In medical devices, PTFE fasteners are most commonly applied in surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, medical implants, and complex fluid handling systems. Their use is critical in applications where components are exposed to bodily fluids, harsh sterilization processes, and aggressive chemicals, ensuring both patient safety and device reliability.
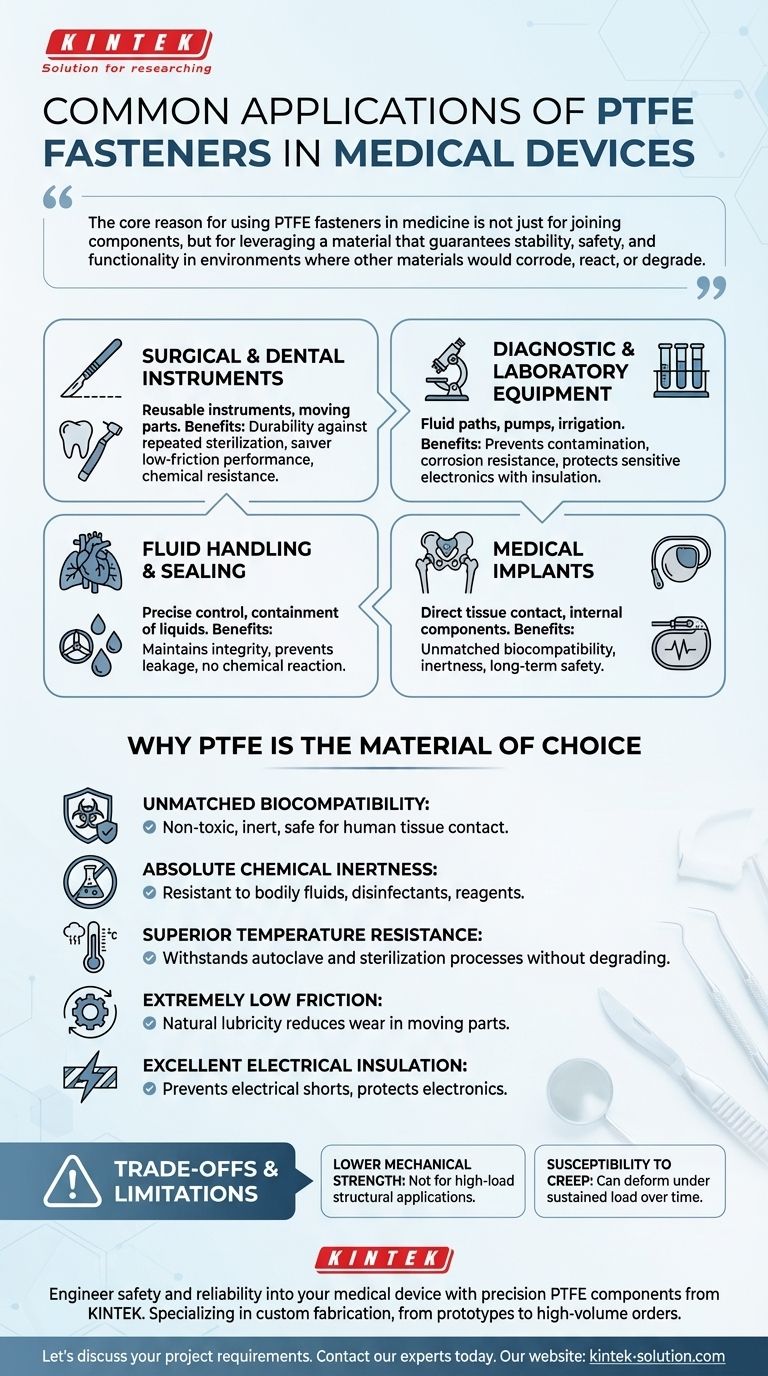
The core reason for using PTFE fasteners in medicine is not just for joining components, but for leveraging a material that guarantees stability, safety, and functionality in environments where other materials would corrode, react, or degrade.
Why PTFE is the Material of Choice for Medical Fastening
The selection of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a deliberate engineering choice driven by a unique set of properties that make it exceptionally well-suited for the demanding conditions of medical and pharmaceutical applications.
