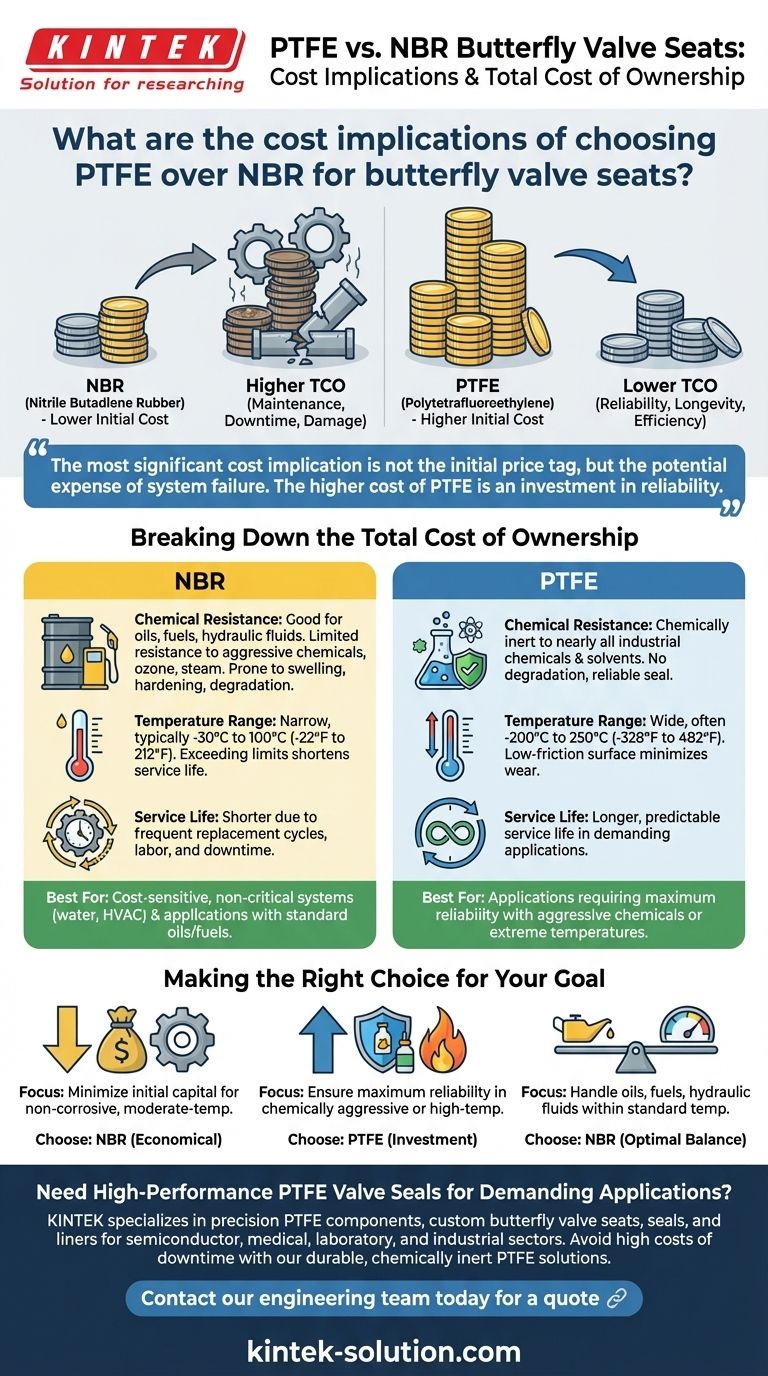
On a per-unit basis, PTFE has a higher initial purchase cost than NBR for butterfly valve seats. This price difference stems directly from PTFE's more complex manufacturing process and its superior performance characteristics. However, focusing solely on the upfront price is a critical mistake; the true cost is revealed over the operational lifetime of the valve.
The most significant cost implication is not the initial price tag, but the potential expense of system failure. The higher cost of PTFE is an investment in reliability, which often prevents far greater costs associated with maintenance, downtime, and damage in demanding applications.
