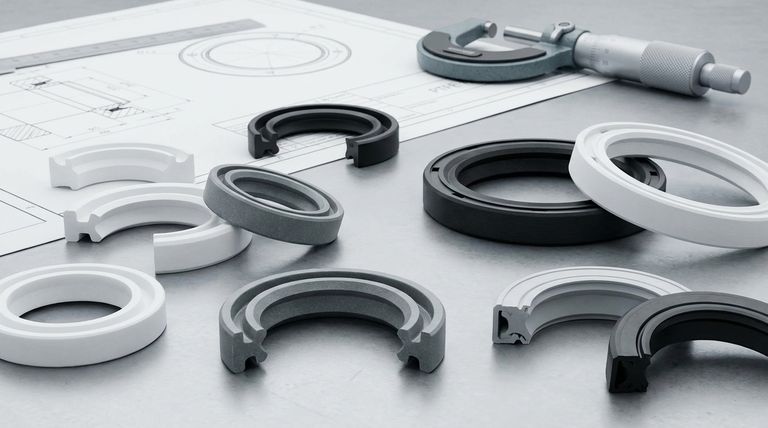
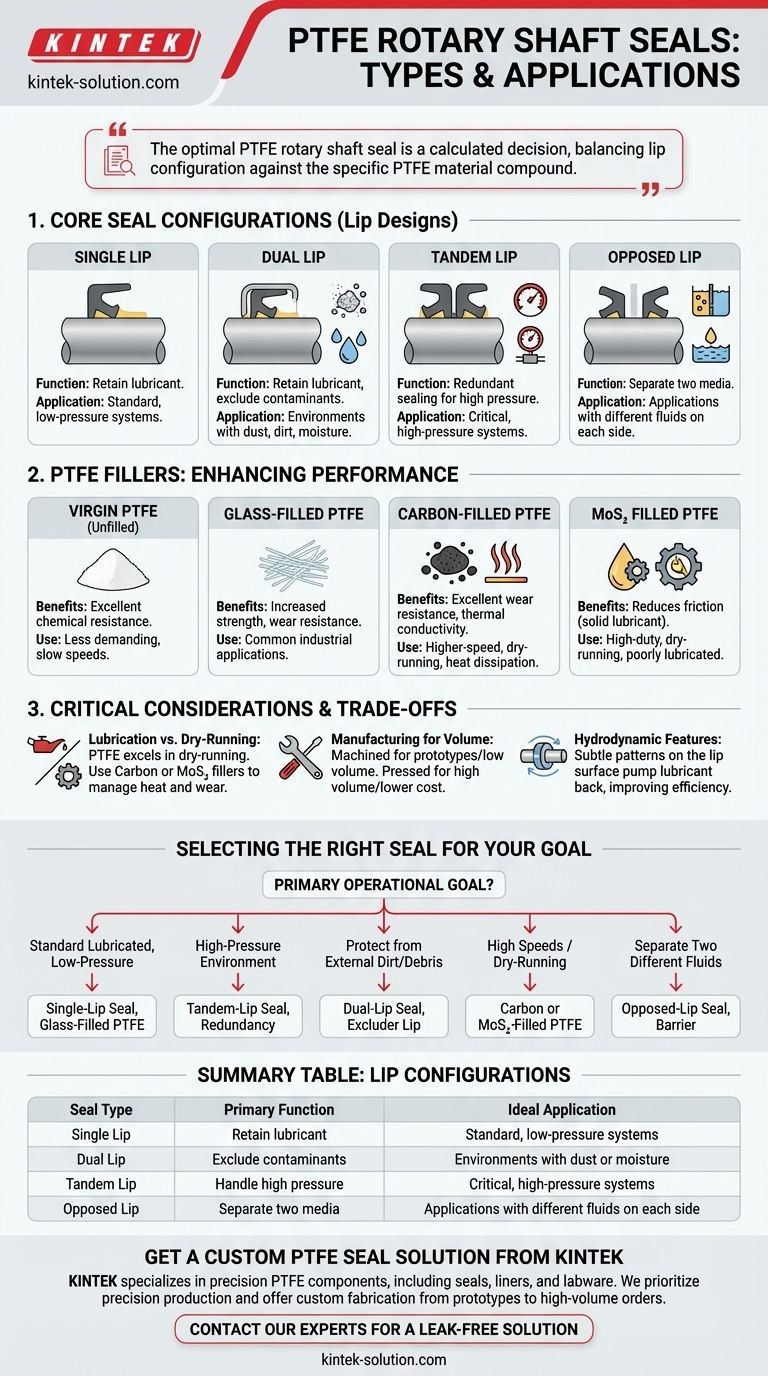
At their core, PTFE rotary shaft seals are categorized by their lip design. The most common types are Single Lip, Dual Lip, Tandem Lip, and Opposed Lip seals, each engineered to manage specific challenges related to pressure, lubrication, and contaminant exclusion. The design you choose is dictated entirely by the operational environment of your machinery.
