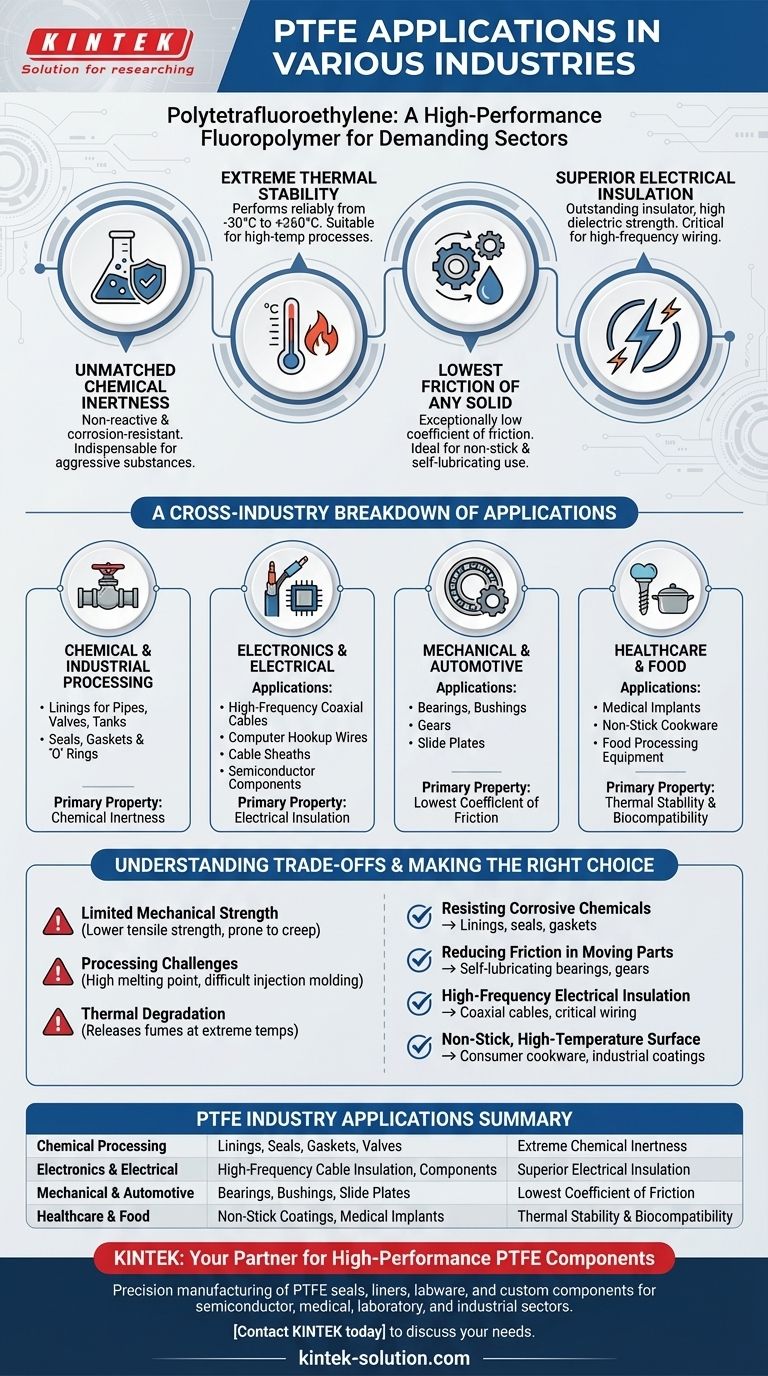
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer whose applications span numerous demanding sectors, including chemical processing, electronics, healthcare, and manufacturing. Its value comes from a unique combination of properties, making it suitable for everything from corrosion-resistant linings and high-frequency cable insulation to non-stick coatings and medical implants.