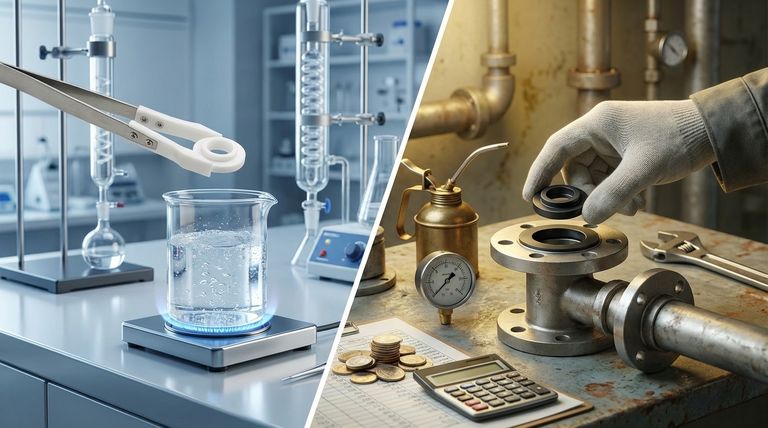

Breaking Down the Total Cost of Ownership
The decision between PTFE and NBR is a classic engineering trade-off between initial cost and long-term value. Understanding where each material excels is key to making a sound financial choice.
The Role of Chemical Resistance
NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) provides good, reliable performance in applications involving oils, fuels, and common hydraulic fluids. It is a cost-effective choice for these specific media.
However, NBR has limited resistance to more aggressive chemicals, ozone, and steam. Exposure to these substances can cause the material to swell, harden, or degrade quickly, leading to premature valve failure.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is chemically inert to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This exceptional resistance means it will not degrade when exposed to corrosive media, ensuring a reliable seal and protecting the integrity of the entire system.
The Impact of Service Life and Temperature
A valve seat's longevity is a primary driver of its true cost. Frequent replacement cycles introduce significant labor and downtime expenses.
NBR has a narrower operational temperature range, typically from -30°C to 100°C (-22°F to 212°F). Exceeding these limits drastically shortens its service life.
PTFE boasts a much wider temperature tolerance, often from -200°C to 250°C (-328°F to 482°F). Its low-friction surface also minimizes wear during valve operation, directly contributing to a longer, more predictable service life in any application.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When NBR is the Right Choice
While PTFE offers superior performance in harsh conditions, it is not always the most cost-effective solution. Over-specifying a component is as financially inefficient as under-specifying it.
Cost-Sensitive and Non-Critical Systems
For general-purpose applications like water lines, HVAC systems, or air services, the demanding properties of PTFE are unnecessary. In these cases, NBR provides perfectly adequate performance at a significantly lower initial cost.
Applications with Standard Oils and Fuels
NBR was specifically developed for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based products. In systems handling gasoline, diesel, or lubricating oils within its temperature limits, NBR is the industry-standard material for good reason.
The Cost of Failure
The most critical factor is the consequence of a valve seat failing. A leak in a water line is an inconvenience. A leak in a highly corrosive chemical line can be a catastrophic event, posing safety risks and causing extensive system damage that costs orders of magnitude more than the valve itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the most cost-effective material, you must align the choice with the specific demands of the application.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital expense for a non-corrosive, moderate-temperature application: NBR is the more economical and appropriate choice.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum reliability in a chemically aggressive or high-temperature system: The higher upfront cost of PTFE is a necessary investment to prevent costly downtime and failure.
- If your primary focus is handling oils, fuels, or hydraulic fluids within a standard temperature range: NBR provides the optimal balance of performance and cost-effectiveness.
Ultimately, the most cost-effective decision is based on a thorough understanding of your application's specific operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Factor | NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Chemical Resistance | Good for oils, fuels, hydraulic fluids | Excellent; inert to nearly all industrial chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -30°C to 100°C (-22°F to 212°F) | -200°C to 250°C (-328°F to 482°F) |
| Long-Term Reliability | Good for standard applications | Superior in harsh, demanding conditions |
| Best For | Cost-sensitive, non-critical systems with standard media | Applications requiring maximum reliability with aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures |
Need High-Performance PTFE Valve Seals for Demanding Applications?
Choosing the right material is critical to your system's reliability and total cost of ownership. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom butterfly valve seats, seals, and liners for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We help you avoid the high costs of downtime and system failure by providing durable, chemically inert PTFE solutions that extend service life and protect your operations.
Let's discuss your specific requirements: Contact our engineering team today for a quote to explore custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















