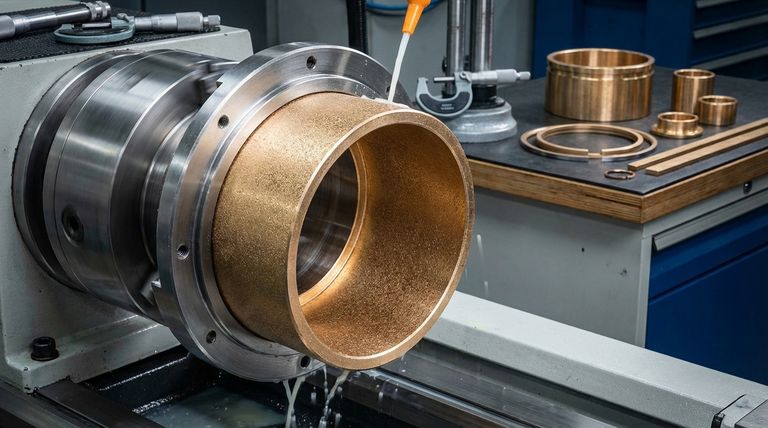
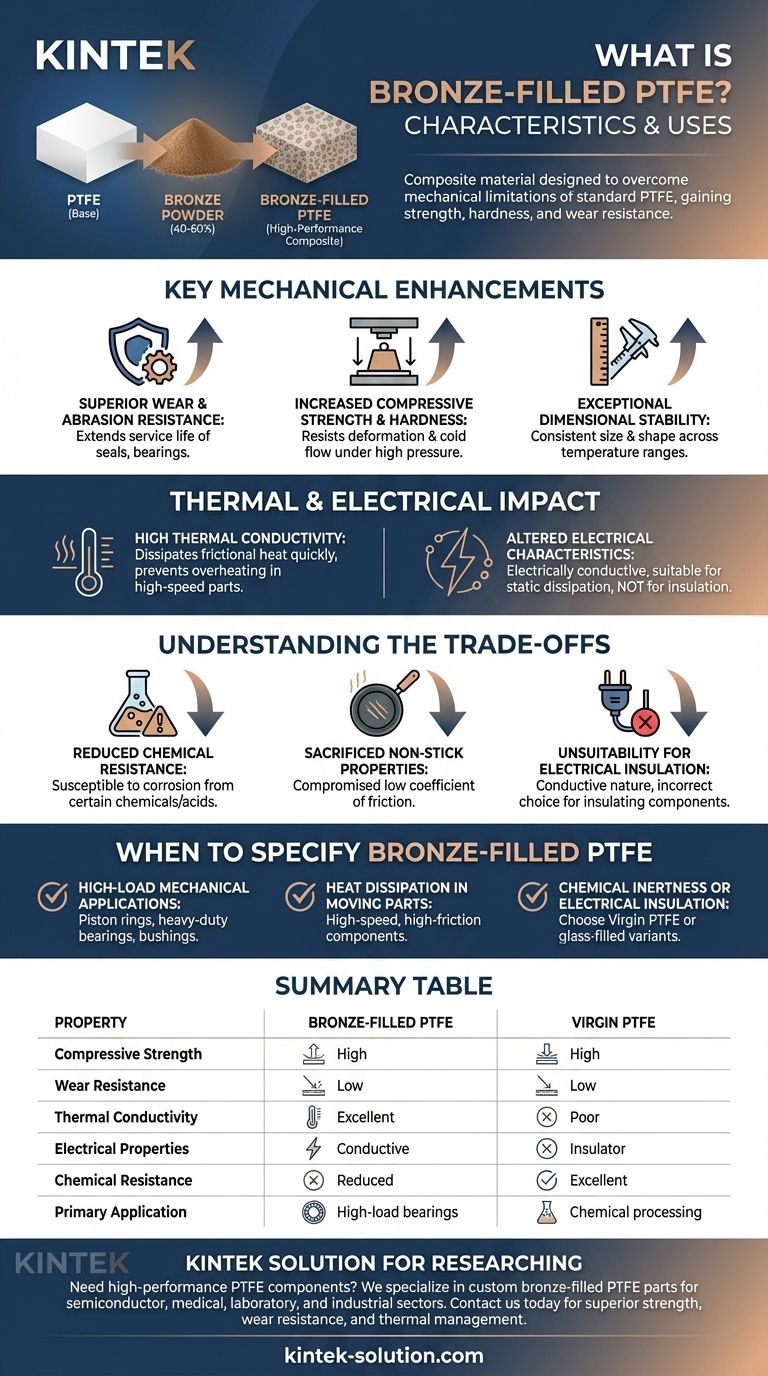
In essence, bronze-filled PTFE is a high-performance composite material designed to overcome the mechanical limitations of standard PTFE. By blending bronze powder (typically 40-60%) into a PTFE base, it gains significant improvements in compressive strength, hardness, and wear resistance, making it suitable for demanding mechanical applications where virgin PTFE would fail.
