To put it directly, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) possesses an elite combination of dielectric and thermal insulation properties, making it a benchmark material for extreme engineering applications. It is an exceptional electrical insulator that maintains its performance across a vast range of temperatures and frequencies. Thermally, it operates reliably from cryogenic conditions of -200°C up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C.
The core reason PTFE is so valued is its profound stability. Its electrical and thermal insulation capabilities do not degrade under conditions—high frequency, extreme temperatures, chemical exposure—where most other materials would fail.

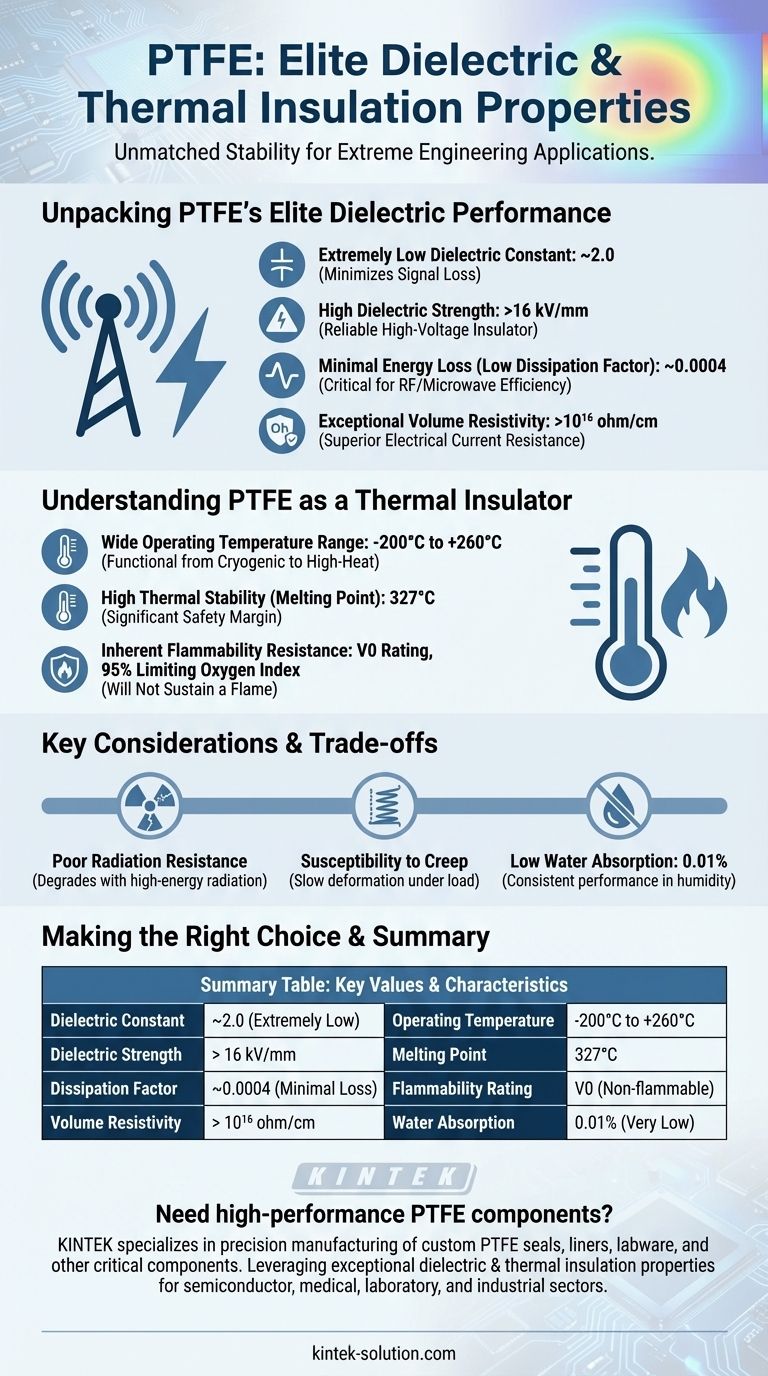
Unpacking PTFE's Elite Dielectric Performance
PTFE's molecular structure results in electrical insulation properties that are nearly ideal for demanding applications, especially in high-frequency electronics.
Extremely Low Dielectric Constant
PTFE has a very low dielectric constant of approximately 2.0. This means it stores very little electrical energy when subjected to an electric field, minimizing signal loss and distortion in high-frequency circuits.
High Dielectric Strength
The material exhibits a high dielectric strength, exceeding 16 kV/mm. This is a measure of its ability to withstand a strong electric field without breaking down, making it a reliable insulator for high-voltage applications.
Minimal Energy Loss (Low Dissipation Factor)
With a dissipation factor around 0.0004, PTFE loses an exceptionally small amount of energy as heat when an alternating electric field is applied. This is critical for efficiency and thermal management in radio frequency (RF) and microwave components like cables and circuit boards.
Exceptional Volume Resistivity
PTFE's volume resistivity is greater than 10¹⁶ ohm/cm, confirming its status as a superior electrical insulator that strongly resists the flow of electrical current.
Understanding PTFE as a Thermal Insulator
Beyond its electrical performance, PTFE provides robust insulation across a massive temperature spectrum, ensuring mechanical and electrical integrity in harsh thermal environments.
Wide Operating Temperature Range
The defining thermal characteristic of PTFE is its vast operating temperature range of -200°C to 260°C. It remains functional and stable from cryogenic lows to high-heat industrial processes.
High Thermal Stability
PTFE has a very high melting point of 327°C. While its continuous use is rated for 260°C, this high melting point provides a significant safety margin against temperature excursions.
Inherent Flammability Resistance
The material is highly non-flammable, with a flammability rating of V0 and a limiting oxygen index of 95%. This means it will not sustain a flame in normal atmospheric conditions, adding a critical layer of safety to its applications.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, no material is perfect. Understanding PTFE's limitations is crucial for proper application.
Poor Radiation Resistance
PTFE is known to degrade when exposed to high-energy radiation. The molecular chains can be broken, leading to a loss of mechanical properties.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under mechanical load, PTFE is prone to "creep," or slow deformation over time. This must be accounted for in structural designs where tight tolerances are required.
Low Water Absorption
With a water absorption rate of just 0.01% over 24 hours, PTFE is highly resistant to moisture. This stability ensures its dielectric properties remain consistent even in humid environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE's unique profile matches your project's primary requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electronics (RF/microwave): PTFE is an industry-standard choice due to its ultra-low dielectric constant and dissipation factor.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation in extreme temperatures: Its combination of high dielectric strength and a massive operating temperature range makes it uniquely suitable.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance combined with insulation: PTFE's near-total chemical inertness ensures it will not degrade in corrosive environments where electrical performance is also required.
Ultimately, PTFE is the material of choice when you require consistent, high-level insulation performance in environments too demanding for conventional polymers.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Value / Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant | ~2.0 (Extremely Low) |
| Dielectric Strength | > 16 kV/mm |
| Dissipation Factor | ~0.0004 (Minimal Loss) |
| Volume Resistivity | > 10¹⁶ ohm/cm |
| Operating Temperature | -200°C to +260°C |
| Melting Point | 327°C |
| Flammability Rating | V0 (Non-flammable) |
| Water Absorption | 0.01% (Very Low) |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your most demanding applications?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, and other critical components. We leverage PTFE's exceptional dielectric and thermal insulation properties to create solutions for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components meet the highest standards of performance and reliability in extreme environments.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















