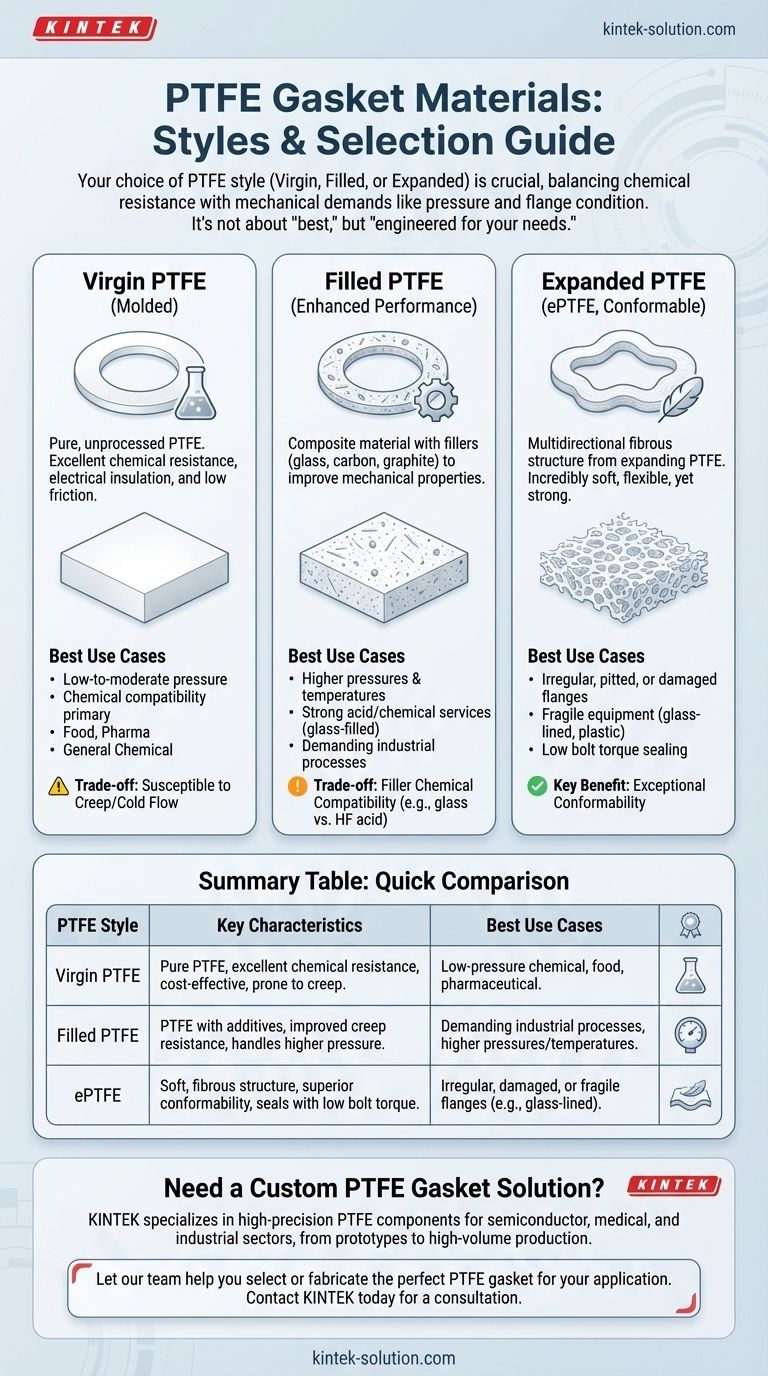
The primary styles of PTFE gasket materials are Virgin (or Molded) PTFE, Filled PTFE, and Expanded PTFE (ePTFE). While all are built on Polytetrafluoroethylene's unmatched chemical resistance, their physical structures are engineered for entirely different mechanical demands. The choice between them depends entirely on your application's pressure, temperature, and flange conditions.
The core decision is not about which PTFE is "best," but which material structure is engineered for your specific operational needs. While all styles share exceptional chemical inertness, their mechanical properties—especially resistance to pressure and ability to conform to surfaces—vary significantly.