The optimal PTFE rotary shaft seal is never chosen based on a single feature. It is a calculated decision that balances the seal's physical lip configuration against the specific PTFE material compound required to withstand your application's unique pressure, temperature, speed, and chemical environment.

Understanding the Core Seal Configurations
The physical shape of the seal's lip is the first and most fundamental design choice. It directly determines how the seal interacts with the rotating shaft and manages system fluids and pressures.
Single Lip Seals
A single-lip seal is the most basic configuration. It is designed with one primary sealing lip that makes contact with the shaft.
This design is highly effective and economical for standard applications where the primary goal is to retain lubricant within a system under low-pressure conditions.
Dual Lip Seals
Dual-lip seals add a secondary, non-spring-loaded lip, often called an excluder or dust lip. This second lip faces outward.
Its purpose is to prevent external contaminants like dust, dirt, and moisture from reaching the primary sealing lip, thereby extending the seal's life in moderately harsh environments.
Tandem Lip Seals
This configuration features two primary sealing lips oriented in the same direction. It is essentially a redundant sealing system in a single package.
Tandem lip seals are specified for high-pressure applications or where safety and reliability are critical. The first lip takes the majority of the pressure, with the second lip providing backup sealing.
Opposed Lip Seals
In an opposed-lip design, two sealing lips face in opposite directions. This allows the seal to perform two distinct functions simultaneously.
This configuration is ideal for separating two different types of media (e.g., oil on one side, water on the other) or for providing robust protection against severe external contamination.
Beyond Configuration: The Critical Role of PTFE Fillers
The "PTFE" in the seal's name is just the base polymer. The true performance comes from the fillers blended into it. The choice of filler is as critical as the lip design.
Virgin PTFE
Unfilled, virgin PTFE is used for less demanding applications with slow speeds. While it has excellent chemical resistance, it has lower wear resistance compared to filled grades.
Glass-Filled PTFE
Adding glass fibers significantly increases the seal's strength and wear resistance. It is a common, all-around choice for many industrial applications.
Carbon-Filled PTFE
Carbon provides excellent wear resistance and good thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat from the sealing point. This makes it ideal for higher-speed or dry-running applications where friction-generated heat can be an issue.
MoS₂ (Molybdenum Disulfide) Filled PTFE
MoS₂ acts as a solid lubricant, reducing the seal's running friction. It is often combined with other fillers, like glass or carbon, to improve performance in high-duty, dry-running, or poorly lubricated conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Selecting a seal involves more than just matching a name to an application. You must consider the interplay of several factors to avoid premature failure and ensure reliable operation.
Lubrication vs. Dry-Running
While many PTFE seals are used in lubricated environments, their low-friction properties make them one of the few seal types that can perform well in dry-running applications. For this, a carbon or MoS₂-filled compound is almost always necessary to manage heat and wear.
Manufacturing for Volume
The seal's metal casing can be produced in two ways. For prototypes or low-volume production, shells are often machined, avoiding high tooling costs. For high-volume production, pressed shells are used to significantly lower the unit cost.
Hydrodynamic Features
For enhanced performance, some PTFE lips are designed with hydrodynamic features. These are subtle patterns on the lip surface that actively pump lubricant back into the system as the shaft rotates, improving sealing efficiency and reducing wear.
Selecting the Right Seal for Your Application
Your choice must be driven by your primary operational goal. Analyze your system's demands and prioritize accordingly.
- If your primary focus is standard lubricated, low-pressure sealing: A single-lip seal with a glass-filled PTFE compound is a reliable and cost-effective starting point.
- If your primary focus is operating in a high-pressure environment: A tandem-lip configuration is specifically designed to handle the increased load and provide sealing redundancy.
- If your primary focus is protecting against external dirt and debris: A dual-lip seal provides the necessary excluder lip to shield the primary sealing surface.
- If your primary focus is high speeds or potential dry-running conditions: A carbon-filled or MoS₂-filled PTFE compound is essential to manage friction and dissipate heat effectively.
- If your primary focus is separating two different fluids: An opposed-lip seal is the correct configuration to create an effective barrier between media.
Ultimately, a systematic approach to selecting both the seal configuration and the material compound is the key to achieving long-term, leak-free performance.
Summary Table:
| Seal Type | Primary Function | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| Single Lip | Retain lubricant | Standard, low-pressure systems |
| Dual Lip | Exclude contaminants | Environments with dust or moisture |
| Tandem Lip | Handle high pressure | Critical, high-pressure systems |
| Opposed Lip | Separate two media | Applications with different fluids on each side |
Get a Custom PTFE Seal Solution from KINTEK
Choosing the right PTFE rotary shaft seal is critical for your equipment's performance and longevity. The optimal seal balances lip design and material compound to withstand your specific pressure, temperature, speed, and chemical environment.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get a seal engineered for your exact application.
Let us help you achieve leak-free, reliable operation. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and get a solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