Unmatched Biocompatibility
PTFE is renowned for being biologically inert. This means it is non-toxic and does not cause an adverse reaction when it comes into contact with human tissue or bodily fluids. This property is non-negotiable for any component used in medical implants.
Absolute Chemical Inertness
Fasteners made from PTFE are highly resistant to corrosion and will not react with the vast majority of chemicals. This makes them ideal for diagnostic equipment that handles diverse biological samples and cleaning agents, as well as for instruments that are repeatedly exposed to disinfectants.
Superior Temperature Resistance
A critical requirement for many medical devices is the ability to withstand sterilization. PTFE can handle the extreme temperatures of an autoclave or steam sterilization process without degrading, losing its shape, or compromising its integrity.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a natural lubricity. This is highly advantageous in devices with moving parts, such as rotary tools for cutting or valves within fluid systems, as it reduces wear and ensures smooth operation.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
As a superb electrical insulator, PTFE is used to fasten components in sophisticated diagnostic and surgical equipment. This property is vital for preventing electrical shorts and ensuring the safety of both the patient and the operator.
Key Application Areas in Detail
The unique properties of PTFE allow its fasteners to be deployed in several critical areas within the medical field, each leveraging a different combination of its strengths.
Surgical and Dental Instruments
In reusable instruments, especially those with moving parts like rotary tools, PTFE fasteners provide durability against repeated sterilization cycles and low-friction performance. Their chemical resistance ensures they are not damaged by cleaning solutions.
Diagnostic and Laboratory Equipment
These complex machines handle a wide array of fluids and reagents. PTFE fasteners are used to secure components within the fluid path, such as in pumps and irrigation systems, because they will not contaminate samples or corrode. Their insulating properties also protect sensitive electronics.
Fluid Handling and Sealing
Devices like heart-lung machines or fluid pumps rely on precise control and containment of liquids. PTFE fasteners, seals, and valves are used to maintain the integrity of these fluid streams, ensuring there is no leakage or chemical reaction with the material itself.
Medical Implants
For any fastener used inside the human body, biocompatibility is the most important factor. Solid PTFE fasteners are chosen for their inertness, ensuring they will not be rejected by the body or degrade over time, providing long-term safety and reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PTFE offers significant advantages, it is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to proper application.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals like stainless steel or titanium, PTFE is a much softer material with lower tensile strength. It is not suitable for high-load, structural applications where mechanical failure would be catastrophic.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a constant, sustained load, PTFE can slowly deform over time in a process known as "creep." This must be accounted for in designs where a fastener must maintain a precise clamping force or torque for the life of the device.
Solid PTFE vs. PTFE Coatings
It is important to distinguish between fasteners made entirely of solid PTFE and metal fasteners with a PTFE coating. While a coating enhances corrosion resistance, only a solid PTFE fastener provides complete biocompatibility and electrical insulation throughout the entire part.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your decision should be guided by the primary performance requirement of the device component.
- If your primary focus is direct tissue contact or implantation: Prioritize solid, medical-grade PTFE for its unmatched biocompatibility and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is reusable surgical instruments: Select PTFE for its ability to withstand repeated, high-temperature sterilization cycles without degrading.
- If your primary focus is fluid path integrity in diagnostic machines: Use PTFE for its non-reactivity to prevent contamination and its reliable sealing properties.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load: Evaluate alternatives like titanium or 316 stainless steel, as PTFE's lower strength is a significant design constraint.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is a strategic decision to engineer safety, reliability, and material stability into the most demanding medical environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Medical Devices |
|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Non-toxic, safe for tissue contact and implants. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists bodily fluids, disinfectants, and reagents. |
| Temperature Resistance | Withstands autoclave and steam sterilization. |
| Low Friction | Reduces wear in instruments with moving parts. |
| Electrical Insulation | Protects sensitive diagnostic and surgical electronics. |
Engineer safety and reliability into your medical device with precision PTFE components from KINTEK.
Whether you are developing surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, medical implants, or complex fluid handling systems for the semiconductor, medical, or laboratory industries, KINTEK delivers. We specialize in the custom fabrication of high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and fasteners—from prototypes to high-volume orders. Our commitment to precision production ensures your components meet the stringent demands of biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and sterilization.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