The core decision to use bronze-filled PTFE is a trade-off: you gain exceptional mechanical strength and thermal conductivity but sacrifice the superior chemical resistance and electrical insulation that define pure, unfilled PTFE.

Key Mechanical Enhancements
The primary reason to specify bronze-filled PTFE is for its vastly improved mechanical properties under load. It transforms PTFE from a soft, compliant material into a robust engineering plastic.
Superior Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Bronze is a hard metal alloy. Adding it to the softer PTFE matrix creates a composite with dramatically higher resistance to wear and abrasion, extending the service life of components like seals and bearings.
Increased Compressive Strength and Hardness
This is perhaps its most critical feature. Bronze-filled PTFE has a much lower tendency to deform or "creep" under a constant load, a common failure point for virgin PTFE known as cold flow. This makes it ideal for high-pressure applications.
Exceptional Dimensional Stability
The material exhibits a lower coefficient of thermal expansion compared to unfilled PTFE. This means its size and shape remain more consistent across a range of temperatures, a crucial trait for components with tight tolerances.
The Impact on Thermal and Electrical Properties
Beyond pure strength, the addition of bronze fundamentally alters how the material manages energy, both thermal and electrical.
High Thermal Conductivity
Bronze is an excellent conductor of heat. This property allows bronze-filled PTFE to dissipate frictional heat quickly, preventing thermal buildup in high-speed applications like bearings and bushings, thereby improving performance and lifespan.
Altered Electrical Characteristics
Unlike virgin PTFE, which is an excellent electrical insulator, bronze-filled PTFE is electrically conductive. This makes it suitable for applications requiring static dissipation but entirely unsuitable for parts that need to provide electrical insulation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting this material requires a clear understanding of what is being sacrificed in exchange for its mechanical prowess.
Reduced Chemical Resistance
Bronze is susceptible to corrosion from certain chemicals and acids. Consequently, bronze-filled PTFE should not be used in highly corrosive environments where the chemical inertness of virgin PTFE is required.
Sacrificed Non-Stick Properties
The inclusion of a metal filler compromises the famously low coefficient of friction and non-stick surface of pure PTFE. While still a low-friction material, it does not match the performance of its unfilled counterpart in this regard.
Unsuitability for Electrical Insulation
This cannot be overstated. If your application requires a material to insulate electrical components, bronze-filled PTFE is the wrong choice due to its conductive nature.
When to Specify Bronze-Filled PTFE
Use these guidelines to determine if bronze-filled PTFE is the correct material for your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is high-load mechanical applications: Its superior compressive strength and wear resistance make it ideal for piston rings, heavy-duty bearings, and bushings.
- If your primary focus is heat dissipation in moving parts: Its high thermal conductivity is critical for preventing overheating in high-speed or high-friction components.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness or electrical insulation: You must choose virgin PTFE or a PTFE variant with a non-metallic filler, such as glass.
By understanding these specific trade-offs, you can confidently select bronze-filled PTFE for applications where robust mechanical performance is the paramount requirement.
Summary Table:
| Property | Bronze-Filled PTFE | Virgin PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | High | Low |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (dissipates heat) | Low (thermal insulator) |
| Electrical Properties | Conductive | Excellent Insulator |
| Chemical Resistance | Reduced (susceptible to corrosion) | Excellent |
| Primary Application | High-load bearings, seals, bushings | Chemical processing, electrical insulation |
Need a high-performance PTFE component for a demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom bronze-filled PTFE parts for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures you get a component that delivers superior strength, wear resistance, and thermal management.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our team provide a solution that enhances your product's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications



