The Foundation: Virgin PTFE
What It Is
Virgin PTFE is pure, unprocessed Polytetrafluoroethylene. It is typically formed into sheets through molding or skiving (shaving a thin layer from a larger block). This is the most basic and cost-effective form of PTFE gasket material.
Key Properties
This material possesses all the inherent qualities of PTFE: near-universal chemical resistance, excellent electrical insulation properties, and a very low coefficient of friction. It is a reliable choice for a wide range of general-purpose applications.
Best Use Cases
Virgin PTFE is best suited for low-to-moderate pressure and temperature services where chemical compatibility is the primary concern. It is frequently used in food processing, pharmaceutical, and general chemical applications.
Enhanced Performance: Filled PTFE
What It Is
Filled PTFE is a composite material created by adding a filler substance to virgin PTFE. Common fillers include glass fibers, carbon, or graphite, which enhance the base material's mechanical properties.
The Role of Fillers
Fillers are added to counteract PTFE's natural tendency to deform under load (a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow). This results in a gasket with greater dimensional stability, improved wear resistance, and a higher tolerance for pressure.
Best Use Cases
This material is the standard for more demanding industrial processes involving higher pressures or temperatures. Glass-filled PTFE is a common choice for strong acid and general chemical services, but not for hydrofluoric acid or strong caustics.
Maximum Conformability: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
What It Is
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is produced by expanding virgin PTFE, which creates a multidirectional fibrous structure. This process results in a material that is incredibly soft and flexible yet retains immense tensile strength.
Key Properties
The defining characteristic of ePTFE is its exceptional conformability. It can create a tight seal on irregular, pitted, or damaged flange surfaces with very low bolt torque. This makes it ideal for protecting fragile equipment.
Best Use Cases
ePTFE is the premier choice for stress-sensitive joints, such as those on glass-lined, plastic, or ceramic flanges. It is also perfect for large or non-standard flange shapes where a traditional cut gasket is impractical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Creep and Cold Flow
The most significant limitation of Virgin PTFE is its susceptibility to cold flow, where the material deforms permanently under pressure. Filled PTFE was specifically engineered to mitigate this problem, offering a more stable seal in high-pressure applications.
Chemical Compatibility of Fillers
While the PTFE itself is nearly inert, the filler material may not be. For example, glass fillers can be attacked by hydrofluoric acid or strong alkalis. It is critical to ensure both the PTFE and its filler are compatible with your process media.
Pressure and Temperature Limits
No single gasket material is suitable for both high temperature and high pressure simultaneously. The relationship between pressure and temperature (often expressed as a "Pr value") must be considered. Always consult the manufacturer's specifications for the material's operational limits.
How to Select the Right PTFE Material
Choosing the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general chemical use: Virgin PTFE is your baseline standard, offering excellent chemical resistance for low-demand applications.
- If your primary focus is handling higher pressures or reducing creep: A Filled PTFE provides the necessary mechanical strength and dimensional stability for a reliable seal.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular, damaged, or fragile flanges: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) offers unmatched conformability and seals effectively with minimal bolt load.
Matching the material's mechanical properties to your specific flange conditions is the key to a reliable, long-lasting seal.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Style | Key Characteristics | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin (Molded) PTFE | Pure PTFE, excellent chemical resistance, cost-effective, prone to creep. | Low-pressure chemical, food, pharmaceutical applications. |
| Filled PTFE | PTFE with additives (glass, carbon), improved creep resistance, handles higher pressure. | Demanding industrial processes with higher pressures/temperatures. |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Soft, fibrous structure, superior conformability, seals with low bolt torque. | Irregular, damaged, or fragile flanges (e.g., glass-lined, plastic). |
Need a Custom PTFE Gasket Solution?
Choosing the right PTFE material is critical for performance and safety. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom gaskets, seals, liners, and labware.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, providing solutions from prototypes to high-volume production. Our expertise ensures you get a gasket engineered for your specific pressure, temperature, and chemical requirements.
Let our team help you select or fabricate the perfect PTFE gasket for your application.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















