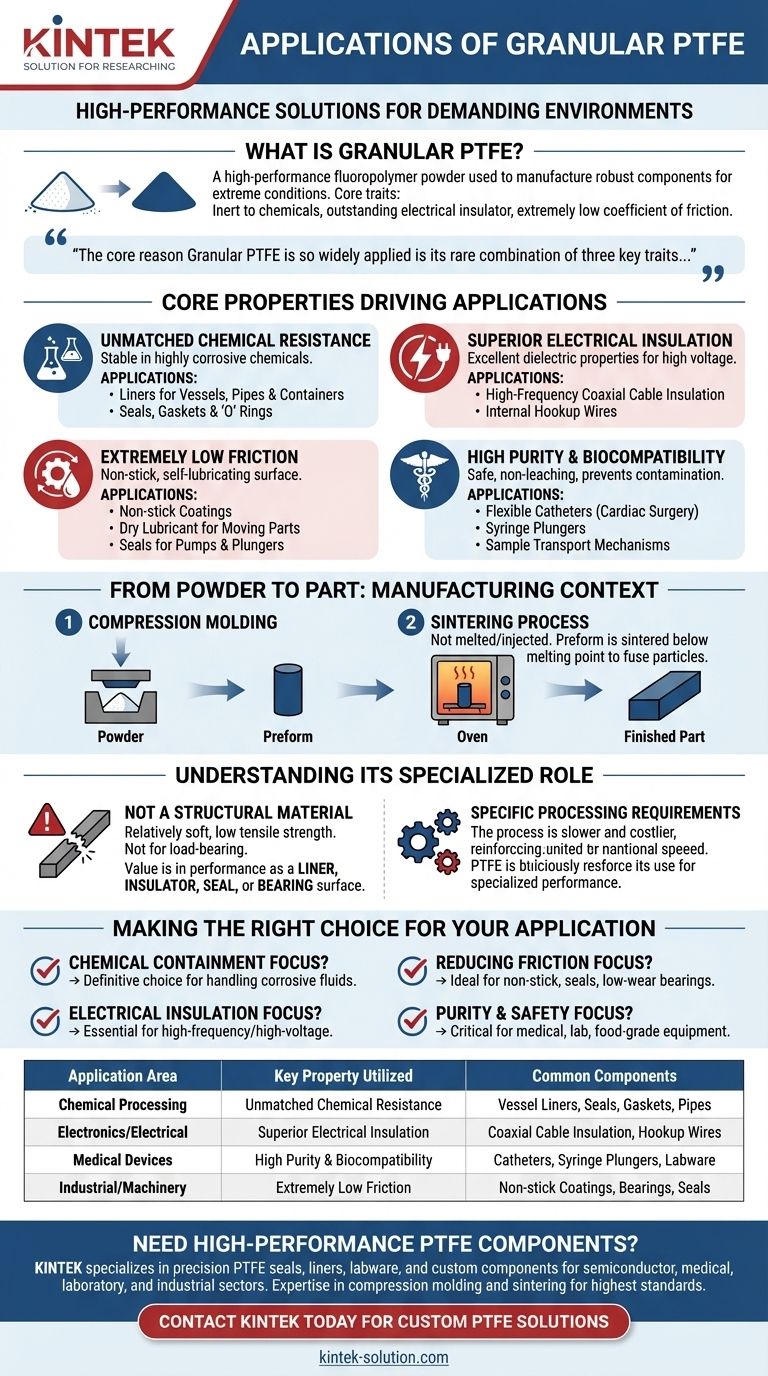
To be precise, Granular PTFE is a high-performance fluoropolymer powder used to manufacture robust components for demanding environments. Its primary applications are found in industrial sealing, chemical processing equipment, high-frequency electrical insulation, and critical medical devices where its unique combination of properties is essential.
The core reason Granular PTFE is so widely applied is its rare combination of three key traits: it is almost completely inert to chemicals, it is an outstanding electrical insulator, and it has an extremely low coefficient of friction. Few other materials can deliver this level of performance across such different domains.