The versatility of PTFE does not stem from a single attribute but from its rare combination of four key characteristics: extreme chemical inertness, high thermal stability, the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid, and excellent electrical insulation. This makes it a primary material for solving engineering challenges where other materials would fail.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE's Versatility
To understand where PTFE is used, we must first understand why it is chosen. Its widespread adoption is a direct result of its fundamental material characteristics.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The powerful carbon-fluorine bonds in PTFE's molecular structure make it almost completely inert. It is non-reactive and resists corrosion from nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents.
This property makes it indispensable for handling aggressive and high-purity substances.
Extreme Thermal Stability
PTFE maintains its properties across a vast temperature range, typically from -30°C up to a continuous operating temperature of +260°C (+500°F).
This allows it to perform reliably in high-temperature industrial processes and environments where other polymers would degrade.
The Lowest Friction of Any Solid
PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, meaning surfaces have very little resistance to sliding against each other. It is one of the most "slippery" materials known.
This quality is the reason behind its use as both a non-stick coating and a self-lubricating material for mechanical parts.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with a high dielectric strength, even at high radio frequencies.
This makes it a critical material in the electronics and telecommunications industries for high-performance wiring and cable insulation.
A Cross-Industry Breakdown of Applications
These core properties translate into specific, high-value applications across a wide range of industries.
In Chemical and Industrial Processing
PTFE's chemical resistance makes it ideal for linings in pipes, valves, tanks, and fittings. This protects equipment from corrosive contents and prevents contamination.
It is also machined into seals, gaskets, and 'O' rings to create durable, leak-proof connections in harsh chemical environments.
In Electronics and Electrical Engineering
Due to its excellent dielectric properties, PTFE is the standard for insulating high-frequency coaxial cables and computer hookup wires.
Its high-temperature tolerance also makes it suitable for cable sheaths and components in semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
In Mechanical and Automotive Systems
The low-friction nature of PTFE is leveraged to create components that require smooth, sliding action with no external lubrication.
Common examples include bearings, bushings, gears, and slide plates that reduce friction, wear, and energy consumption in machinery.
In Healthcare and Food Production
PTFE is non-toxic and biocompatible, allowing for its use in some medical implants where inertness is critical.
Its most famous application is as a non-stick coating for cookware and food processing equipment, preventing adhesion and simplifying cleaning.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, PTFE is not the solution for every problem. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Limited Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE is relatively soft and has lower tensile strength. It is not suitable for high-load structural applications and can be prone to "creep" under constant pressure.
Processing Challenges
PTFE has a very high melting point and melt viscosity, which makes it more difficult to process using conventional methods like injection molding. It is often machined from stock shapes or applied as a coating.
Thermal Degradation
Although it is stable at high temperatures, PTFE will begin to degrade and release fumes if heated to extreme temperatures well beyond its specified continuous service limit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a material requires matching its properties to the primary demands of the task.
- If your primary focus is resisting corrosive chemicals: PTFE's inertness makes it an ideal choice for linings, seals, and gaskets in aggressive environments.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in moving parts: Its ultra-low coefficient of friction is perfect for creating self-lubricating bearings, gears, and slide plates.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its excellent dielectric properties make it the standard for applications like coaxial cables and other critical wiring.
- If your primary focus is a non-stick, high-temperature surface: Its combination of thermal stability and non-adhesiveness is unmatched for both consumer cookware and industrial coatings.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique combination of properties secures its role as a premier problem-solving material for the most demanding engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key PTFE Applications | Primary PTFE Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Linings, Seals, Gaskets, Valves | Extreme Chemical Inertness |
| Electronics & Electrical | High-Frequency Cable Insulation, Components | Superior Electrical Insulation |
| Mechanical & Automotive | Bearings, Bushings, Slide Plates | Lowest Coefficient of Friction |
| Healthcare & Food | Non-Stick Coatings, Medical Implants | Thermal Stability & Biocompatibility |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your industry?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine material expertise with advanced fabrication techniques to deliver solutions that meet your exact requirements, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE components can enhance your product's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