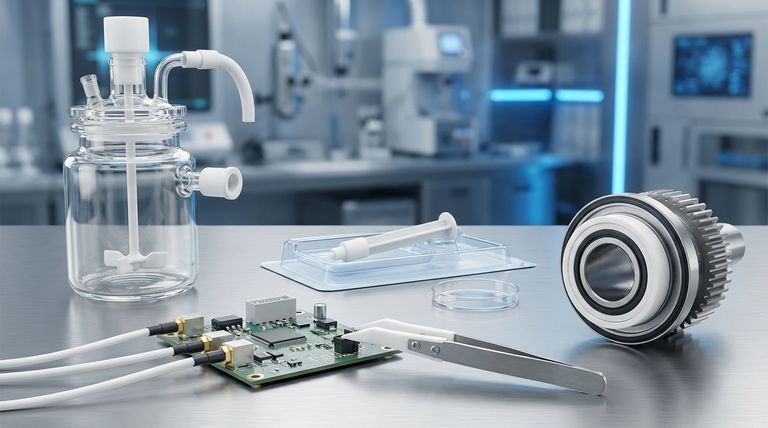

The Core Properties Driving PTFE Applications
Granular PTFE is not a general-purpose plastic. It is a specialty material selected when standard materials would fail. Its applications are a direct result of its fundamental chemical and physical properties.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is renowned for its non-reactive nature, making it stable even when exposed to highly corrosive and reactive chemicals.
This property makes it indispensable for components in chemical processing plants, including linings for vessels, pipes, and containers. It is also the material of choice for seals, gaskets, and 'O' rings that must prevent leaks while resisting chemical attack.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE possesses exceptional dielectric properties, meaning it does not conduct electricity and can withstand high voltages.
This makes it a critical material in the electronics and computer industries. It is commonly used for insulating high-frequency coaxial cables and internal hookup wires, ensuring signal integrity and preventing electrical shorts.
Extremely Low Friction
Often recognized by its brand name Teflon, PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, creating a "non-stick" and self-lubricating surface.
This characteristic is leveraged for non-stick coatings on cookware, as a dry lubricant to reduce friction between moving parts, and in seals for pumps and plungers where smooth, frictionless movement is required.
High Purity and Biocompatibility
The inherent purity and inertness of PTFE mean it does not leach chemicals or support bacterial growth, making it safe for sensitive applications.
In the medical field, this allows for its use in devices like flexible catheters for cardiac surgery, plungers for syringes, and sample transport mechanisms where preventing contamination is a primary concern.
From Powder to Part: The Manufacturing Context
Understanding how Granular PTFE is processed is key to appreciating its applications. Unlike common plastics, it is not melted and injected into a mold.
The Role of Compression Molding
Granular PTFE starts as a powder. This powder is poured into a mold and compressed under high pressure to form a pre-shaped object, often a solid block, rod, or tube.
This initial shape is known as a "preform" and is relatively fragile before the next step.
The Sintering Process
The preform is then carefully heated in an oven to a temperature just below its melting point in a process called sintering.
During sintering, the individual PTFE particles fuse together, creating a solid, dense, and durable finished part that exhibits all the material's exceptional properties. This final part can then be machined into more complex components.
Understanding Its Specialized Role
While incredibly capable, PTFE is a highly specialized material. It is chosen for its unique surface properties and resistance, not for its mechanical strength.
Not a Structural Material
PTFE is relatively soft and has low tensile strength compared to engineering plastics like nylon or PEEK. It is not used for load-bearing structural components.
Its value lies entirely in its performance as a liner, insulator, seal, or bearing surface where its chemical and physical properties are the primary requirements.
Specific Processing Requirements
The compression molding and sintering process is slower and often more costly than the high-volume injection molding used for many other plastics.
This reinforces its role as a performance material, specified only when its unique capabilities justify the specialized manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting Granular PTFE is a decision driven by overcoming a specific environmental challenge.
- If your primary focus is chemical containment: Its near-total chemical inertness makes it the definitive choice for handling corrosive fluids.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Its excellent dielectric properties are essential for high-frequency and high-voltage applications.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: Its ultra-low friction surface is ideal for non-stick coatings, seals, and low-wear bearing applications.
- If your primary focus is purity and safety: Its biocompatibility and inertness are critical for medical, laboratory, and food-grade equipment.
Ultimately, Granular PTFE is specified for components where performance and reliability under extreme chemical, electrical, or frictional demands are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Property Utilized | Common Components |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Unmatched Chemical Resistance | Vessel Liners, Seals, Gaskets, Pipes |
| Electronics/Electrical | Superior Electrical Insulation | Coaxial Cable Insulation, Hookup Wires |
| Medical Devices | High Purity & Biocompatibility | Catheters, Syringe Plungers, Labware |
| Industrial/Machinery | Extremely Low Friction | Non-stick Coatings, Bearings, Seals |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your specialized application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We leverage our expertise in compression molding and sintering to deliver parts that meet the highest standards for chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and purity—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our custom PTFE solutions can solve your most demanding challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















